Engine lubrication
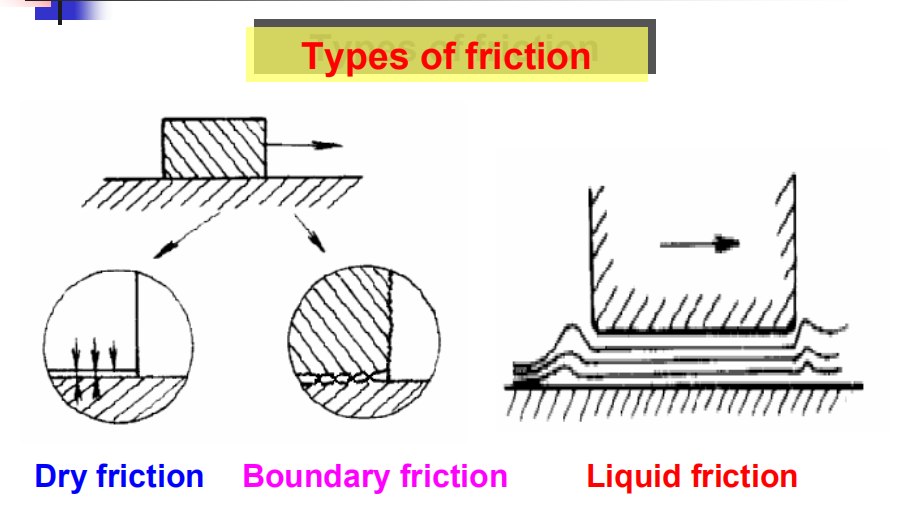
Friction between engine components is reduced by:
1)boundary lubrication — relies on oil being splashed up onto the surfaces ,
2)full film lubrication — an oil film is maintained by forcing the oil between the surfaces by an oil pump .
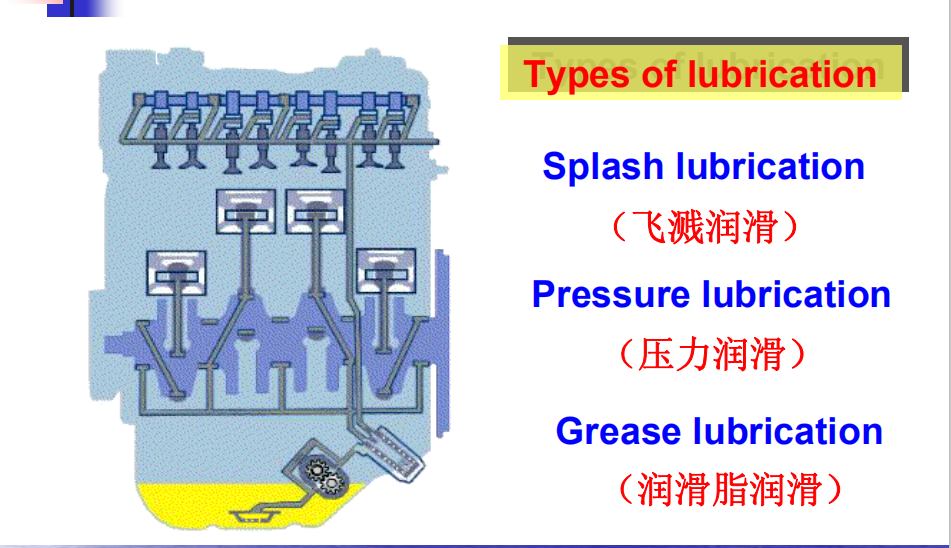
The purpose of the lubrication system is to circulate oil through the engine. An engine must have a good lubrication system. Without it, the friction heat from the contact of the moving parts would wear the parts and cause power loss. Oil, when placed between two moving parts,separates them with a film. This oil film prevents the parts from rubbing against each other. This oil film also cushions the parts, giving quieter and smoother engine operation.
The system used on a modern engine combines both methods :pistons are lubricated by splash and bearings are pressure fed .The main parts of a lubrication system are pump , main oil gallery , relief valve and filters .

1) pump
In most cars , the oil pump is in the crankcase above the sump . It draws oil through a tube that extends downward into the sump. This tube, called the oil-pump pickup tube , has a filter screen over its bottom end . The screen keeps large pieces of sludge and dirt from being drawn into the pump . The tube may be hinged on the pump end so that it can move up and down as the oil level changes in the sump . Thus , the pump always draws oil from the top of the sump , not from the bottom where the dirt and sludge tend to settle . Modern cars use one of two common types of oil pumps—the gear-type and rotor-type .
2) main oil gallery and relief valve
The main oil gallery runs the length of the engine . Drillings from the gallery allow oil to be supplied to the bearing surfaces .Generally the relief valve fitted in the gallery , this spring loaded valve opens when the pressure reaches the maximum allowed .
3) filters
Besides the gauze screen that prevents pieces of the metal entering the pump there is an external filter which can be renewed periodically . A modern engine uses a full – flow filtering system . In this system , the output of the oil pump flows through the oil filter before each trip through the engine . When an engine runs at 3000r/min its entire five quarts of oil pass through the filter at least once every minutes . Thus the oil filter ensures that only clean oil enters the engine .


