8.3 Global Production and Supply-ChainManagement
Key Takeaways
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Understand the differences between outsourcing and offshoring.
Explain three strategies for locating production operations.
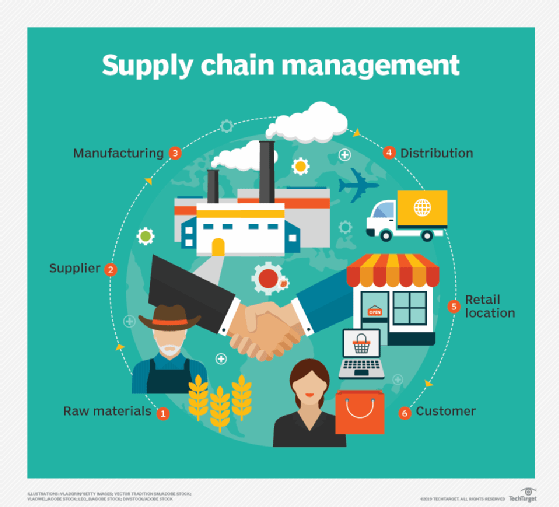
Know the value of supply-chain management.
Supply-chain management is the coordination of a host of activities that can give a company a distinct competitive advantage. Cross-organizational teams are the best way to take advantage of the perspectives of each supply-chain function for the benefit of all.
Offshoring means setting up operations in a low-cost country for the purpose of hiring local workers at lower labor rates. Offshoring differs from outsourcing in that the firm retains control of the operations and directly hires the employees. In outsourcing, by contrast, the company delegates an entire process (such as accounts payable) to the outsource vendor. The vendor takes control of the operations and runs the operations as they see fit. The company pays the outsource vendor for the end result; how the vendor achieves those end results is up to the vendor.
阅读材料:Supply chains during the covid-19 pandemic
视频:Supply chain management
课件分享:Introduction to supply chian
课后思考:FOOD FOR THOUGHT
What processes does supply-chain management encompass?
If you were going to build a plant overseas, what factors would you take into account when making your location decisions?