Standard Financial Statements
Income Statement (利润表)
How much we made in a period (e.g. a month, a quarter, or a year)?
Statement of Retained Earnings (利润分配表)
How much earned value has been kept in the business vs. being paid out in dividends to the owners?
Balance Sheet (资产负债表)
How much do we have at a given point in time, and where did the money come from to acquire this?
Cash Flow Statement (财务计划现金流量表)
How much money flowed into and out of our business in a time period (e.g. a month, a quarter, or a year).
Income Statement
Income Statement indicates whether a company is making or losing money in a stated period, usually a year. It measures the profitability of a business within a stated period.
Profit (also known as gain or net income), measured by the accumulation of money, is simply a measure of the creation of value within a business.
A business that is unprofitable in the long term does not create commercial value, and hence should not exist.
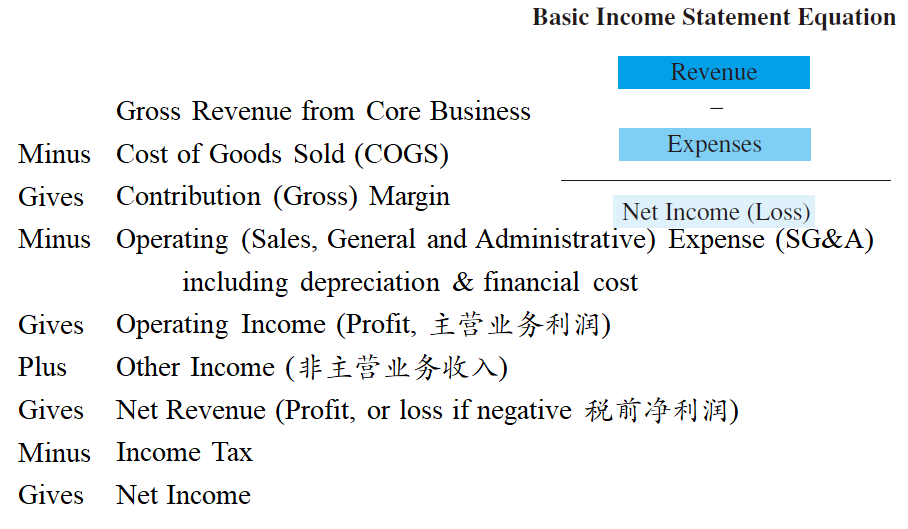
COGS are direct costs of making a product or delivering a service.
SG&A are indirect costs that are related to the making of a product or the delivery of a service.
Contribution Margin measures the ability of a business to continuously earn value from the customer from the goods that are sold. It is used in pricing marginal sales.
A positive Operating Income shows that the firm is creating value.
Other Income
An unusual ''one time'' cost/revenue that is related to the business or revenue and expenses that are not related to the core business.
Extraordinary other income can distort the picture of what a business will do in the future.
Net Income is calculated both pre (aka. Net Revenue) and after income tax.
Statement of Retained Earnings
Retained earnings of former years will be cumulated to current year.
Retained earnings can be negative, and in fact frequently are for start up companies and for exploration companies.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet shows at a given point in time, what assets a business has and where the money came from to acquire those assets.
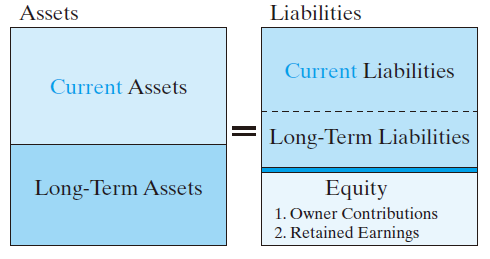
Current Assets (流动资产)
Accounts Receivable (应收帐款): money that is owed by other firms, but that has not yet been paid.
Prepaid expense (预付帐款): money that has been paid for raw materials, labor, etc., which has not yet been received.
Inventory (存货): money that is invested in raw materials, work in process, and finished goods available for sale.
Fixed Assets (固定资产)
Investments paid for the plant and equipment, e.g. land, machine, buildings.
Fixed assets are relatively permanent and take time to convert into cash.
Other Assets
Investments made in other firms and intangible assets such as goodwill, copyrights, franchises, and so forth.
Goodwill indicates any additional amount paid for the business above the fair market value of the business.
Current Liabilities (流动负债)
Debts that must be paid in the near future (normally, within one year).
Short-term credit line (短期借贷): a bank account of a firm that can go positive or negative.
Accounts payables (应付帐款): money owed to suppliers and wages, salaries, interest, rent, taxes, etc., owed, but not yet due for payment.
Advance payments (预收帐款): money and deposits prepaid from customers.
Current Portion of Long-term Debt: amount of long-term debt to be paid in this year.
Long-term Liabilities (长期负债)
Debts that are due and payable more than one year in the future, e.g. bonds, mortgages.
Working Capital (流动资金/运营资本)
The difference between current assets and current liabilities.
Working capital should be almost always positive.
![]()
Shareholders/Owners Equity (权益金)
It represents the amount that is available to the owners after all other debts have been paid.
It consists of preferred and common stock, treasury stock, capital surplus, and retained earnings.
Retained earnings records the cumulative net income of the firm since its inception, less the total dividends that have been paid to stockholders.
Cash Flow Statement
Operating Activities (运营活动): Cash flows related to the production and sales of goods or services. All noncash expenses (e.g. depreciation) are added back to net income.
Investing Activities (投资活动): Cash flows related to investment activities, which include purchasing new fixed assets (outflow), reselling old equipment (inflow), and buying and selling financial assets.
Financing Activities (财务活动): Cash flows related to financing any capital used in business, such as, borrowing or selling more stock (inflow), paying off existing debt (outflow).
Cash Inflows: Source of Funds (资金来源)
It is an increase in a liability account year over year.
Depreciation is a source of funds. It represents funds that have come into a firm and are being offset on the firm's books against past asset purchases.
Cash Outflows: Use of Funds (资金使用)
It is an increase in an asset account year over year.
A dividend is a use of funds.
Summary on Financial Statements
Income statement measures rate - how much income do a project make in a given period of time.
Cash flow statement measures health – how well do a project can afford the payback of debt and interest.
Balance sheet measures wealth - how much do a project have and how much do a firm owe at this moment.
Income statement and cash flow statement cover a period of time, and that period must be long enough to be meaningful, normally one year.
Balance sheet is made at a moment in time. It makes sense to do balance sheet at the end of a year.
Financial Statements for Investment Projects
Cash Flow Statement of Project Investment (项目投资现金流量表)
Cash Flow Statement of Equity Investment (资本金投资现金流量表)
Cash Flow Statement of Individual Investors (投资各方现金流量表)
Statement of Repayment of Principals and Interests (借款还本付息计划表)
Statement of Capital Investment (建设投资估算表)
Statement of Interest During Construction (建设期利息估算表)
Statement of Working Capital (流动资金估算表)
Statement of Use and Source of Project Capitals (项目总投资使用计划与资金筹措表)
Statement of Operating Revenue, Tax & Surcharge (营业收入、税金及附加估算表)
Statement of Total Cost & Expense (总成本费用估算表)

