形容词比较级和最高级知识点
一、变化规则
大多数形容词和副词有比较级和最高级的变化,即原级、比较级和最高级,用来表示事物的等级差别。
原级即形容词的原形,比较级和最高级有规则变化和不规则变化两种。
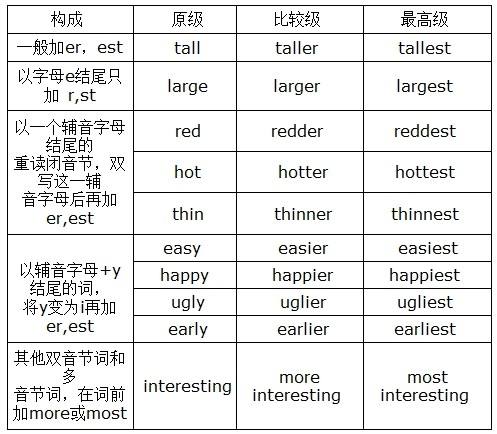
(1)单音节词加词尾-er,-est来构成比较级和最高级
tall(高的) taller tallest
great(巨大的) greater greatest
(2)以不发音的e结尾的单音节词只加-r,-st
nice(好的) nicer nicest
large(大的) larger largest
able(有能力的) abler ablest
(3)以一个辅音字母结尾的闭音节单音节词,双写结尾的辅音字母,再加-er,-est
big(大的) bigger biggest
hot(热的) hotter hottest
red(红色的) redder reddest
(4)“以辅音字母+y”结尾的双音节词,改y为i,再加-er,-est
easy(容易的) easier easiest
busy(忙的) busier busiest
(5)以ly结尾的副词,除early-earlier-earliest,其他都是加more most.
Slowly moreslowly most slowly
bravely morebravely most bravely
quickly morequickly most quickly
(6)少数以-er,-ow结尾的双音节词未尾加-er,-est
clever(聪明的) cleverer cleverest
narrow(窄的) narrower narrowest
*(7)其他双音节词和多音节词在前面加more,most来构成比较级和最高级,如:
important(重要的) moreimportant most important
easily(容易地) moreeasily mosteasily
(8)一些词的比较级和最高级,可以加-er或 -est,也可以加more或most,如:clever, polite等
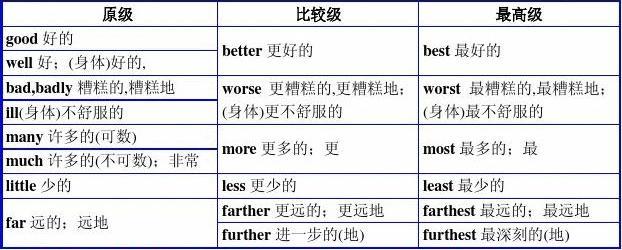
(9)不规则变化
有一些词的比较级、最高级变化是不规则的,需要特殊记忆:
good/well → better → best
bad/ill/badly → worse → worst
many/much → more → most
little → less → least
far → farther → farthest(表示距离)/far → further → furthest(表示程度)
old → older/elder → oldest(表示新旧或年龄)/eldest(表示兄弟姐妹之间的长幼关系)
副词的比较级和最高级的构成规则和形容词比较级和最高级的构成规则一样,所不同的是:形容词最高级前面必须用the,而副词的最高级前面的the可带可不带。
一些词本身没有比较级和最高级形式,如:right, wrong, full, empty, round, complete, wooden, dead, daily等。
二、形容词比较级的用法
1. 两者比较时用形容词比较级,其结构为“... 比较级 + than...”。
如:Actionsspeak louder than words.
2. 在两者之间选择“哪一个更……”时,用句型“Which/Who is + 比较级, ... or ...?”。
如:Whichsweater is cheaper, the red one or the yellow one?
3. 表示“两者之间最……的一个”时,用“the + 比较级”。
如:Lucyis the taller of the twins.
4. 表示“越……,越……”时,用“the + 比较级,the + 比较级”。
如:Themore you eat, the fatter you will become.
5. 表示“越来越……”时,用“比较级 + and + 比较级”,多音节词和部分双音节词用“more and more + 形容词原级”。
如:Weshould make our country more and more beautiful.
6. 形容词比较级前可以用下列词修饰:much,a little, far, a bit, a few, a lot, even, still, rather等。
如:It'smuch colder today than yesterday.
三、形容词最高级的用法
1. 三者或三者以上的人或物进行比较时,用形容词最高级形式。形容词最高级前通常需加定冠词the,句末常接in / of短语来表示范围。
如:Heis the strongest of all the boys.
2. 表示“最……之一”时,用“one of + the + 最高级”。
如:Thelight bulb is one of the most helpful inventions.
3. 形容词最高级前可以由物主代词、指示代词、名词所有格等修饰,此时不用定冠词the。
如:Yesterdayis her happiest day in her life
四、修饰语
1. 比较级的修饰语
Much(……得多),far(……得多),even(甚至,更),still(更),abit(有点),a little(有点),a lot(很),a great deal(大大地),twice(两倍), five times(五倍), two-fifths(五分之二),a half(一半)等修饰比较级表示程度,但决不可用very修饰。
如:
Tom is a little taller than Mike.
Tom比Mike稍高一点。
It is even colder today than yesterday.
今天甚至比昨天更冷。
2. 最高级的修饰语
By far/ far and away 最,很 much ……得多almost 几乎nearly 几乎。另外,second,third,next等也要放在定冠词之后。
如:
The Yellow River is the second longest inChina.
黄河是中国的第二大河。
This is the third largest building in thiscity.
这是这个城市里第三大的建筑物。
The Yellow River is the second longest riverin China.
黄河是中国第二长河。
This is (by) far the best book that I’veever read.
这是我读过的最好的书。


