-
1 Text A ...
-
2 Muscle Contr...
-
3 Muscular System
-
4 Cardiac Musc...
-
5 Key Medical&...
Prerequisites(预备知识):Musclar Cells
Muscle Contraction and Locomotion
Link:https://opentextbc.ca/biology/chapter/19-4-muscle-contraction-and-locomotion/
(Note:this article shares the following key words with Text A{contractile myosin striate skeletal cardiac actin muscle contraction fibre smooth cell protein capable energy element function conscious repeat refer associate})
Muscle cells are specialized for contraction. Muscles allow for motions such as walking, and they also facilitate bodily processes such as respiration and digestion. The body contains three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle (Figure 19.33).
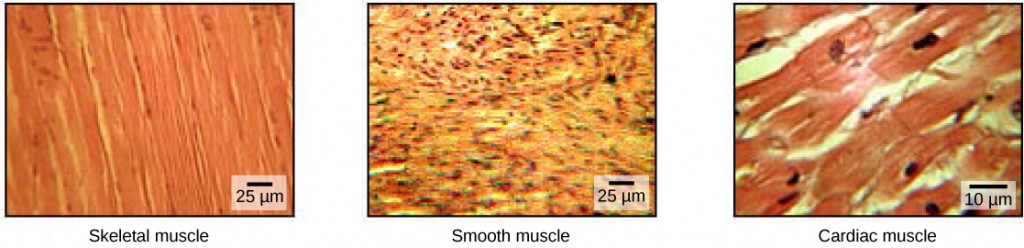
Skeletal muscle tissue forms skeletal muscles, which attach to bones or skin and control locomotion and any movement that can be consciously controlled. Because it can be controlled by thought, skeletal muscle is also called voluntary muscle. Skeletal muscles are long and cylindrical in appearance; when viewed under a microscope, skeletal muscle tissue has a striped or striated appearance. The striations are caused by the regular arrangement of contractile proteins (actin and myosin). Actin is a globular contractile protein that interacts with myosinfor muscle contraction. Skeletal muscle also has multiple nuclei present in a single cell.
Smooth muscle tissue occurs in the walls of hollow organs such as the intestines, stomach, and urinary bladder, and around passages such as the respiratory tract and blood vessels. Smooth muscle has no striations, is not under voluntary control, has only one nucleus per cell, is tapered at both ends, and is called involuntary muscle.
Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart, and cardiac contractions pump blood throughout the body and maintain blood pressure. Like skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated, but unlike skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle cannot be consciously controlled and is called involuntary muscle. It has one nucleus per cell, is branched, and is distinguished by the presence of intercalated disks.
Skeletal Muscle Fiber Structure
Each skeletal muscle fiber is a skeletal muscle cell. These cells are incredibly large, with diameters of up to 100 µm and lengths of up to 30 cm. The plasma membrane of a skeletal muscle fiber is called the sarcolemma. The sarcolemma is the site of action potential conduction, which triggers muscle contraction. Within each muscle fiber are myofibrils—long cylindrical structures that lie parallel to the muscle fiber. Myofibrils run the entire length of the muscle fiber, and because they are only approximately 1.2 µm in diameter, hundreds to thousands can be found inside one muscle fiber. They attach to the sarcolemma at their ends, so that as myofibrils shorten, the entire muscle cell contracts (
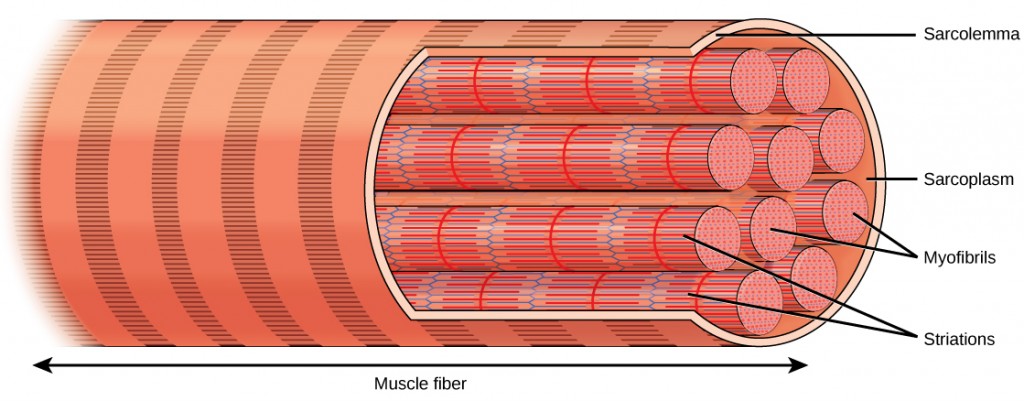
The striated appearance of skeletal muscle tissue is a result of repeating bands of the proteins actin and myosin that are present along the length of myofibrils. Dark A bands and light I bands repeat along myofibrils, and the alignment of myofibrils in the cell causes the entire cell to appear striated or banded.
Each I band has a dense line running vertically through the middle called a Z disc or Z line. The Z discs mark the border of units called sarcomeres, which are the functional units of skeletal muscle. One sarcomere is the space between two consecutive Z discs and contains one entire A band and two halves of an I band, one on either side of the A band. A myofibril is composed of many sarcomeres running along its length, and as the sarcomeres individually contract, the myofibrils and muscle cells shorten (Figure 19.35).
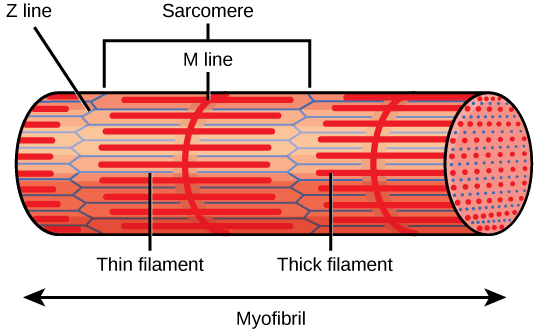
A sarcomere is the region from one Z line to the next Z line. Many sarcomeres are present in a myofibril, resulting in the striation pattern characteristic of skeletal muscle.
Myofibrils are composed of smaller structures called myofilaments. There are two main types of filaments: thick filaments and thin filaments; each has different compositions and locations. Thick filaments occur only in the A band of a myofibril. Thin filaments attach to a protein in the Z disc called alpha-actinin and occur across the entire length of the I band and partway into the A band. The region at which thick and thin filaments overlap has a dense appearance, as there is little space between the filaments. Thin filaments do not extend all the way into the A bands, leaving a central region of the A band that only contains thick filaments. This central region of the A band looks slightly lighter than the rest of the A band and is called the H zone. The middle of the H zone has a vertical line called the M line, at which accessory proteins hold together thick filaments. Both the Z disc and the M line hold myofilaments in place to maintain the structural arrangement and layering of the myofibril. Myofibrils are connected to each other by intermediate, or desmin, filaments that attach to the Z disc.
Thick and thin filaments are themselves composed of proteins. Thick filaments are composed of the protein myosin. The tail of a myosin molecule connects with other myosin molecules to form the central region of a thick filament near the M line, whereas the heads align on either side of the thick filament where the thin filaments overlap. The primary component of thin filaments is the actin protein. Two other components of the thin filament are tropomyosin and troponin. Actin has binding sites for myosin attachment. Strands of tropomyosin block the binding sites and prevent actin–myosin interactions when the muscles are at rest. Troponin consists of three globular subunits. One subunit binds to tropomyosin, one subunit binds to actin, and one subunit binds Ca2+ ions.
Concept in Action

View this animation showing the organization of muscle fibers.
Sliding Filament Model of Contraction
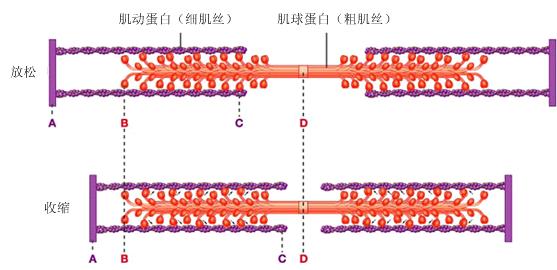
For a muscle cell to contract, the sarcomere must shorten. However, thick and thin filaments—the components of sarcomeres—do not shorten. Instead, they slide by one another, causing the sarcomere to shorten while the filaments remain the same length. The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction was developed to fit the differences observed in the named bands on the sarcomere at different degrees of muscle contraction and relaxation. The mechanism of contraction is the binding of myosin to actin, forming cross-bridges that generate filament movement (Figure 19.36).
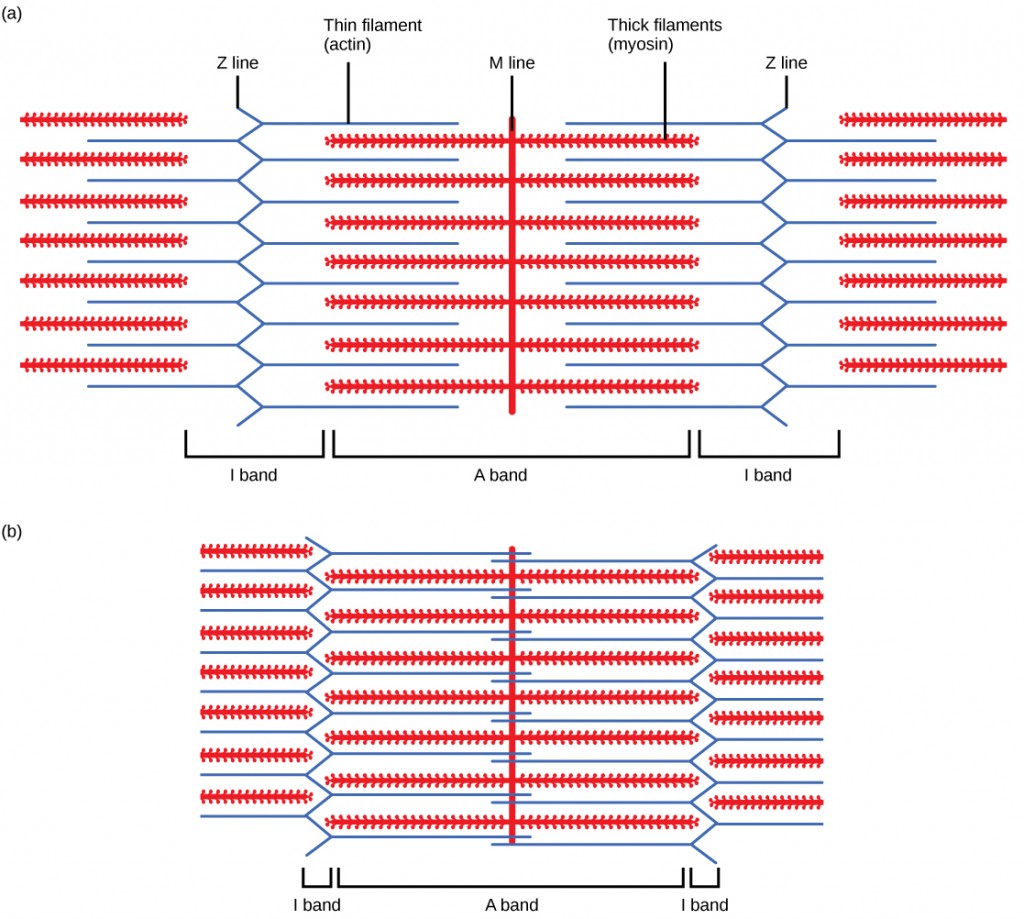
When (a) a sarcomere (b) contracts, the Z lines move closer together and the I band gets smaller. The A band stays the same width and, at full contraction, the thin filaments overlap.
When a sarcomere shortens, some regions shorten whereas others stay the same length. A sarcomere is defined as the distance between two consecutive Z discs or Z lines; when a muscle contracts, the distance between the Z discs is reduced. The H zone—the central region of the A zone—contains only thick filaments and is shortened during contraction. The I band contains only thin filaments and also shortens. The A band does not shorten—it remains the same length—but A bands of different sarcomeres move closer together during contraction, eventually disappearing. Thin filaments are pulled by the thick filaments toward the center of the sarcomere until the Z discs approach the thick filaments. The zone of overlap, in which thin filaments and thick filaments occupy the same area, increases as the thin filaments move inward.
ATP and Muscle Contraction
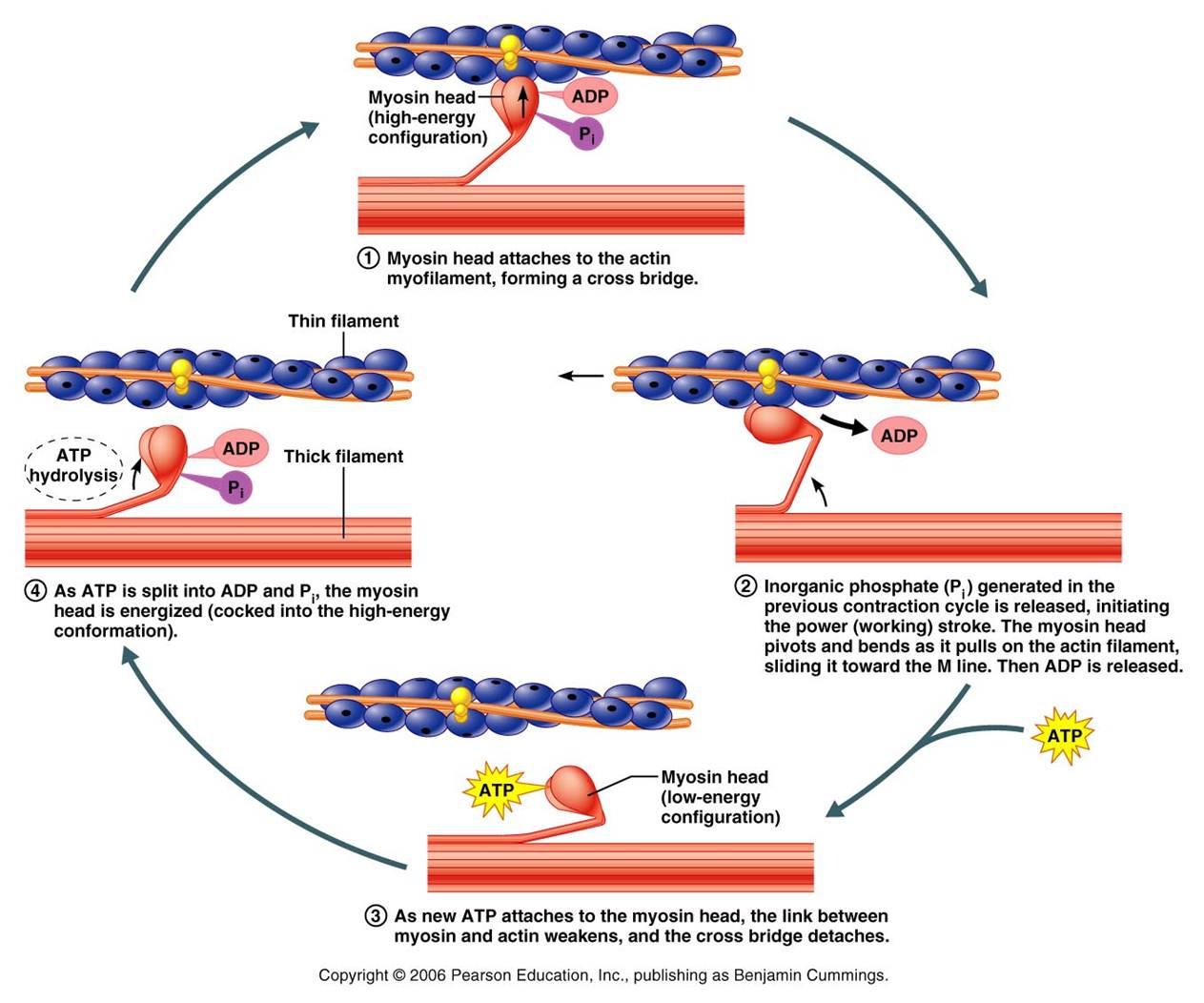
The motion of muscle shortening occurs as myosin heads bind to actin and pull the actin inwards. This action requires energy, which is provided by ATP. Myosin binds to actin at a binding site on the globular actin protein. Myosin has another binding site for ATP at which enzymatic activity hydrolyzes ATP to ADP, releasing an inorganic phosphate molecule and energy.
ATP binding causes myosin to release actin, allowing actin and myosin to detach from each other. After this happens, the newly bound ATP is converted to ADP and inorganic phosphate, Pi. The enzyme at the binding site on myosin is called ATPase. The energy released during ATP hydrolysis changes the angle of the myosin head into a “cocked” position. The myosin head is then in a position for further movement, possessing potential energy, but ADP and Piare still attached. If actin binding sites are covered and unavailable, the myosin will remain in the high energy configuration with ATP hydrolyzed, but still attached.
If the actin binding sites are uncovered, a cross-bridge will form; that is, the myosin head spans the distance between the actin and myosin molecules. Pi is then released, allowing myosin to expend the stored energy as a conformational change. The myosin head moves toward the M line, pulling the actin along with it. As the actin is pulled, the filaments move approximately 10 nm toward the M line. This movement is called the power stroke, as it is the step at which force is produced. As the actin is pulled toward the M line, the sarcomere shortens and the muscle contracts.
When the myosin head is “cocked,” it contains energy and is in a high-energy configuration. This energy is expended as the myosin head moves through the power stroke; at the end of the power stroke, the myosin head is in a low-energy position. After the power stroke, ADP is released; however, the cross-bridge formed is still in place, and actin and myosin are bound together. ATP can then attach to myosin, which allows the cross-bridge cycle to start again and further muscle contraction can occur (Figure 19.37).
Concept in Action

Watch this video explaining how a muscle contraction is signaled.
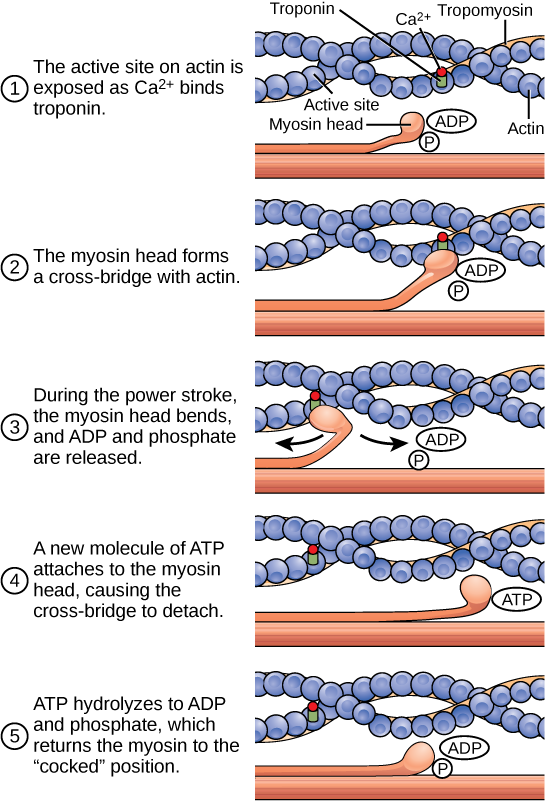
Which of the following statements about muscle contraction is true?
The power stroke occurs when ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP and phosphate.
The power stroke occurs when ADP and phosphate dissociate from the myosin head.
The power stroke occurs when ADP and phosphate dissociate from the actin active site.
The power stroke occurs when Ca2+ binds the calcium head.
Concept in Action

View this animation of the cross-bridge muscle contraction.
Regulatory Proteins
When a muscle is in a resting state, actin and myosin are separated. To keep actin from binding to the active site on myosin, regulatory proteins block the molecular binding sites. Tropomyosin blocks myosin binding sites on actin molecules, preventing cross-bridge formation and preventing contraction in a muscle without nervous input. Troponin binds to tropomyosin and helps to position it on the actin molecule; it also binds calcium ions.
To enable a muscle contraction, tropomyosin must change conformation, uncovering the myosin-binding site on an actin molecule and allowing cross-bridge formation. This can only happen in the presence of calcium, which is kept at extremely low concentrations in the sarcoplasm. If present, calcium ions bind to troponin, causing conformational changes in troponin that allow tropomyosin to move away from the myosin binding sites on actin. Once the tropomyosin is removed, a cross-bridge can form between actin and myosin, triggering contraction. Cross-bridge cycling continues until Ca2+ ions and ATP are no longer available and tropomyosin again covers the binding sites on actin.
Excitation–Contraction Coupling
Excitation–contraction coupling is the link (transduction) between the action potential generated in the sarcolemma and the start of a muscle contraction. The trigger for calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the sarcoplasm is a neural signal. Each skeletal muscle fiber is controlled by a motor neuron, which conducts signals from the brain or spinal cord to the muscle. The area of the sarcolemma on the muscle fiber that interacts with the neuron is called the motor end plate. The end of the neuron’s axon is called the synaptic terminal, and it does not actually contact the motor end plate. A small space called the synaptic cleft separates the synaptic terminal from the motor end plate. Electrical signals travel along the neuron’s axon, which branches through the muscle and connects to individual muscle fibers at a neuromuscular junction.
The ability of cells to communicate electrically requires that the cells expend energy to create an electrical gradient across their cell membranes. This charge gradient is carried by ions, which are differentially distributed across the membrane. Each ion exerts an electrical influence and a concentration influence. Just as milk will eventually mix with coffee without the need to stir, ions also distribute themselves evenly, if they are permitted to do so. In this case, they are not permitted to return to an evenly mixed state.
The sodium–potassium ATPase uses cellular energy to move K+ ions inside the cell and Na+ions outside. This alone accumulates a small electrical charge, but a big concentration gradient. There is lots of K+ in the cell and lots of Na+ outside the cell. Potassium is able to leave the cell through K+ channels that are open 90% of the time, and it does. However, Na+ channels are rarely open, so Na+ remains outside the cell. When K+ leaves the cell, obeying its concentration gradient, that effectively leaves a negative charge behind. So at rest, there is a large concentration gradient for Na+ to enter the cell, and there is an accumulation of negative charges left behind in the cell. This is the resting membrane potential. Potential in this context means a separation of electrical charge that is capable of doing work. It is measured in volts, just like a battery. However, the transmembrane potential is considerably smaller (0.07 V); therefore, the small value is expressed as millivolts (mV) or 70 mV. Because the inside of a cell is negative compared with the outside, a minus sign signifies the excess of negative charges inside the cell, −70 mV.
If an event changes the permeability of the membrane to Na+ ions, they will enter the cell. That will change the voltage. This is an electrical event, called an action potential, that can be used as a cellular signal. Communication occurs between nerves and muscles through neurotransmitters. Neuron action potentials cause the release of neurotransmitters from the synaptic terminal into the synaptic cleft, where they can then diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to a receptor molecule on the motor end plate. The motor end plate possesses junctional folds—folds in the sarcolemma that create a large surface area for the neurotransmitter to bind to receptors. The receptors are actually sodium channels that open to allow the passage of Na+ into the cell when they receive neurotransmitter signal.
Acetylcholine (ACh) is a neurotransmitter released by motor neurons that binds to receptors in the motor end plate. Neurotransmitter release occurs when an action potential travels down the motor neuron’s axon, resulting in altered permeability of the synaptic terminal membrane and an influx of calcium. The Ca2+ ions allow synaptic vesicles to move to and bind with the presynaptic membrane (on the neuron), and release neurotransmitter from the vesicles into the synaptic cleft. Once released by the synaptic terminal, ACh diffuses across the synaptic cleft to the motor end plate, where it binds with ACh receptors. As a neurotransmitter binds, these ion channels open, and Na+ ions cross the membrane into the muscle cell. This reduces the voltage difference between the inside and outside of the cell, which is called depolarization. As ACh binds at the motor end plate, this depolarization is called an end-plate potential. The depolarization then spreads along the sarcolemma, creating an action potential as sodium channels adjacent to the initial depolarization site sense the change in voltage and open. The action potential moves across the entire cell, creating a wave of depolarization.
ACh is broken down by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) into acetyl and choline. AChE resides in the synaptic cleft, breaking down ACh so that it does not remain bound to ACh receptors, which would cause unwanted extended muscle contraction (Figure 19.38).
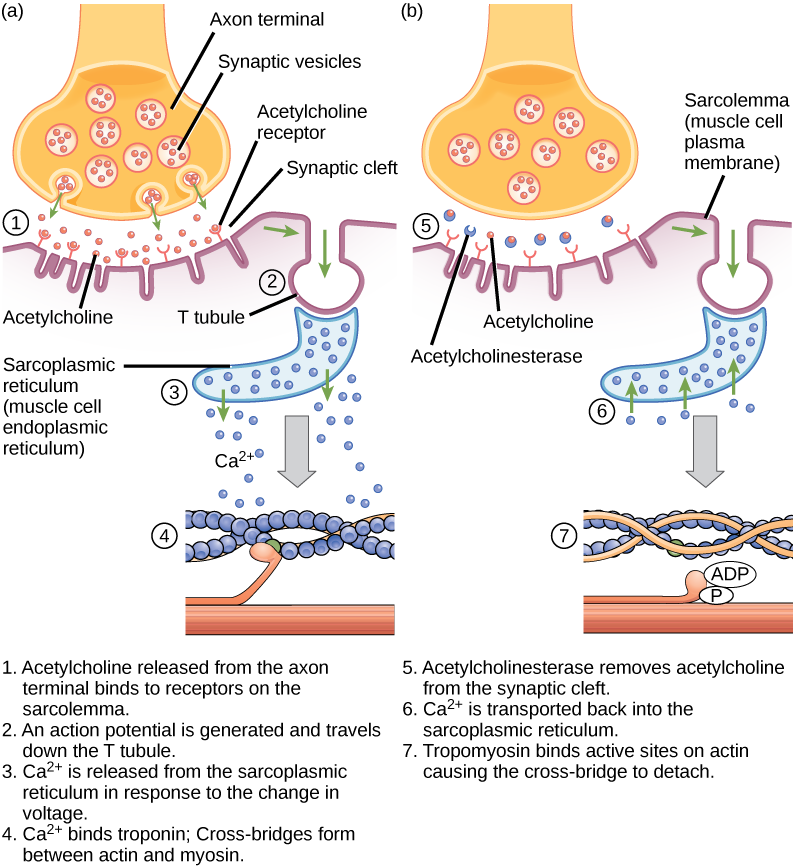
The deadly nerve gas Sarin irreversibly inhibits acetycholinesterase. What effect would Sarin have on muscle contraction?
After depolarization, the membrane returns to its resting state. This is called repolarization, during which voltage-gated sodium channels close. Potassium channels continue at 90% conductance. Because the plasma membrane sodium–potassium ATPase always transports ions, the resting state (negatively charged inside relative to the outside) is restored. The period immediately following the transmission of an impulse in a nerve or muscle, in which a neuron or muscle cell regains its ability to transmit another impulse, is called the refractory period. During the refractory period, the membrane cannot generate another action potential. . The refractory period allows the voltage-sensitive ion channels to return to their resting configurations. The sodium potassium ATPase continually moves Na+ back out of the cell and K+ back into the cell, and the K+ leaks out leaving negative charge behind. Very quickly, the membrane repolarizes, so that it can again be depolarized.
Control of Muscle Tension
Neural control initiates the formation of actin–myosin cross-bridges, leading to the sarcomere shortening involved in muscle contraction. These contractions extend from the muscle fiber through connective tissue to pull on bones, causing skeletal movement. The pull exerted by a muscle is called tension, and the amount of force created by this tension can vary. This enables the same muscles to move very light objects and very heavy objects. In individual muscle fibers, the amount of tension produced depends on the cross-sectional area of the muscle fiber and the frequency of neural stimulation.
The number of cross-bridges formed between actin and myosin determine the amount of tension that a muscle fiber can produce. Cross-bridges can only form where thick and thin filaments overlap, allowing myosin to bind to actin. If more cross-bridges are formed, more myosin will pull on actin, and more tension will be produced.
The ideal length of a sarcomere during production of maximal tension occurs when thick and thin filaments overlap to the greatest degree. If a sarcomere at rest is stretched past an ideal resting length, thick and thin filaments do not overlap to the greatest degree, and fewer cross-bridges can form. This results in fewer myosin heads pulling on actin, and less tension is produced. As a sarcomere is shortened, the zone of overlap is reduced as the thin filaments reach the H zone, which is composed of myosin tails. Because it is myosin heads that form cross-bridges, actin will not bind to myosin in this zone, reducing the tension produced by this myofiber. If the sarcomere is shortened even more, thin filaments begin to overlap with each other—reducing cross-bridge formation even further, and producing even less tension. Conversely, if the sarcomere is stretched to the point at which thick and thin filaments do not overlap at all, no cross-bridges are formed and no tension is produced. This amount of stretching does not usually occur because accessory proteins, internal sensory nerves, and connective tissue oppose extreme stretching.
The primary variable determining force production is the number of myofibers within the muscle that receive an action potential from the neuron that controls that fiber. When using the biceps to pick up a pencil, the motor cortex of the brain only signals a few neurons of the biceps, and only a few myofibers respond. In vertebrates, each myofiber responds fully if stimulated. When picking up a piano, the motor cortex signals all of the neurons in the biceps and every myofiber participates. This is close to the maximum force the muscle can produce. As mentioned above, increasing the frequency of action potentials (the number of signals per second) can increase the force a bit more, because the tropomyosin is flooded with calcium.
Summary
The body contains three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Skeleton muscle tissue is composed of sarcomeres, the functional units of muscle tissue. Muscle contraction occurs when sarcomeres shorten, as thick and thin filaments slide past each other, which is called the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. ATP provides the energy for cross-bridge formation and filament sliding. Regulatory proteins, such as troponin and tropomyosin, control cross-bridge formation. Excitation–contraction coupling transduces the electrical signal of the neuron, via acetylcholine, to an electrical signal on the muscle membrane, which initiates force production. The number of muscle fibers contracting determines how much force the whole muscle produces.
Muscular System
https://www.innerbody.com/image/musfov.html
The muscular system is responsible for the movement of the human body. Attached to the bones of the skeletal system are about 700 named muscles that make up roughly half of a person’s body weight. Each of these muscles is a discrete organ constructed of skeletal muscle tissue, blood vessels, tendons, and nerves. Muscle tissue is also found inside of the heart, digestive organs, and blood vessels. In these organs, muscles serve to move substances throughout the body. Muscular System Anatomy Muscular System Anatomy Muscle Types There are three types of muscle tissue: Visceral, cardiac, and skeletal. Visceral Muscle (Smooth Muscle) Visceral muscle is found inside of organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels. The weakest of all muscle tissues, visceral muscle makes organs contract to move substances through the organ. Because visceral muscle is controlled by the unconscious part of the brain, it is known as involuntary muscle—it cannot be directly controlled by the conscious mind. The term “smooth muscle” is often used to describe visceral muscle because it has a very smooth, uniform appearance when viewed under a microscope. This smooth appearance starkly contrasts with the banded appearance of cardiac and skeletal muscles. Cardiac Muscle Found only in the heart, cardiac muscle is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Cardiac muscle tissue cannot be controlled consciously, so it is an involuntary muscle. While hormones and signals from the brain adjust the rate of contraction, cardiac muscle stimulates itself to contract. The natural pacemaker of the heart is made of cardiac muscle tissue that stimulates other cardiac muscle cells to contract. Because of its self-stimulation, cardiac muscle is considered to be autorhythmic or intrinsically controlled. The cells of cardiac muscle tissue are striated—that is, they appear to have light and dark stripes when viewed under a light microscope. The arrangement of protein fibers inside of the cells causes these light and dark bands. Striations indicate that a muscle cell is very strong, unlike visceral muscles. The cells of cardiac muscle are branched X or Y shaped cells tightly connected together by special junctions called intercalated disks. Intercalated disks are made up of fingerlike projections from two neighboring cells that interlock and provide a strong bond between the cells. The branched structure and intercalated disks allow the muscle cells to resist high blood pressures and the strain of pumping blood throughout a lifetime. These features also help to spread electrochemical signals quickly from cell to cell so that the heart can beat as a unit. Skeletal Muscle Skeletal muscle is the only voluntary muscle tissue in the human body—it is controlled consciously. Every physical action that a person consciously performs (e.g. speaking, walking, or writing) requires skeletal muscle. The function of skeletal muscle is to contract to move parts of the body closer to the bone that the muscle is attached to. Most skeletal muscles are attached to two bones across a joint, so the muscle serves to move parts of those bones closer to each other. Skeletal muscle cells form when many smaller progenitor cells lump themselves together to form long, straight, multinucleated fibers. Striated just like cardiac muscle, these skeletal muscle fibers are very strong. Skeletal muscle derives its name from the fact that these muscles always connect to the skeleton in at least one place. Gross Anatomy of a Skeletal Muscle Most skeletal muscles are attached to two bones through tendons. Tendons are tough bands of dense regular connective tissue whose strong collagen fibers firmly attach muscles to bones. Tendons are under extreme stress when muscles pull on them, so they are very strong and are woven into the coverings of both muscles and bones. Muscles move by shortening their length, pulling on tendons, and moving bones closer to each other. One of the bones is pulled towards the other bone, which remains stationary. The place on the stationary bone that is connected via tendons to the muscle is called the origin. The place on the moving bone that is connected to the muscle via tendons is called the insertion. The belly of the muscle is the fleshy part of the muscle in between the tendons that does the actual contraction. Names of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles are named based on many different factors, including their location, origin and insertion, number of origins, shape, size, direction, and function. Location. Many muscles derive their names from their anatomical region. The rectus abdominis and transverse abdominis, for example, are found in the abdominal region. Some muscles, like the tibialis anterior, are named after the part of the bone (the anterior portion of the tibia) that they are attached to. Other muscles use a hybrid of these two, like the brachioradialis, which is named after a region (brachial) and a bone (radius). Origin and Insertion. Some muscles are named based upon their connection to a stationary bone (origin) and a moving bone (insertion). These muscles become very easy to identify once you know the names of the bones that they are attached to. Examples of this type of muscle include the sternocleidomastoid (connecting the sternum and clavicle to the mastoid process of the skull) and the occipitofrontalis (connecting the occipital bone to the frontal bone). Number of Origins. Some muscles connect to more than one bone or to more than one place on a bone, and therefore have more than one origin. A muscle with two origins is called a biceps. A muscle with three origins is a triceps muscle. Finally, a muscle with four origins is a quadriceps muscle. Shape, Size, and Direction. We also classify muscles by their shapes. For example, the deltoids have a delta or triangular shape. The serratus muscles feature a serrated or saw-like shape. The rhomboid major is a rhombus or diamond shape. The size of the muscle can be used to distinguish between two muscles found in the same region. The gluteal region contains three muscles differentiated by size—the gluteus maximus (large), gluteus medius (medium), and gluteus minimus (smallest). Finally, the direction in which the muscle fibers run can be used to identify a muscle. In the abdominal region, there are several sets of wide, flat muscles. The muscles whose fibers run straight up and down are the rectus abdominis, the ones running transversely (left to right) are the transverse abdominis, and the ones running at an angle are the obliques. Function. Muscles are sometimes classified by the type of function that they perform. Most of the muscles of the forearms are named based on their function because they are located in the same region and have similar shapes and sizes. For example, the flexor group of the forearm flexes the wrist and the fingers. The supinator is a muscle that supinates the wrist by rolling it over to face palm up. In the leg, there are muscles called adductors whose role is to adduct (pull together) the legs. Groups Action in Skeletal Muscle Skeletal muscles rarely work by themselves to achieve movements in the body. More often they work in groups to produce precise movements. The muscle that produces any particular movement of the body is known as an agonist or prime mover. The agonist always pairs with an antagonist muscle that produces the opposite effect on the same bones. For example, the biceps brachii muscle flexes the arm at the elbow. As the antagonist for this motion, the triceps brachii muscle extends the arm at the elbow. When the triceps is extending the arm, the biceps would be considered the antagonist. In addition to the agonist/antagonist pairing, other muscles work to support the movements of the agonist. Synergists are muscles that help to stabilize a movement and reduce extraneous movements. They are usually found in regions near the agonist and often connect to the same bones. Because skeletal muscles move the insertion closer to the immobile origin, fixator muscles assist in movement by holding the origin stable. If you lift something heavy with your arms, fixators in the trunk region hold your body upright and immobile so that you maintain your balance while lifting. Skeletal Muscle Histology Skeletal muscle fibers differ dramatically from other tissues of the body due to their highly specialized functions. Many of the organelles that make up muscle fibers are unique to this type of cell. The sarcolemma is the cell membrane of muscle fibers. The sarcolemma acts as a conductor for electrochemical signals that stimulate muscle cells. Connected to the sarcolemma are transverse tubules (T-tubules) that help carry these electrochemical signals into the middle of the muscle fiber. The sarcoplasmic reticulum serves as a storage facility for calcium ions (Ca2+) that are vital to muscle contraction. Mitochondria, the “power houses” of the cell, are abundant in muscle cells to break down sugars and provide energy in the form of ATP to active muscles. Most of the muscle fiber’s structure is made up of myofibrils, which are the contractile structures of the cell. Myofibrils are made up of many proteins fibers arranged into repeating subunits called sarcomeres. The sarcomere is the functional unit of muscle fibers. (See Macronutrients for more information about the roles of sugars and proteins.) Sarcomere Structure Sarcomeres are made of two types of protein fibers: thick filaments and thin filaments. Thick filaments. Thick filaments are made of many bonded units of the protein myosin. Myosin is the protein that causes muscles to contract. Thin filaments. Thin filaments are made of three proteins: Actin. Actin forms a helical structure that makes up the bulk of the thin filament mass. Actin contains myosin-binding sites that allow myosin to connect to and move actin during muscle contraction. Tropomyosin. Tropomyosin is a long protein fiber that wraps around actin and covers the myosin binding sites on actin. Troponin. Bound very tightly to tropomyosin, troponin moves tropomyosin away from myosin binding sites during muscle contraction. Muscular System Physiology Function of Muscle Tissue The main function of the muscular system is movement. Muscles are the only tissue in the body that has the ability to contract and therefore move the other parts of the body. Related to the function of movement is the muscular system’s second function: the maintenance of posture and body position. Muscles often contract to hold the body still or in a particular position rather than to cause movement. The muscles responsible for the body’s posture have the greatest endurance of all muscles in the body—they hold up the body throughout the day without becoming tired. Another function related to movement is the movement of substances inside the body. The cardiac and visceral muscles are primarily responsible for transporting substances like blood or food from one part of the body to another. The final function of muscle tissue is the generation of body heat. As a result of the high metabolic rate of contracting muscle, our muscular system produces a great deal of waste heat. Many small muscle contractions within the body produce our natural body heat. When we exert ourselves more than normal, the extra muscle contractions lead to a rise in body temperature and eventually to sweating. Skeletal Muscles as Levers Skeletal muscles work together with bones and joints to form lever systems. The muscle acts as the effort force; the joint acts as the fulcrum; the bone that the muscle moves acts as the lever; and the object being moved acts as the load. There are three classes of levers, but the vast majority of the levers in the body are third class levers. A third class lever is a system in which the fulcrum is at the end of the lever and the effort is between the fulcrum and the load at the other end of the lever. The third class levers in the body serve to increase the distance moved by the load compared to the distance that the muscle contracts. The tradeoff for this increase in distance is that the force required to move the load must be greater than the mass of the load. For example, the biceps brachia of the arm pulls on the radius of the forearm, causing flexion at the elbow joint in a third class lever system. A very slight change in the length of the biceps causes a much larger movement of the forearm and hand, but the force applied by the biceps must be higher than the load moved by the muscle. Motor Units Nerve cells called motor neurons control the skeletal muscles. Each motor neuron controls several muscle cells in a group known as a motor unit. When a motor neuron receives a signal from the brain, it stimulates all of the muscles cells in its motor unit at the same time. The size of motor units varies throughout the body, depending on the function of a muscle. Muscles that perform fine movements—like those of the eyes or fingers—have very few muscle fibers in each motor unit to improve the precision of the brain’s control over these structures. Muscles that need a lot of strength to perform their function—like leg or arm muscles—have many muscle cells in each motor unit. One of the ways that the body can control the strength of each muscle is by determining how many motor units to activate for a given function. This explains why the same muscles that are used to pick up a pencil are also used to pick up a bowling ball. Contraction Cycle Muscles contract when stimulated by signals from their motor neurons. Motor neurons contact muscle cells at a point called the Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ). Motor neurons release neurotransmitter chemicals at the NMJ that bond to a special part of the sarcolemma known as the motor end plate. The motor end plate contains many ion channels that open in response to neurotransmitters and allow positive ions to enter the muscle fiber. The positive ions form an electrochemical gradient to form inside of the cell, which spreads throughout the sarcolemma and the T-tubules by opening even more ion channels. When the positive ions reach the sarcoplasmic reticulum, Ca2+ ions are released and allowed to flow into the myofibrils. Ca2+ ions bind to troponin, which causes the troponin molecule to change shape and move nearby molecules of tropomyosin. Tropomyosin is moved away from myosin binding sites on actin molecules, allowing actin and myosin to bind together. ATP molecules power myosin proteins in the thick filaments to bend and pull on actin molecules in the thin filaments. Myosin proteins act like oars on a boat, pulling the thin filaments closer to the center of a sarcomere. As the thin filaments are pulled together, the sarcomere shortens and contracts. Myofibrils of muscle fibers are made of many sarcomeres in a row, so that when all of the sarcomeres contract, the muscle cells shortens with a great force relative to its size. Muscles continue contraction as long as they are stimulated by a neurotransmitter. When a motor neuron stops the release of the neurotransmitter, the process of contraction reverses itself. Calcium returns to the sarcoplasmic reticulum; troponin and tropomyosin return to their resting positions; and actin and myosin are prevented from binding. Sarcomeres return to their elongated resting state once the force of myosin pulling on actin has stopped. Certain conditions or disorders, such as myoclonus, can affect the normal contraction of muscles. You can learn about musculoskeletal health problems in our section devoted to diseases and conditions. Also, learn more about advances in DNA health testing that help us understand genetic risk of developing early-onset primary dystonia. Types of Muscle Contraction The strength of a muscle’s contraction can be controlled by two factors: the number of motor units involved in contraction and the amount of stimulus from the nervous system. A single nerve impulse of a motor neuron will cause a motor unit to contract briefly before relaxing. This small contraction is known as a twitch contraction. If the motor neuron provides several signals within a short period of time, the strength and duration of the muscle contraction increases. This phenomenon is known as temporal summation. If the motor neuron provides many nerve impulses in rapid succession, the muscle may enter the state of tetanus, or complete and lasting contraction. A muscle will remain in tetanus until the nerve signal rate slows or until the muscle becomes too fatigued to maintain the tetanus. Not all muscle contractions produce movement. Isometric contractions are light contractions that increase the tension in the muscle without exerting enough force to move a body part. When people tense their bodies due to stress, they are performing an isometric contraction. Holding an object still and maintaining posture are also the result of isometric contractions. A contraction that does produce movement is an isotonic contraction. Isotonic contractions are required to develop muscle mass through weight lifting. Muscle tone is a natural condition in which a skeletal muscle stays partially contracted at all times. Muscle tone provides a slight tension on the muscle to prevent damage to the muscle and joints from sudden movements, and also helps to maintain the body’s posture. All muscles maintain some amount of muscle tone at all times, unless the muscle has been disconnected from the central nervous system due to nerve damage. Functional Types of Skeletal Muscle Fibers Skeletal muscle fibers can be divided into two types based on how they produce and use energy: Type I and Type II. Type I fibers are very slow and deliberate in their contractions. They are very resistant to fatigue because they use aerobic respiration to produce energy from sugar. We find Type I fibers in muscles throughout the body for stamina and posture. Near the spine and neck regions, very high concentrations of Type I fibers hold the body up throughout the day. Type II fibers are broken down into two subgroups: Type II A and Type II B. Type II A fibers are faster and stronger than Type I fibers, but do not have as much endurance. Type II A fibers are found throughout the body, but especially in the legs where they work to support your body throughout a long day of walking and standing. Type II B fibers are even faster and stronger than Type II A, but have even less endurance. Type II B fibers are also much lighter in color than Type I and Type II A due to their lack of myoglobin, an oxygen-storing pigment. We find Type II B fibers throughout the body, but particularly in the upper body where they give speed and strength to the arms and chest at the expense of stamina. Muscle Metabolism and Fatigue Muscles get their energy from different sources depending on the situation that the muscle is working in. Muscles use aerobic respiration when we call on them to produce a low to moderate level of force. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to produce about 36-38 ATP molecules from a molecule of glucose. Aerobic respiration is very efficient, and can continue as long as a muscle receives adequate amounts of oxygen and glucose to keep contracting. When we use muscles to produce a high level of force, they become so tightly contracted that oxygen carrying blood cannot enter the muscle. This condition causes the muscle to create energy using lactic acid fermentation, a form of anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration is much less efficient than aerobic respiration—only 2 ATP are produced for each molecule of glucose. Muscles quickly tire as they burn through their energy reserves under anaerobic respiration. To keep muscles working for a longer period of time, muscle fibers contain several important energy molecules. Myoglobin, a red pigment found in muscles, contains iron and stores oxygen in a manner similar to hemoglobin in the blood. The oxygen from myoglobin allows muscles to continue aerobic respiration in the absence of oxygen. Another chemical that helps to keep muscles working is creatine phosphate. Muscles use energy in the form of ATP, converting ATP to ADP to release its energy. Creatine phosphate donates its phosphate group to ADP to turn it back into ATP in order to provide extra energy to the muscle. Finally, muscle fibers contain energy-storing glycogen, a large macromolecule made of many linked glucoses. Active muscles break glucoses off of glycogen molecules to provide an internal fuel supply. When muscles run out of energy during either aerobic or anaerobic respiration, the muscle quickly tires and loses its ability to contract. This condition is known as muscle fatigue. A fatigued muscle contains very little or no oxygen, glucose or ATP, but instead has many waste products from respiration, like lactic acid and ADP. The body must take in extra oxygen after exertion to replace the oxygen that was stored in myoglobin in the muscle fiber as well as to power the aerobic respiration that will rebuild the energy supplies inside of the cell. Oxygen debt (or recovery oxygen uptake) is the name for the extra oxygen that the body must take in to restore the muscle cells to their resting state. This explains why you feel out of breath for a few minutes after a strenuous activity—your body is trying to restore itself to its normal state. Prepared by Tim Taylor, Anatomy and Physiology Instructor
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Link:https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-ap/chapter/cardiac-muscle-tissue/
Microscopic Anatomy
Cardiac muscle appears striated due to the presence of sarcomeres, the highly-organized basic functional unit of muscle tissue.
Key Points
Cardiac muscle, composed of the contractile cells of the heart, has a striated appearance due to alternating thick and thin filaments composed of myosin and actin.
Actin and myosin are contractile protein filaments, with actin making up thin filaments, and myosin contributing to thick filaments. Together, they are considered myofibrils.
Myosin and actin adenosine triphosphate ( ATP ) binding allows for muscle contraction. It is regulated by action potentials and calcium concentrations.
Adherens junctions, gap junctions, and desmosomes are intercalated discs that connect cardiac muscle cells. Gap junctions specifically allow for the transmission of action potentials within cells.
Key Terms
intercalated discs: Junctions that connect cardiomyocytes together, some of which transmit electrical impulses between cells.
sarcomere: The basic unit of contractile muscle which contains myosin and actin, the two proteins that slide past one another to cause a muscle contraction.

Muscle Contraction and Actin-Myosin Interactions: Skeletal muscle contracts following activation by an action potential. Binding of Acetylcholine at the motor end plate leads to intracellular calcium release and interactions between myofibrils, eliciting contraction.

The Sarcomere: A single sarcomere unit with all functional areas labeled, including thick and thin filaments, Z lines, H zone, I bands, and A band.
Key Medical Terms
The internal framework of a eukaryotic cell, composed of protein filaments that provide structural support and drive the movement of the cell and its internal components, typically divided into three categories (microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules) based on the diameter and composition of the filaments.
from https://www.thefreedictionary.com
a protein that forms (together with myosin) the contractile filaments of muscle cells, and is alsoinvolved in motion in other types of cells.
from https://www.merriam-webster.com
comprise a family of ATP-dependent motor proteins and are best known for their role in muscle contraction and their involvement in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are responsible for actin-based motility. Multiple myosin II molecules generate force in skeletal muscle through a power stroke mechanism fuelled by the energy released from ATP hydrolysis. The power stroke occurs at the release of phosphate from the myosin molecule after the ATP hydrolysis while myosin is tightly bound to actin.
from https://en.wikipedia.org/
α- and β-tubulin polymerize into dynamic microtubules. In eukaryotes, microtubules are one of the major components of the cytoskeleton, and function in many processes, including structural support, intracellular transport, and DNA segregation.
from https://en.wikipedia.org/

