1 engine term
Linking the piston by a connecting rod to a crankshaft causes the gas to rotate the shaft through half a turn. The power stroke“uses up”the gas , so means must be provided to expel the burnt gas and recharge the cylinder with a fresh petrol-air mixture :this control of gas movement is the duty of the valves;an inlet valve allows the new mixture to enter at the right time and an exhaust valve lets out the burnt gas afterthe gas has done its job. Engine terms are:
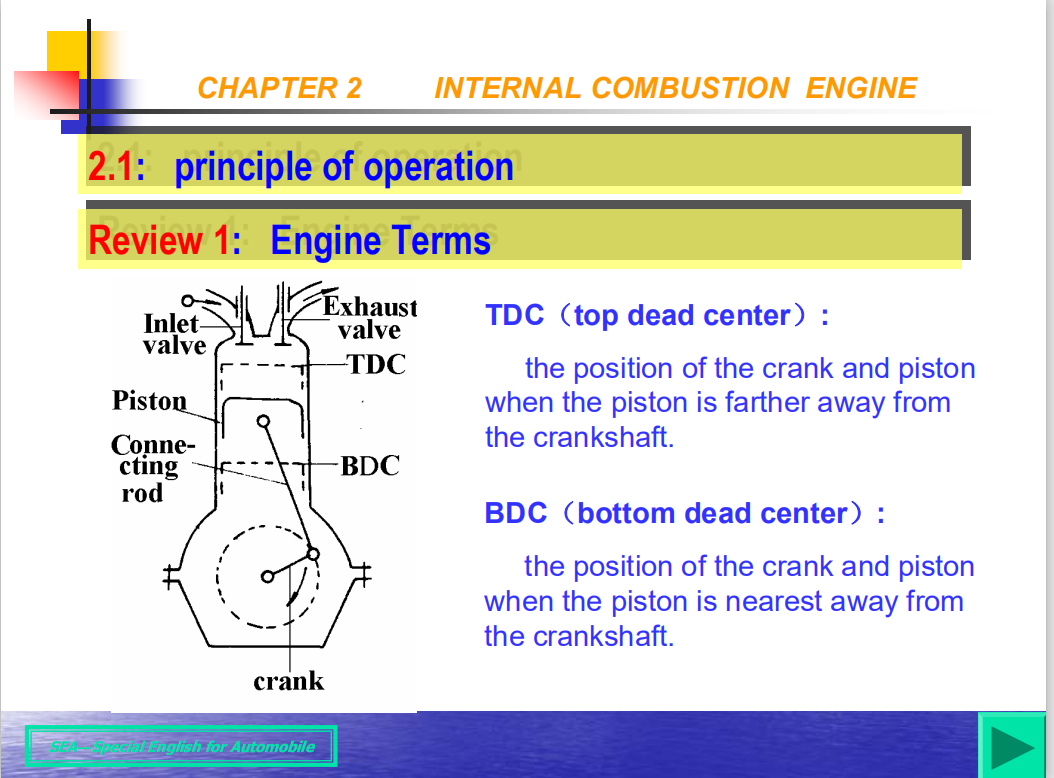
1) TDC(Top Dead Center):the position of the crank and piston when the piston is farther away from the crankshaft.
2) BDC(Bottom Dead Center):the position of the crank and piston when the piston is nearest to the crankshaft.
3) Stroke : the distance between BDC and TDC; stroke is controlled by the crankshaft.
4)Bore : the internal diameterof the cylinder.
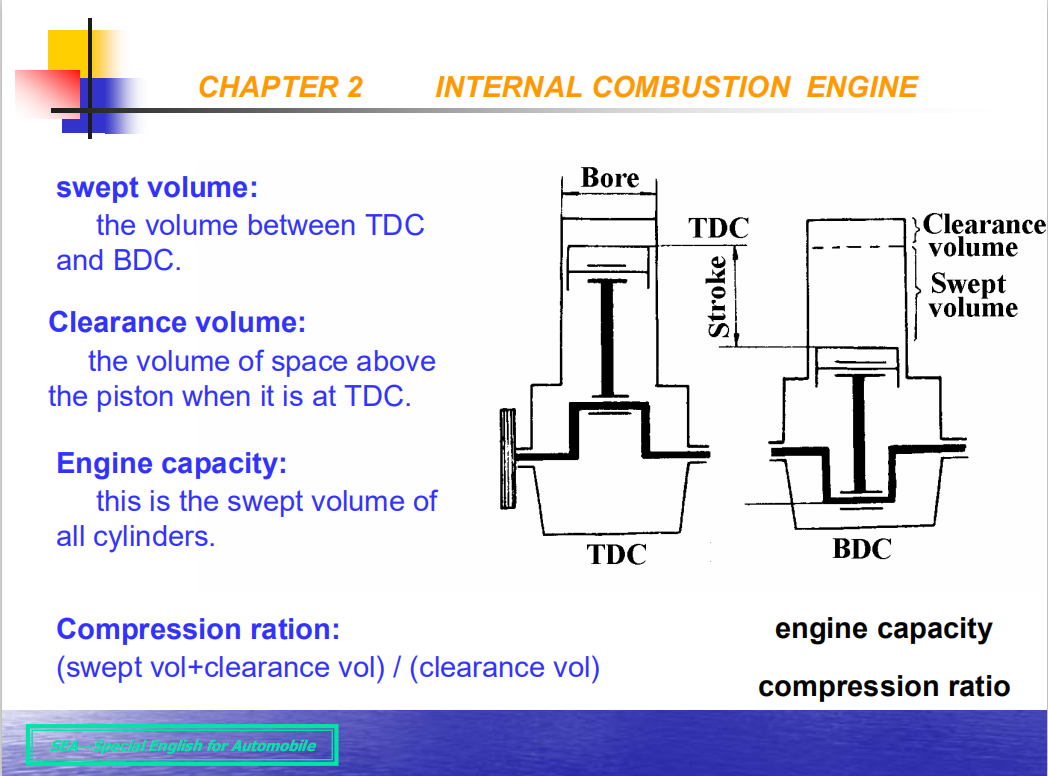
5)Swept volume : the volume between TDC and BDC.
6)Engine capacity : this is the swept volume of all the cylinders.
e.g. a four-cylinder engine having a capacity of two liters(2000cm3) has a cylinder swept volume of 500cm3.
7)Clearance volume: the volume of the space above the piston when it is at TDC.
8)Compression ratio έ= (swept vol + clearance vol)∕(clearance vol)
9)Two-stroke : a power stroke every revolution of the crank.
10)Four-stroke: a powerstroke every other revolution of the crank.
2 The Four-stroke Spark-ignition Engine Cycle
The spark-ignition engine is an internal-combustion engine with externally supplied in ignition ,which converts the energy contained in the fuel to kinetic energy.The cycle of operations is spread over four piston strokes. To complete the full cycle it takes two revolutions of the crankshaft. the operating strokes are:
1) Intake(induction) stroke
The downward-moving piston increases the volume in the cylinder and draws in fresh air-fuel mixture through the open intake valve.
2) Compression stroke
The upward-moving piston reduces the volume in the cylinder and compresses the air-fuel mixture.Shortly before TDC is reached ,the spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture and thus initiates the combustion process. A higher compression ratio means better utilization of thefuel. The extent of compression is restricted by the knock limit.
3) Power stroke
After the ignition spark at the spark plug has ignited the compressed air-fuel mixture,the temperature increases as the result of combustion of the mixture.The pressure in the cylinder increases and forces the piston downwards. The piston transfers power to the crankshaft via the connecting rod.
4) Exhaust stroke
The upward-moving piston expels the combusted gases (exhaust gas) through the open exhaust valve. After this 4th stroke,the cycle is repeated.
3 Engine Overall Mechanics
The engine has hundreds of other parts . The major parts of engine are engine block , engine heads, pistons, connecting rods, crankshaft and valves. The other parts are joined to make systems. These systems are the fuel system, intake system, ignition system, cooling system, lubrication system and exhaust system. Each of these systems has a definite function. These systems will be discussed in detail later。