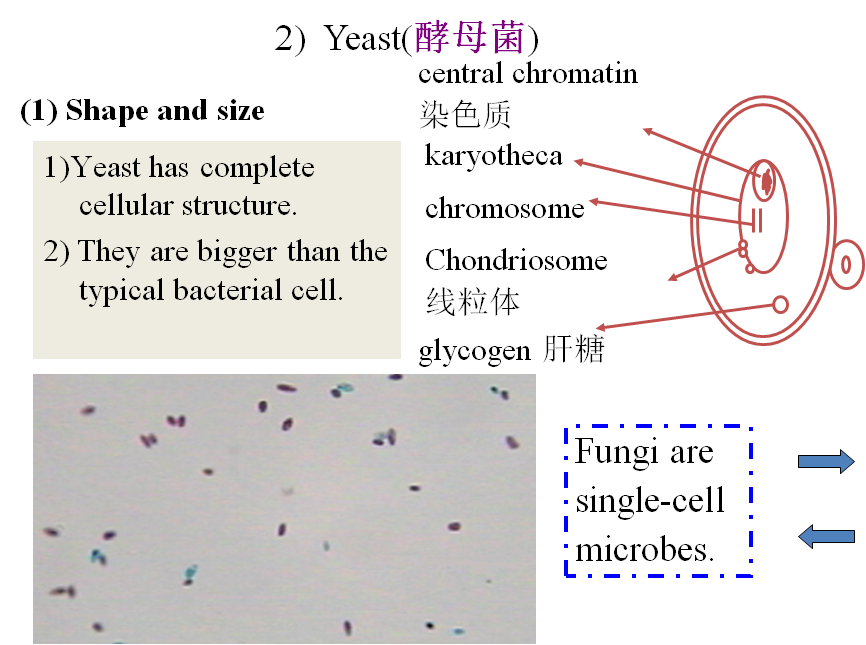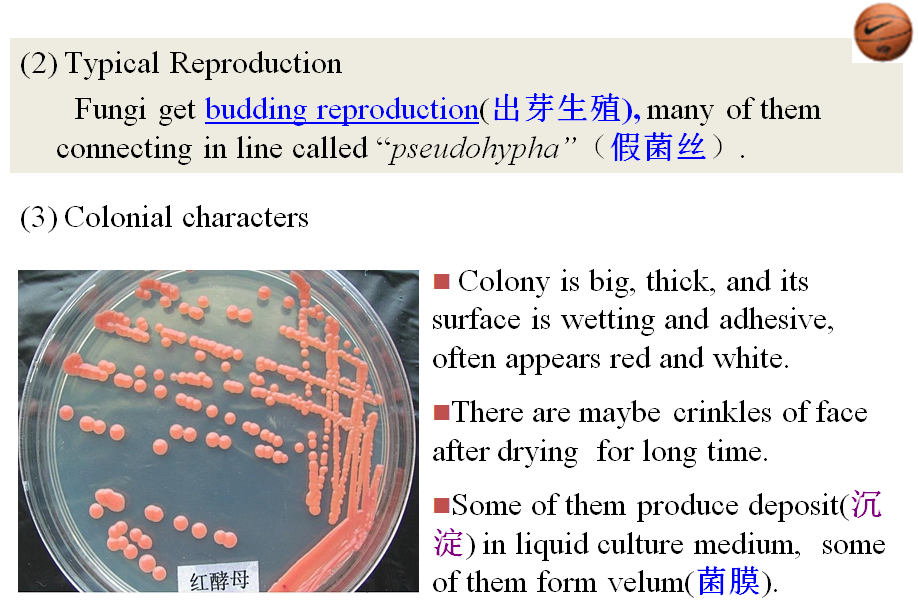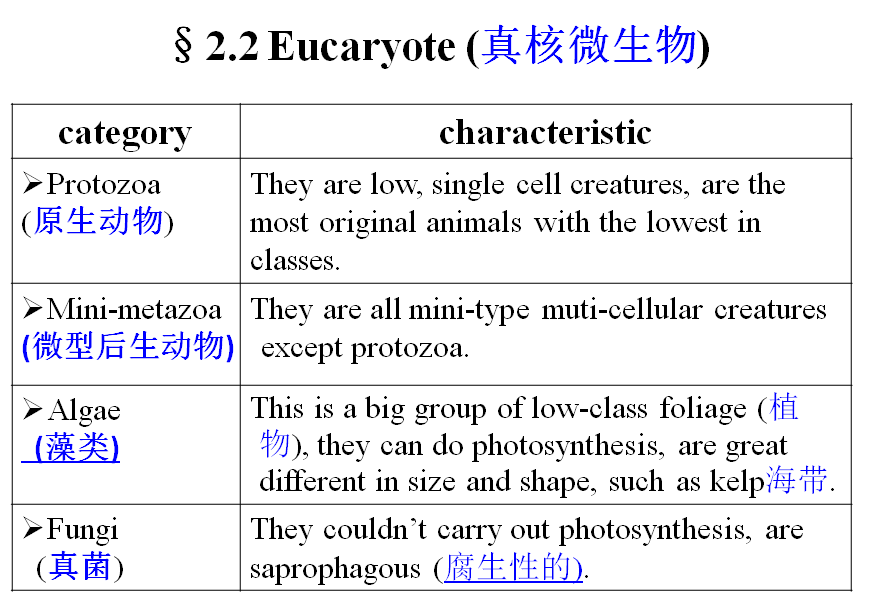
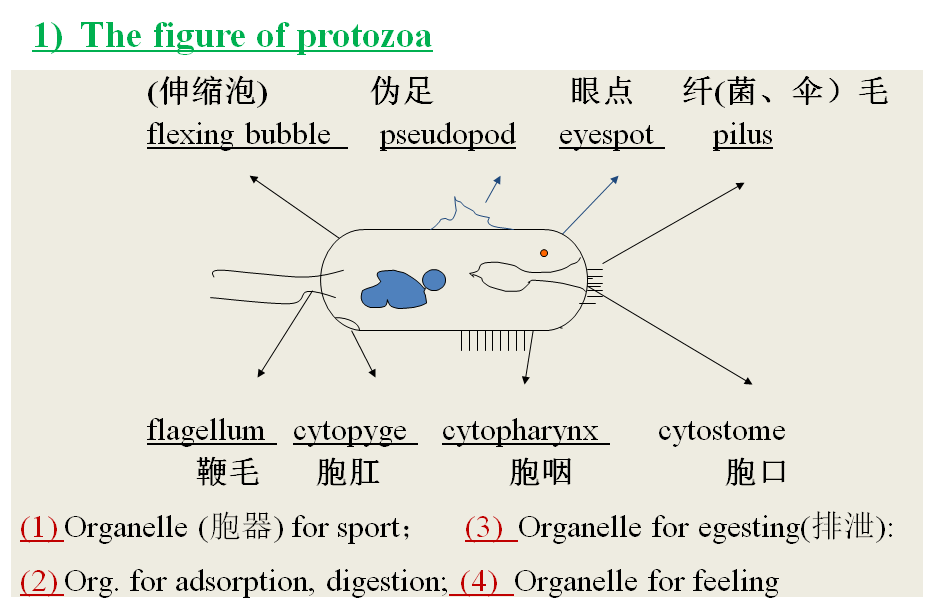


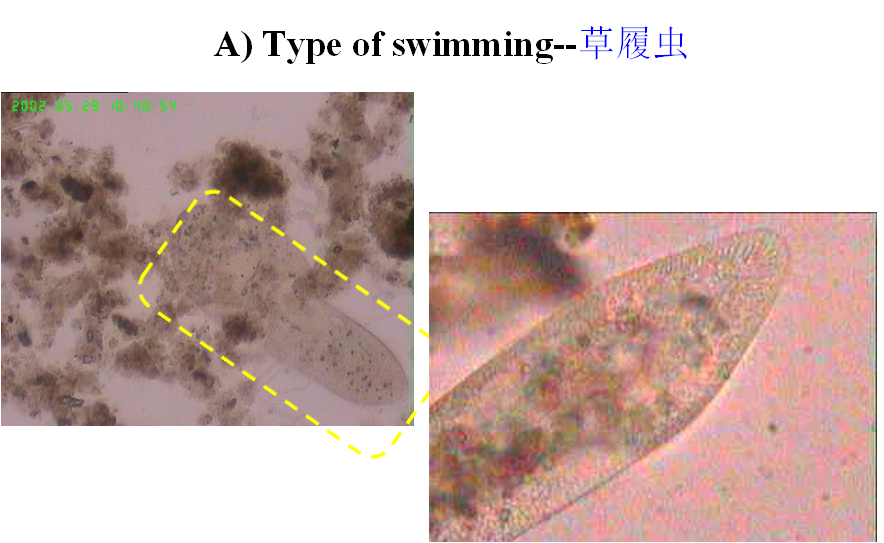
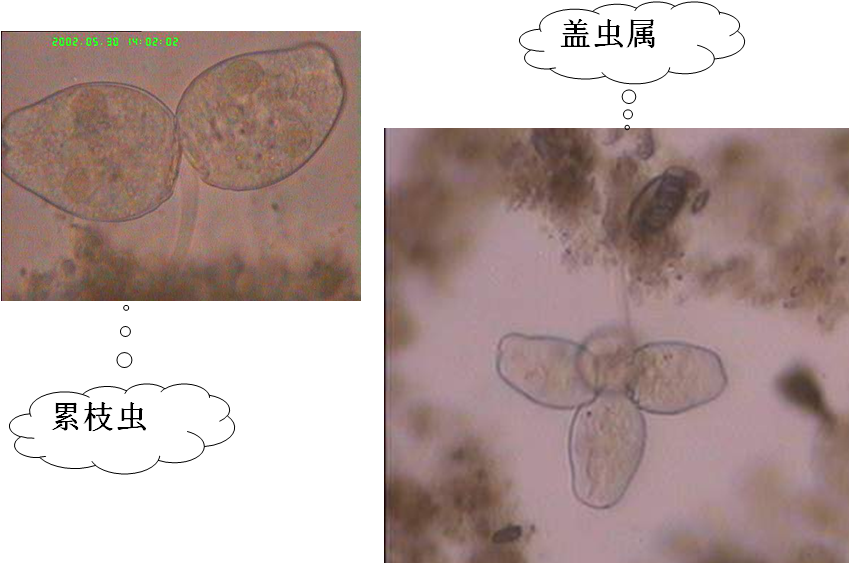
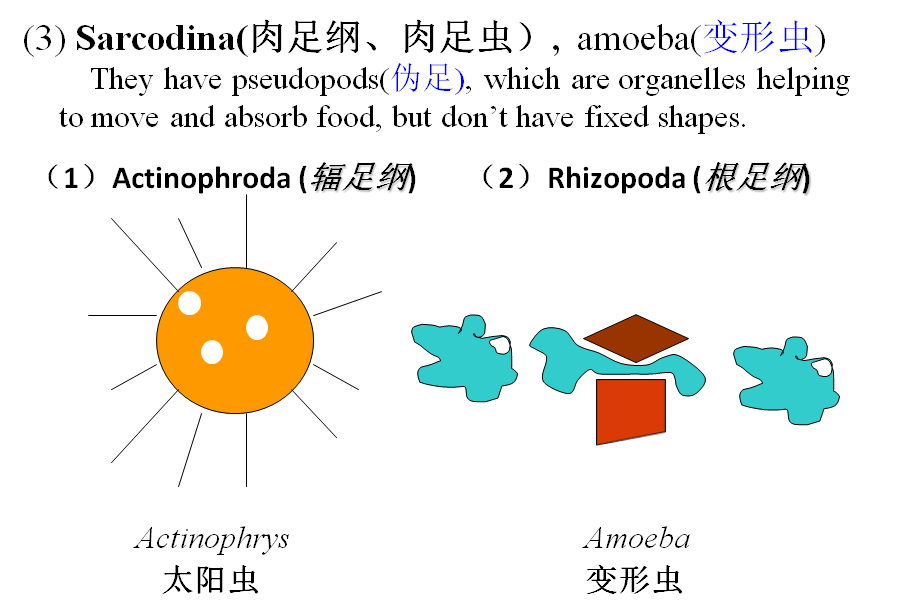
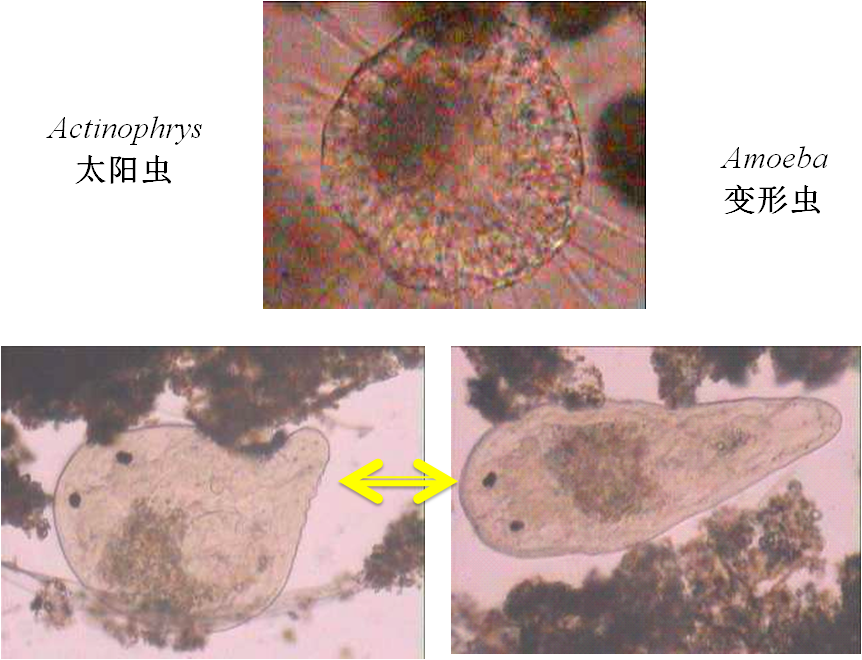

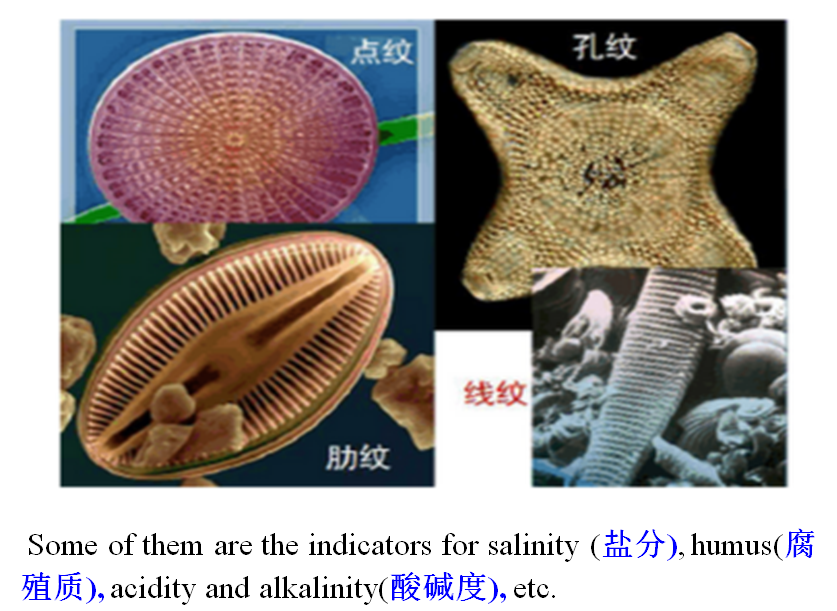
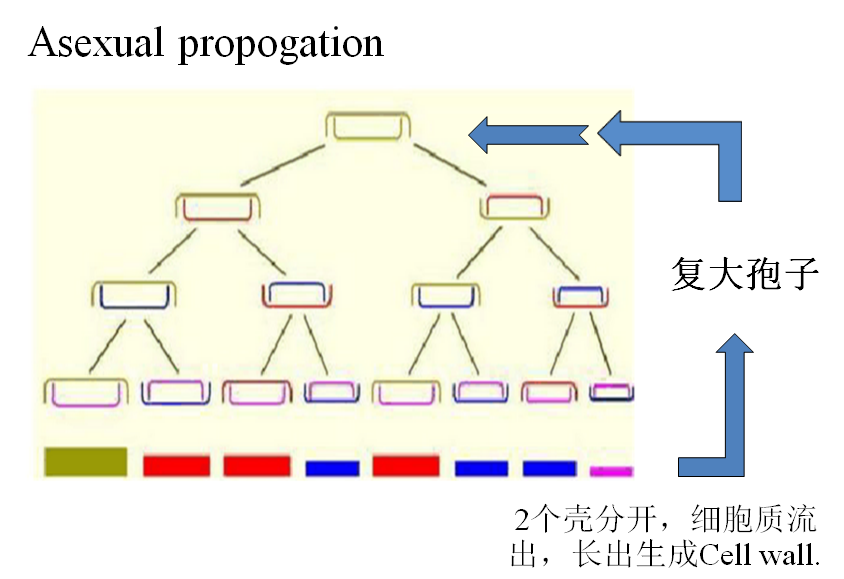
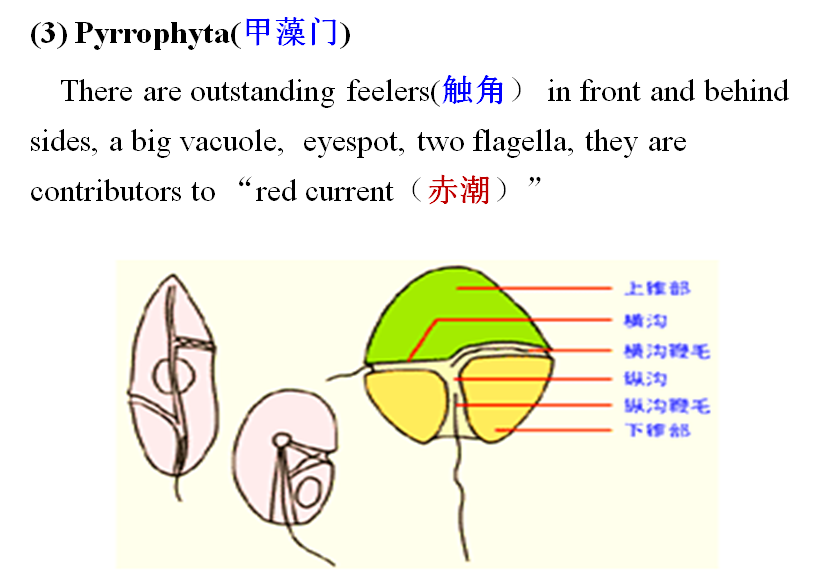
3、Algae(藻类)
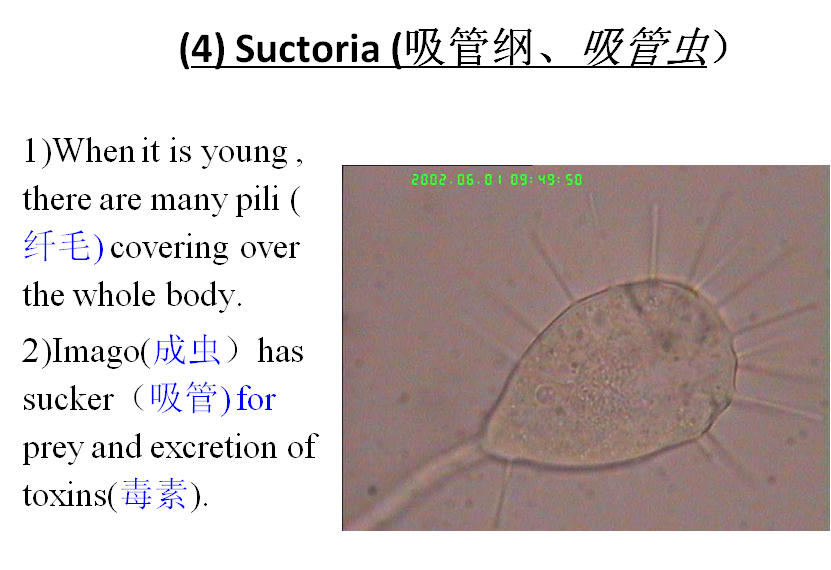
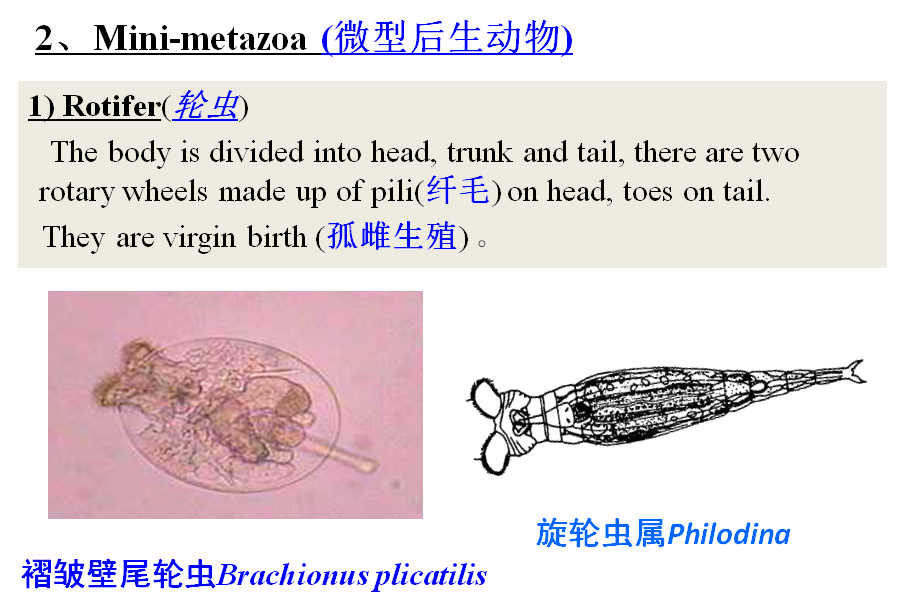
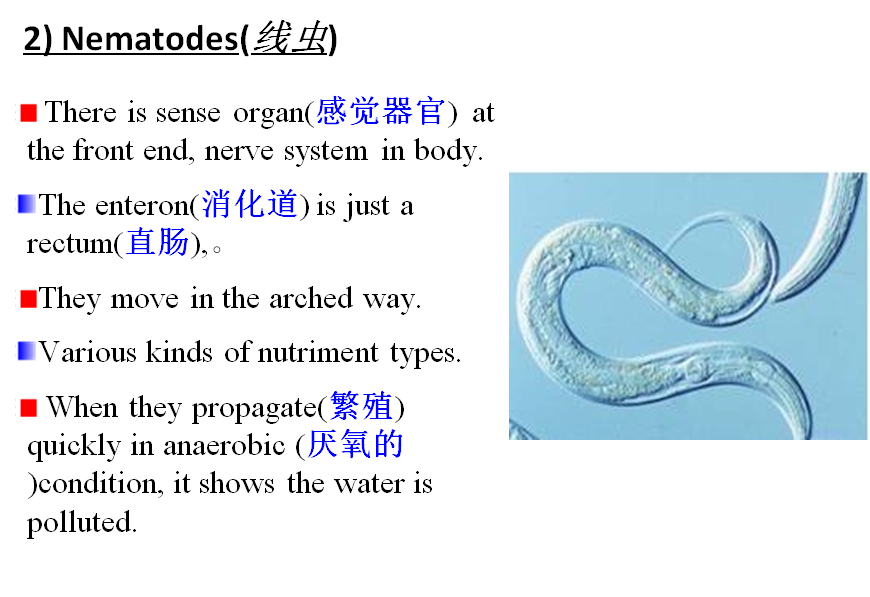
1) Shape andstructure
Their figures are various, majority ofthem have cell wall (细胞壁). Single cell alga can move from place to another by flagellum,so do spores of multi-cellular (多细胞) algae.
There are chloroplasts(色素体)in cells,contain chlorophyll (叶绿素) a, b, c, d,β-carotene (胡萝卜素) and lutein (叶黄素).
2)Physiological characters
Carry through photosynthesis (光合) withsunlight. Most are mesothermal (中温的), but some cansurvive in hotspring with 85℃, others can exist iceberg (冰山).
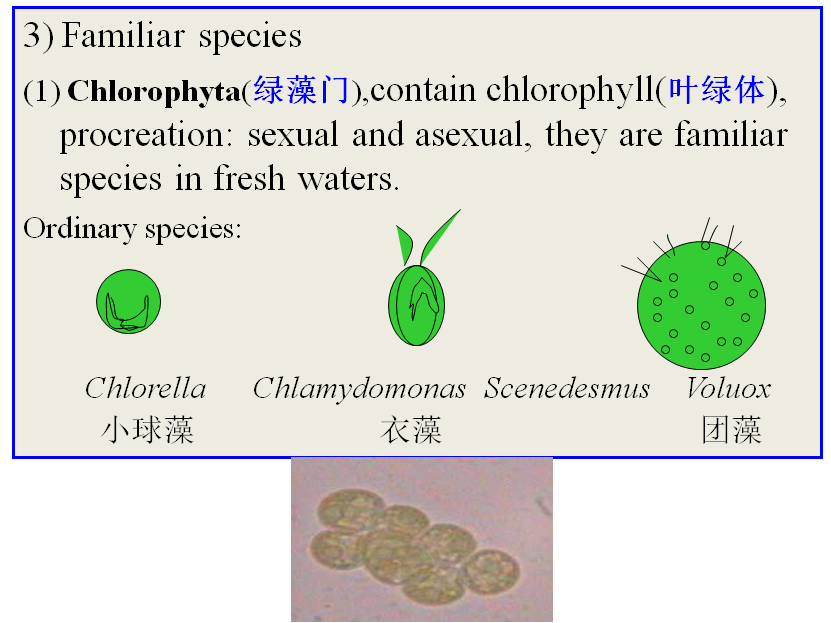

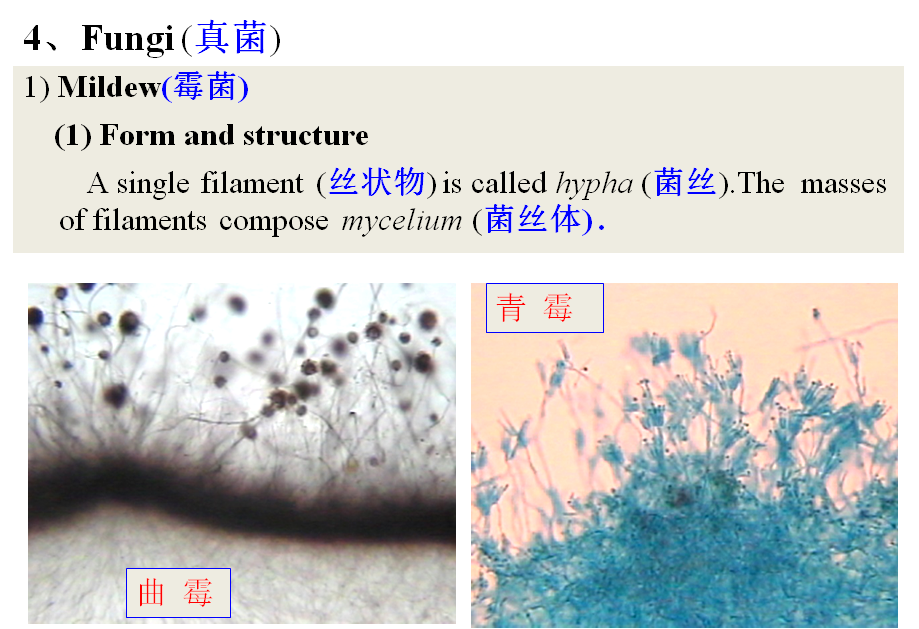
A)Hypha hasdifferentiation: vegetative mycelium, aerial mycelium and sporangium(孢子囊).
B) Differenceof hypha between mildew and actinomycete:
a)The diameter of mildew hyphais decades times as actinomycete (放线菌),
b)The mildew aremulti-cellular individuals with section-area, and have the bigger vacuoles(液泡) in olderone.