Emission Control
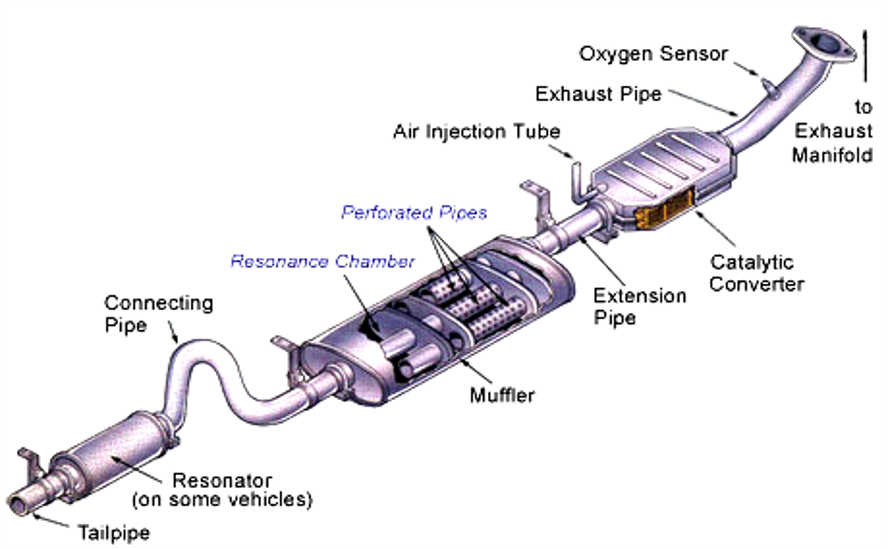
The system that carries exhaust gases from the combustion chamber to the rear of the car is called the exhaust system.
The exhaust system has one or two exhaust manifolds, and an exhaust pipe, intermediate pipe, and tail pipe. The exhaust manifold collects exhaust from the engine's cylinders.The exhaust pipe, intermediate pipe and tail pipe carry exhaust to the back end of the car.The mufler quiets engine noise.
The burned gases removed from the combustion chamber contain such harmful emissions as hydrocarbons (unburned) ,carbon monoxide , nitrogen oxides
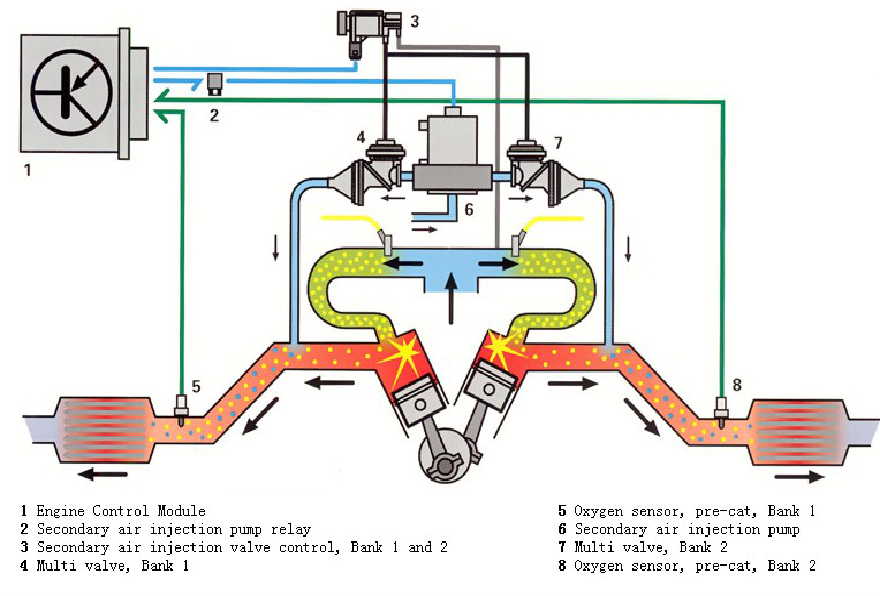
There are five popular systems used to reduce emissions: the crankcase ventilation system, the evaporative emission control system, the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system, the air injection system and the catalytic converter system.
In addition to these emission systems, modern vehicles incorporate an electronically controlled fuel injection system, which further reduces emissions. Note: Not all vehicles are equipped with these emission systems.
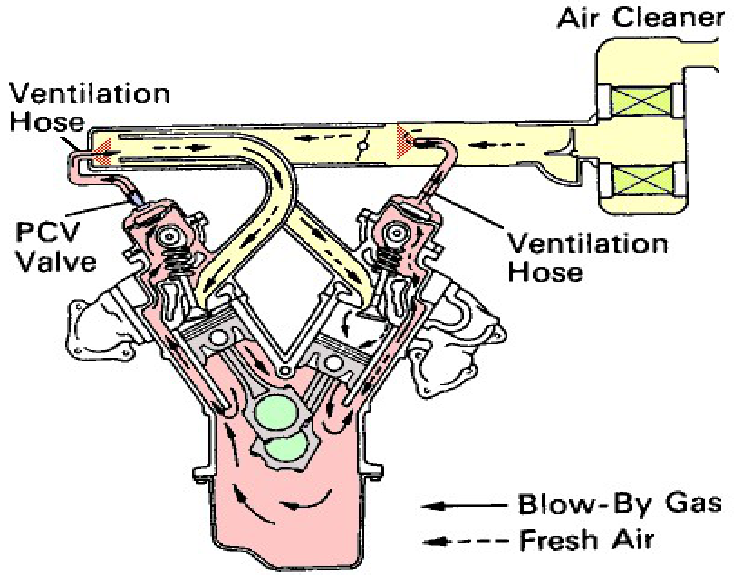
The purpose of the positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system is to take the vapors produced in the crankcase and piston blow-by, and redirect them into the air/fuel intake system to be burned during combustion.
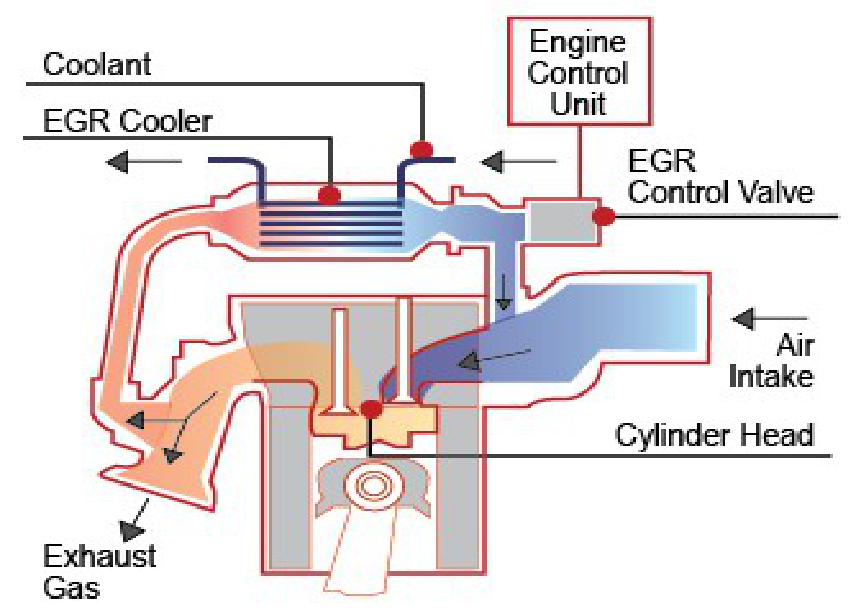
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems reduce the amount of oxides of nitrogen produced during the combustion process.
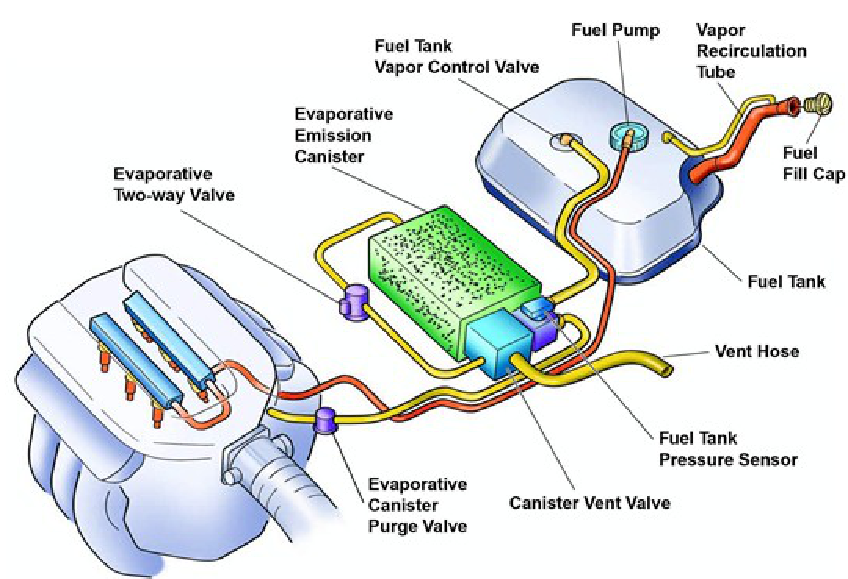
The function of the fuel evaporative control system is to trap and store evaporative emissions from the gas tank and carburetor. A charcoal canister is used to trap the fuel vapors. The fuel vapors adhere to the charcoal, until the engine is started, and engine vacuum can be used to draw the vapors into the engine, so that they can be burned along with the fuel/air mixture.
The catalytic converter looks like a muffler. It is located in the exhaust system ahead of the muffler. As hydrocarbons or carbon monoxide in the exhaust are passed over the catalyst, it is chemically oxidized or converted to carbon dioxide and water.