Basic features of Braking system

Energy is required when a vehicle is accelerated from rest to a certain speed. A proportion of that energy is now stored in the vehicle and is called kinetic energy. In order to reduce the speed of the vehicle, the brakes have to convert the kinetic energy to heat energy; the speed of conversion governs the rate at which the vehicle slows down.
The three types of braking systems are in use today: service braking system, parking braking system and additional braking system. The service braking system and the parking braking system have separate control and transmission devices. The service braking system is normally foot- operated, while the parking braking system is hand-operated.
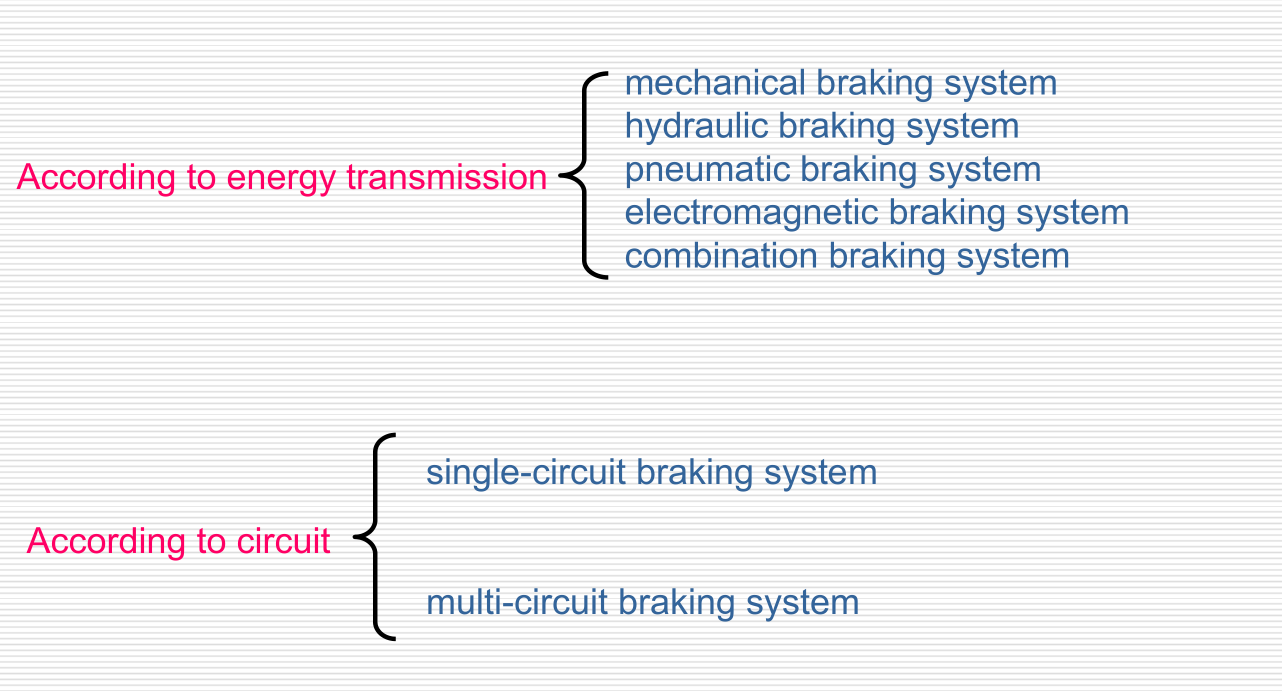
Braking systems are diferentiated acconding to the type of energy used: muscular-energy braking system, energy-assisted braking system, non-museular energy braking system, inertia braking system and gravity braking system.
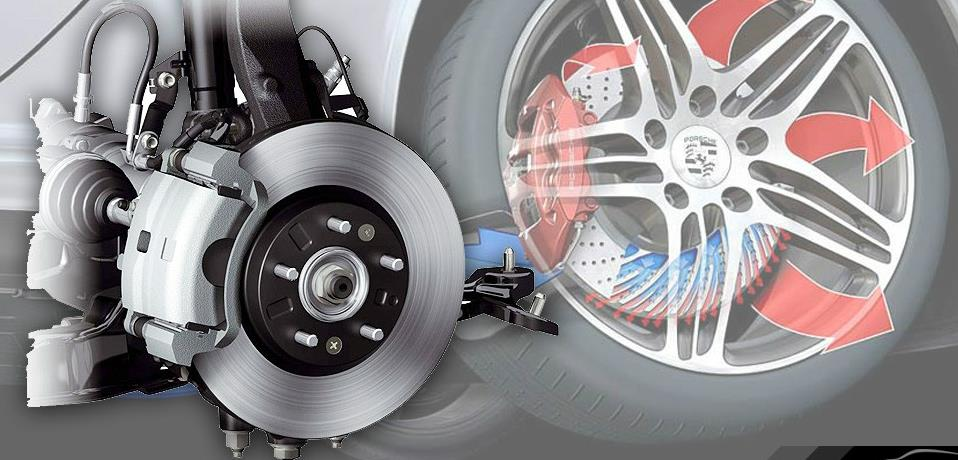
Two types of brakes are used in modern cars: drum brakes and dise brakes. Most cars use disc brakes on the front wheels and drum brakes on the rear wheels. In both drum and disc brakes, a hydraulic system applies the brakes. The hydraulic system connects the brake pedal to brake parts at each wheel.
Two types of hydraulic braking systems are used. The manual braking system is the simplest Here, the force of the foot on the pedal applies all the force to the hydraulic system.Another system, the power braking system, uses parts that assist a driver in applying force to the hydraulic system. There is also an antiskid system that prevents the brakes from locking up the wheels and causing skidding.
Braking systems are differentiated according to transmission device: single-circuit braking system and multicircuit braking system, as well as
1) braking systems with mechanical force transmission
2) braking systems with hydraulic force transmission
3) braking systems with pneumatic force transmission
4) braking systems with electrical force transmission