§5.2 DNA Damage repair (DNA 损伤修复)
5.2 DNA Damage repair (DNA 损伤修复)
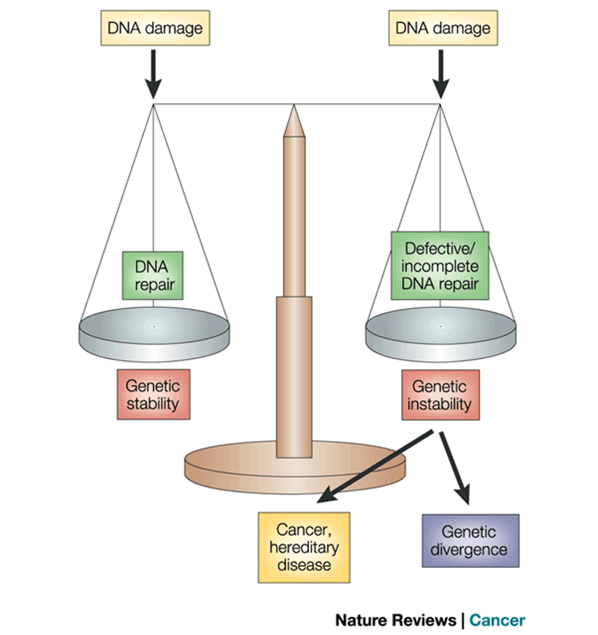
★DNA repairing - resume natural structures and normal biological functions.
★DNA repairing- a supplementary to the proofreading-correction mechanism in DNA replication.
★Basis: genetic data is stored in multiple copies.
· 1.Direct repair (直接修复)
· 2.Excision repair(切除修复)
· 3.Mismatch repair(错配修复)
· 4.Double strand break repair(双链断裂修复)
· 5.Recombination repair(重组修复)
· 6.SOS repair(SOS修复)
· 7.Transcription coupled repair(转录伴随修复)
1. Direct repair (直接修复)
★1.裂口:DNA连接酶;2.光复活;3.烷基转移:甲基转移酶
2.Excision repair (切除修复)
★The most important and effective repair approach(人体内最重要和有效的修复方式).
· Nucleotide excision repair(NER-核苷酸切除修复)
· Base excision repair(BER-碱基切除修复)
★E.Coli nucleotide excision repair(核苷酸切除修复)
· UvrA+UvrB: recognize and bind the damaged region of DNA.
· UvrB+UvrC:excise the damaged segment.
· UvrD: Helicase activity, release damage fragment.
· DNA-pol Ⅰ: gap filling
· DNA ligase: seal the nick
★Base excision repair(碱基切除修复)
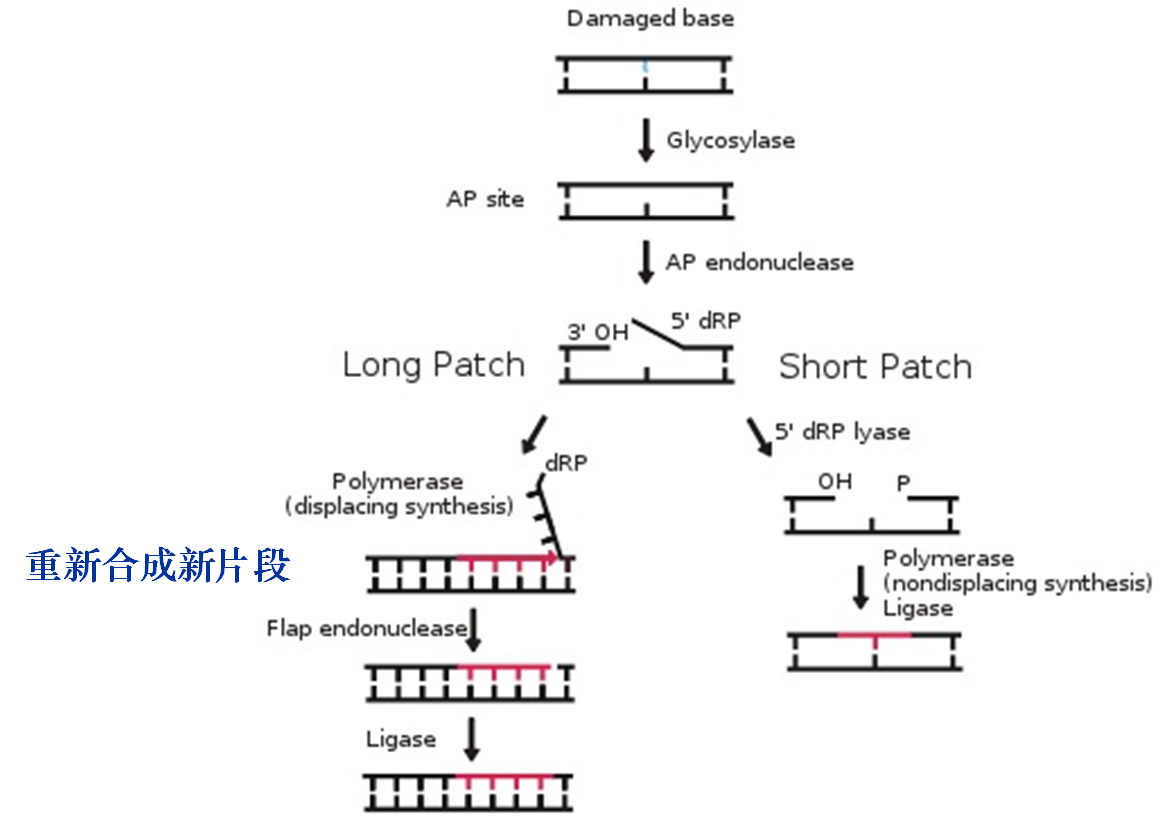
AP site :apurinic/apyrimidinic site(脱嘌呤/嘧啶位点)
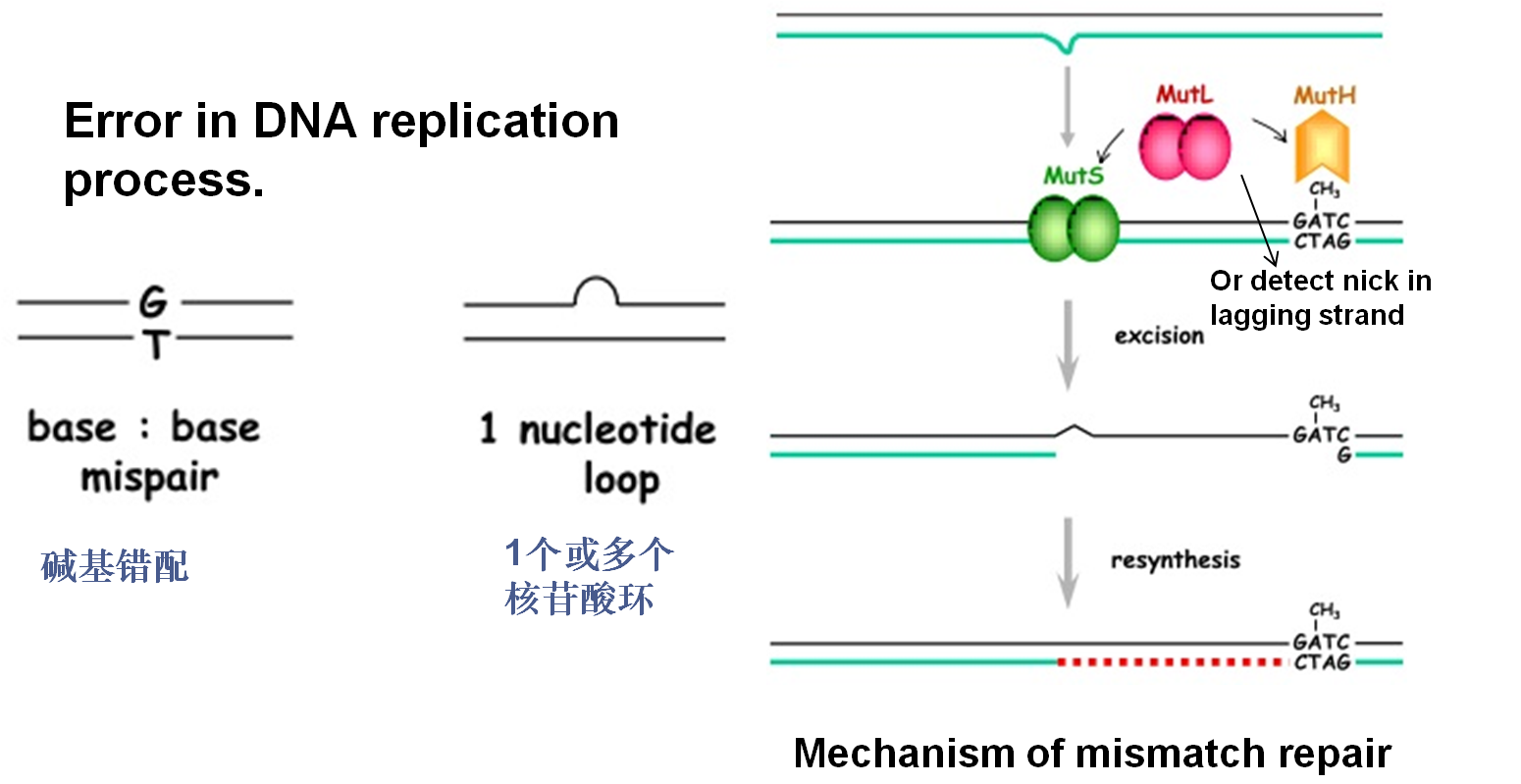
3. Mismatch repair(错配修复)
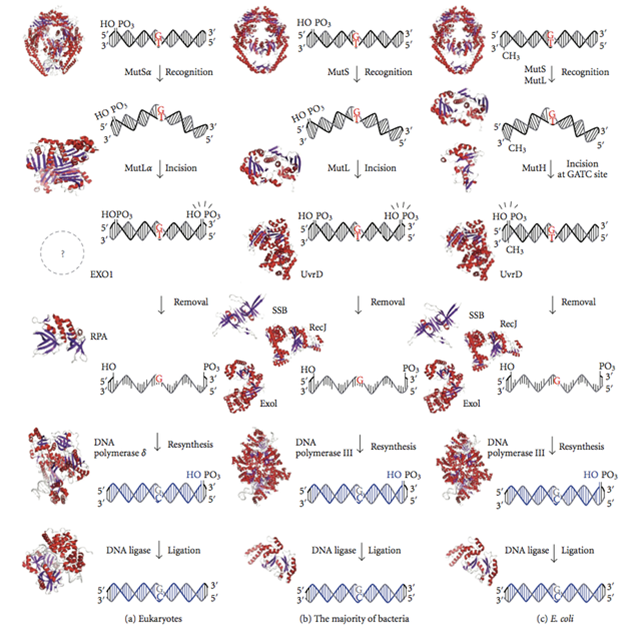
4. Double strand break repairing(双链断裂修复)
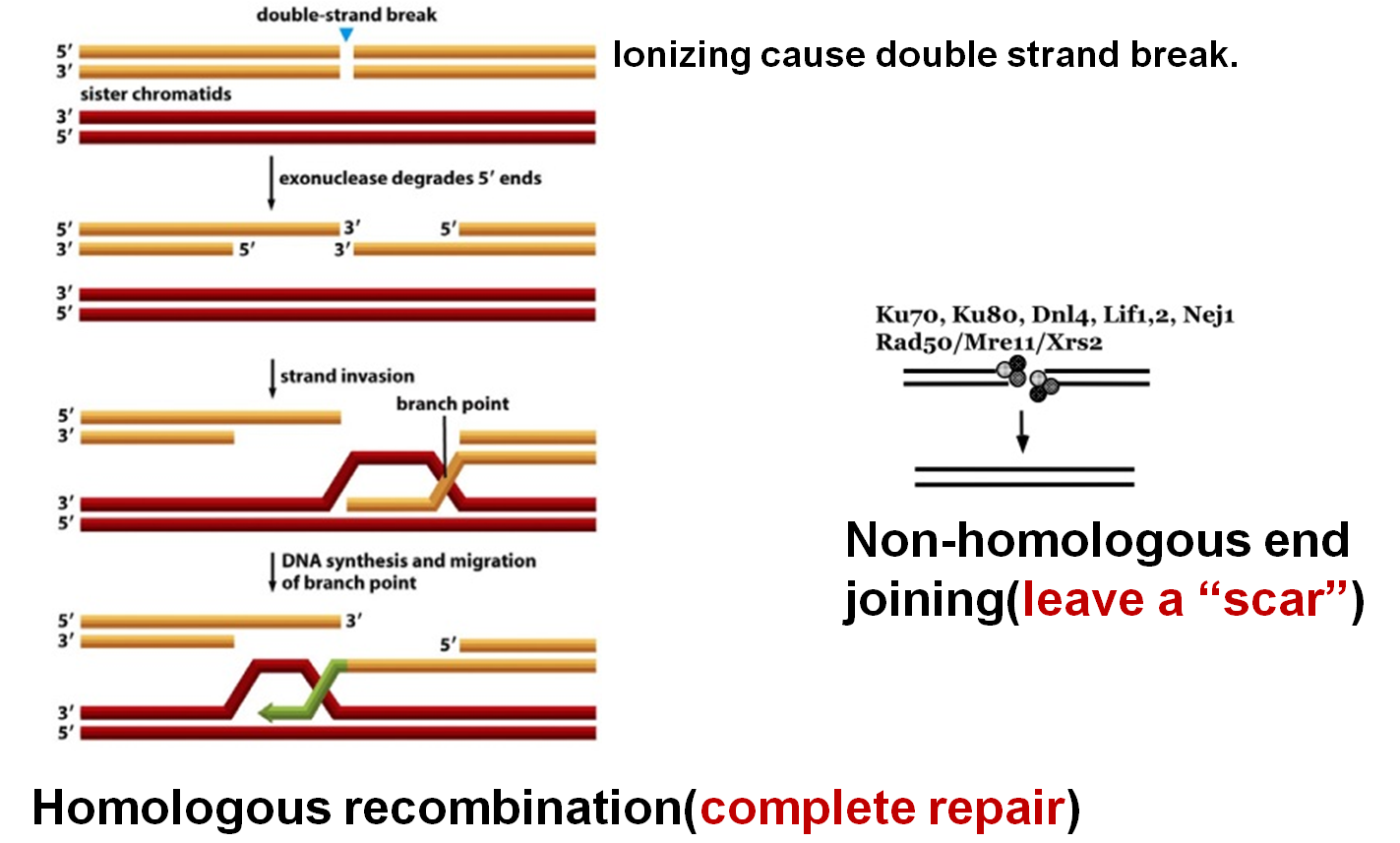
5.Recombination repairing(重组修复)
★Error prone repairing(错误保留)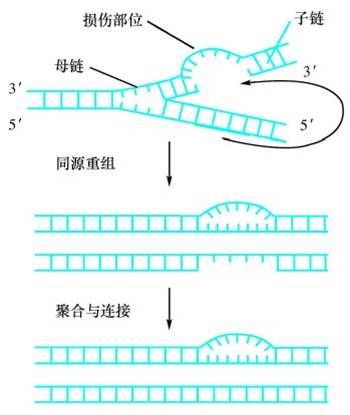
·Repairing a large segment of DNA damaged.
·Recombination protein RecA, RecB and RecC participate in this repairing.
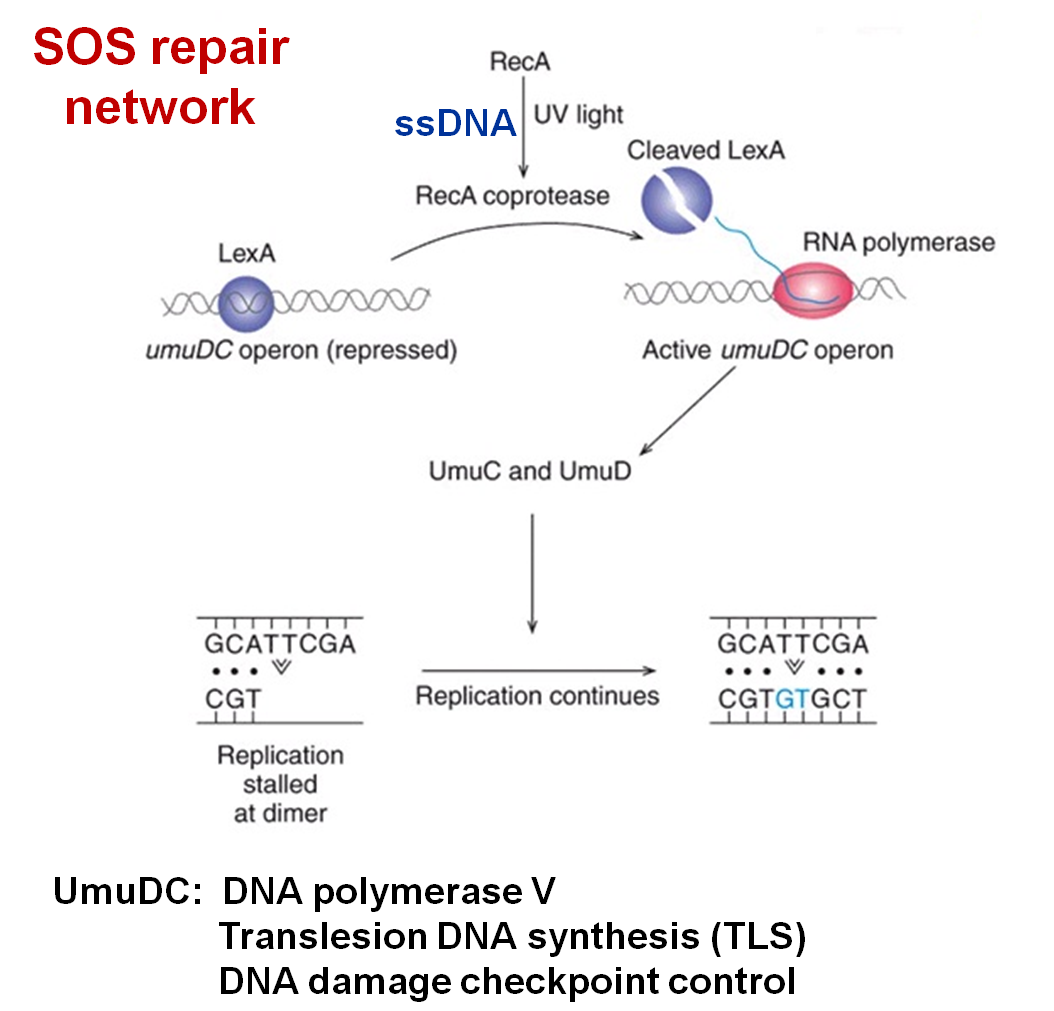
6. SOS repair
★DNA is severely damaged and the replication is hard to continue.(损伤广泛严重)
★If workable, the cell could be survived, but may leave many errors.(保留大量错误)
★In E. coli, uvr gene and rec gene as well as Lex A(阻遏蛋白) protein constitute a regulatory network-regulator.(调节网络系统)
7. Transcription coupled repair(转录伴随修复)
★RNA polymerase pauses at DNA lesions Recruits repair enzymes
· 1. Base excision repair
· 2. Nucleotide excision repair
Specific to the template strand
Xeroderma pigmentosum (
XP , 着色性干皮病)
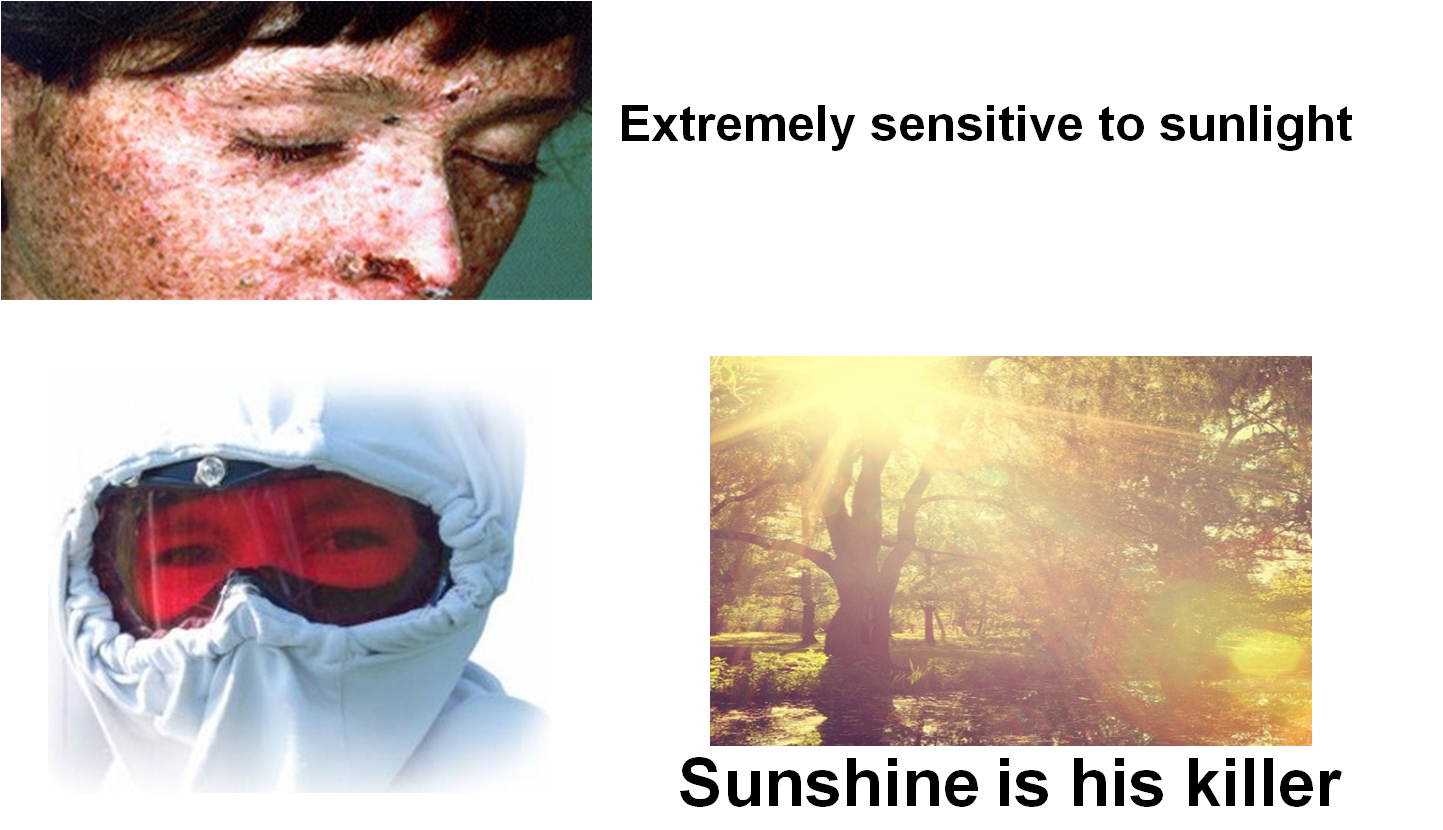


★XP: an autosomal recessive genetic disease. Patients will be suffered with hyper-sensitivity to UV(皮肤光敏) which results in multiple skin cancers(皮肤癌变).
★The cause is due to the low enzymatic activity for the nucleotide excision-repairing process, particular thymine dimer. (切除修复缺陷)
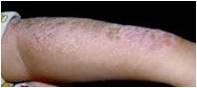

Genesinvolved in XP
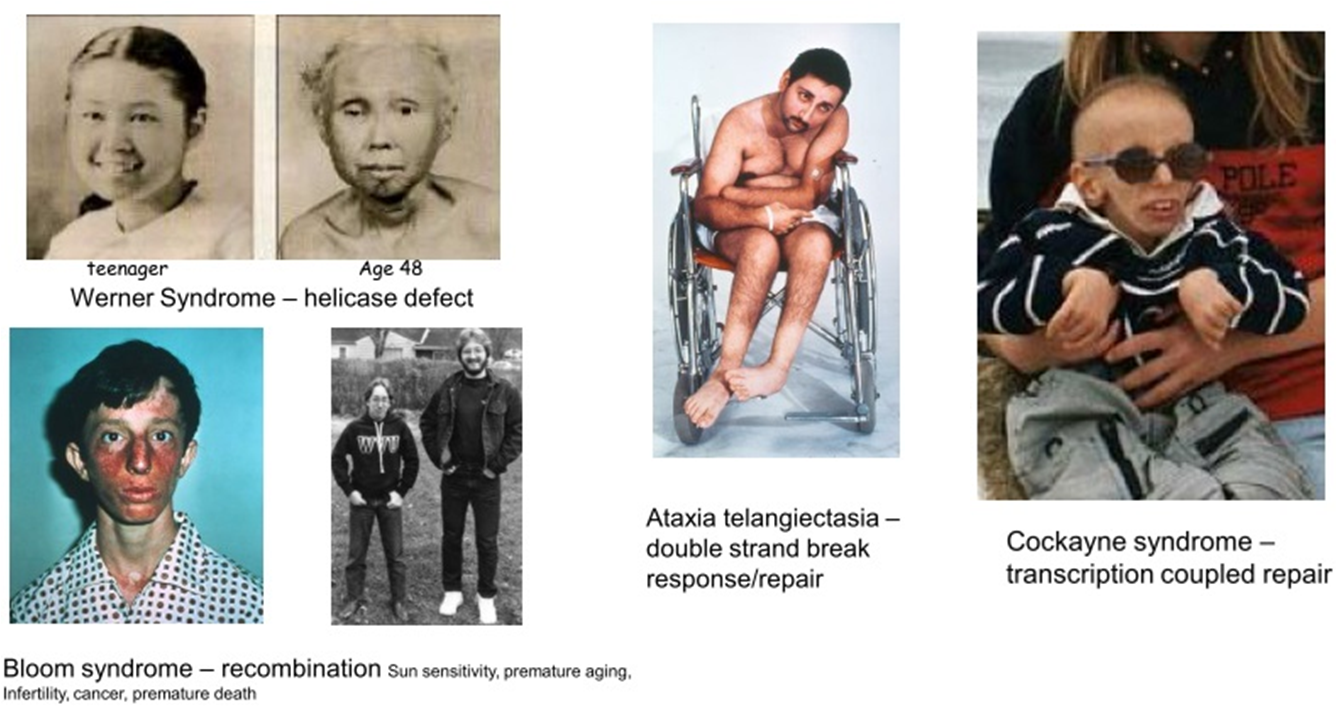
Otherdiseases associated with DNA repair dificiency
Summary 
1.General principles ofDNA replication: semi-conservative/discontiuous;bidirectional;
2.There are 6major enzymes involving in DNA replication
3.The process of DNA replication: initiation; elongation; termination
4.Types of DNA damage
5.Mechanism of DNArepair (BERand NER)
6.Reverse transcription (in telomere)


