engine cooling
Some form of cooling must be provided to take away the heat from the cylinder and working parts of an engine . This heat comes from combustion of the fuel and from friction between rubbing parts. An uncooled engine would result in :
1) seizure of working parts due to heat expansion; 2) excessive wear — the oil would be burnt ; 3) pre-ignition of the petrol-air mixture . This means that the mixture would be ignited before time by some red-hot particle in the combustion chamber .
There are two methods of cooling : air cooling and liquid cooling .
1 air cooling
Most motor-cycle engines are air cooled . The principle is to fin the cylinder so as to increase the area of the hot surface exposed to the flow of cool air . This method of cooling is cheap , light-weight ans is not subject to troubles such as leakage and freezing problems .
Airflow for cooling a multi-cylinder engine is provided by a centrifugal fan ; this forces the air through ducted passages and over the finned cylinders .
2 liquid cooling
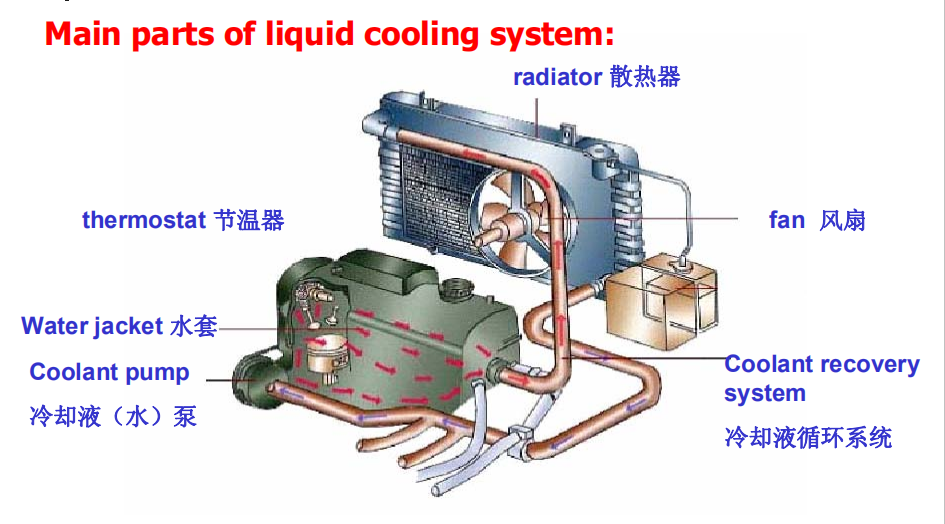
This system consists of several interdependent parts that function together to maintain proper engine temperature. The parts include: radiator, fan, coolant recovery system, coolant pump, water jacket, thermostat, pressure cap, soft plugs.To dissipate excess engine heat, the cooling system performs four function: 1) absorption 2) circulation 3) radiation 4) control
Absorption occurs as coolant moves through the engine block . Heat energy from the burning fuel in the cylinders passes into the cylinder walls and cylinder head . Liquid coolant circulates through hollow spaces within the engine block and head to absorb the heat from the metal parts of the engine . The hollow spaces are known as the water jacket .
After absorbing the heat , the hot coolant passes out through the cylinder head and eaters the radiator . As the coolant circulates through the radiator , it gives up its heat to the metal tubes of the radiator . The radiator is made of brass or aluminum , metals that conduct heat well . As air passes through the radiator fins and around the tubes ,heat is transferred to air .
However , if coolant circulated at all times from the engine to radiator , the engine would run very cool on cold days . Remember that chemical reaction , including the burning of the fuel , occur more efficiently at high temperature . Thus , for the engine to operate efficiently , there must be a control mechanism . This control system is the thermostat . It regulates hoe much coolant is permitted to flow through the radiator . After you start the engine , it should heat an efficient operating temperature as quickly as possible and maintain that temperature without overheating .
1) Thermostat circulation:
When the engine is cool, the thermostat remains closed so that coolant cannot circulate through the radiator. Instead, coolant is recirculated within the engine block and cylinder head until the coolant reaches a predetermined temperature. At that temperature, a wax-like pellet expands inside the thermostat to open it and allow the coolant to flow. Today, most original-equipment thermostats open at approximately 85ºC to 90ºC. In hotter climates, a “cooler” thermostat may be used to help avoid overheating. In most cases ,when the thermostat fails , it remains closed ans the engine overheats because coolant cannot flow into the radiator .
2) Pressurized Water Cooling
Water subjected to atmospheric pressure boils at about 100℃. When the cooling system is pressurized, the increase in the boiling point enables the engine to operate at a higher temperature with the result that power, economy and engine life are all improved.
The operating pressure of the system is controlled by the radiator cap: the pre-set pressure of the cap is marked on the top surface .
3) anti-freeze
This is a solution which is added to the cooling system to lower the temperature at which freezing of the coolant occurs : the actual freezing temperature is governed by the quantity of anti-freeze added to the system . Ice increases its volume as its temperature decreases, so extensive damage to the cylinder block will result if the coolant freezes .Most modern anti-freeze solutions contain special chemical additives called inhibitors to reduce corrosion of the metal parts . Care must be taken to avoid splashing anti-freeze on the vehicle paintwork, since some of the chemicals can soften the paint .


