ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC SYSTEM
1 Overview of Electrical and Electronic System
Electricity is the flow of electrons. They are forced to move by electrical voltage. In an automobile, the electrical voltage is created by chemical action in the storage battery and by magnetic induction in the alternator.
An electric motor, called the starting motor, cranks the engine to enable it to draw in a combustible air-fuel mixture for starting. The ignition system furnishes the spark which ignites the compressed mixture. It increases the battery voltage to 20kV which is delivered to each spark plug in turn. The lighting system changes electron into light and the horn into sound. If the battery were the only supply of electrons necessary to operate all of the automotive electrical equipment, it would soon become discharged. To prevent this, an alternator, driven by the engine, produces enough electricity to operate the various electrical circuits. The excess is used to recharge the battery. To control the charging rate, according to the needs of the battery, a regulator is connected in the alternator circuit. It causes the charging rate to increase when the battery is low and to decrease when the battery becomes fully charged.
To understand the functioning of your electrical system, you should be aware of its major parts.
1) Battery supplies energy to operate the components which are needed when the engine is stationary or when the output from the charging system is low.
2) Starting enables the engine to be cranked over at a speed sufficient for it to"fire"
3) Charging supplies the electrical energy when the engine is running, and maintains the battery in a fully charged state.
4) Ignition provides a spark to"fire"the engine.
5) Lighting is needed for exterior and illumination.
6) Auxiliary includes the various accessories such as windsereen wipers and washers, direction indicators. ete.
7) Electronic devices are used on mordern automobiles.
2 Battery
The purpose of the battery is to store electrical energy. It does this by converting the electrical energy supplied to it into chemical energy so that when an electrical current is required the energy change is reversed.
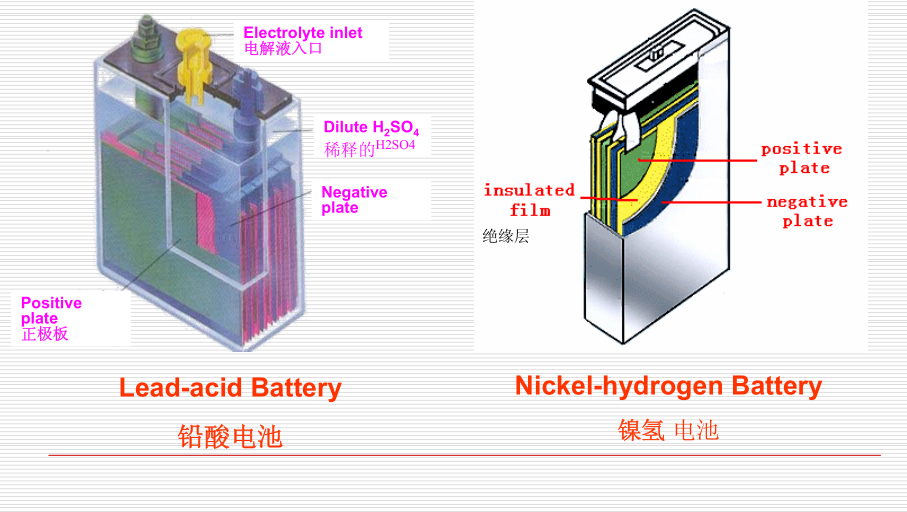
In making the battery, several similar plates are properly spaced and welded to form a plate group. Plates of two types are used, one for the positive plate group, the other for the negative plate group. A positive plate is nested with a negative plate group, with separators placed between the plates to form an element. Separators are designed to hold the plates apart so that they do not touch, and at the same time they must be porous enough to permit electrolyte to circulate between the plates.
3 Charging System
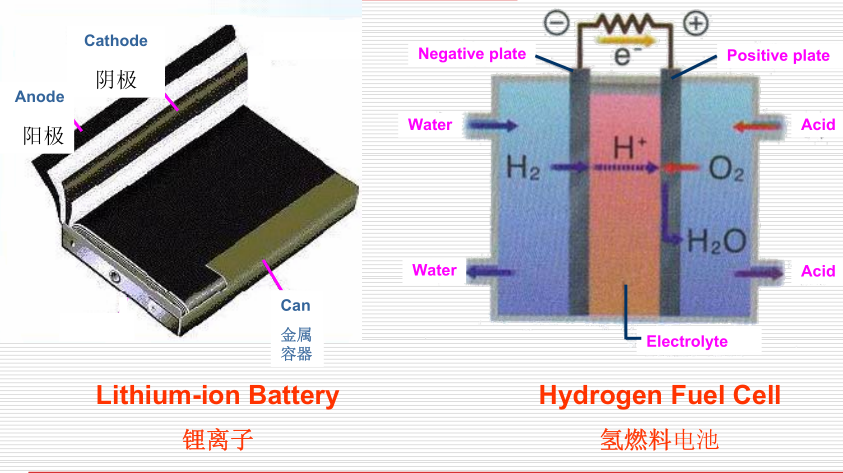
The charging system provides the electrical energy a car needs once its engine starts. The charging system does two jobs. First, it provides electrical power for the ignition system and the car's electrical accessories. Second, it replaces the power used by the battery in starting the car. In other words, the charging system maintains the battery’s state of charge.
Electromagnetic Introduction Principle
Electricity can be produced by moving a conductor through a magnetic field, The opposite also holds true. By moving the magnetic field and holding the conductor, electricity can be generated in the conductor. This current is called an induced current. This is the basic principle of the alternator, an electromechanical device that changes mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Let us imagine that the wire loop is rotated between the north and south poles of the magnetic field. If the ends of the loop are now connected via collector rings and carbon brushes to a voltmeter, it will be possible to read off an alternating voltage owing to the constantly changing position of the loop with respect to the poles.
4 Starting System
The starter must crank the engine at a specified minimum speed (starting speed) in order to generate the air-fuel mixture necessary for self-sustained operation of spark-ignition engines, even under adverse conditions, and must support the engine as it runs up to minimum self-sustained speed after initial ignition.
Electric motors (DC, AC and three-phase), as well as hydraulic and pneumatic motors are used as starting motors for internal-combustion engines.
the starting conditions of Starter

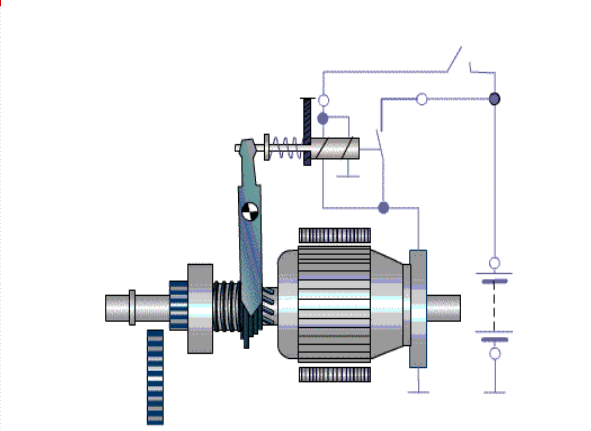
When current from the battery is passed through the wire, the steel core becomes a strong magnet. The magnetic force of the core pulls in the plunger. The shift lever is attached to one end of the plunger. Then the movement of the plunger causes the shift lever to move outward. This lever, in turn, moves the pinion gear into mesh with the ring gear. The solenoid uses magnetic force to do the mechanical work of moving the shift lever that engages the two gears.
The solenoid also does another important job. There is a contact disc on the other end of the plunger. When current flows through the coil of wire, the contact disc attached to the plunger moves and makes contact with two terminals.
current flows from the battery to the starter motor, and the crankshaft begins to rotate. When current stops flowing to the solenoid, the bottom of the shift lever moves back. This disengages the pinion gear from the ring gear.
5 Lighting System
The lighting system in a typical automobile includes the headlights, direction-signal lights, side marker lights, brake lights, tail lights, and the interior lights. The interior lights include instrument-panel lights, various warning, indicator, and courtesy lights which turn on when a car door is opened.



