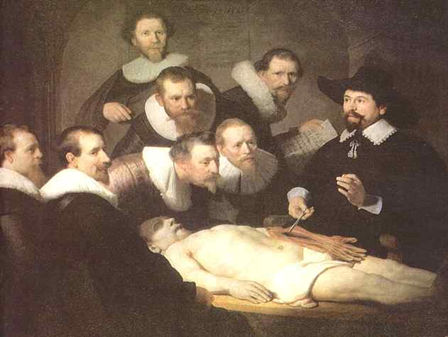
The Anatomy Lesson
The Anatomy Lessonof Dr. NicolaesTulp by Rembrandt shows an anatomy lesson taking place in Amsterdam in 1632.
The development of anatomy as a science began in the golden age of Greece (460-377 B.C.).

Hippocrates Claudius Galen Andreas Vesalius
Lead-In
Anatomy is primarily the study of body structure and the relationships among structures.It was first studied by dissection,the careful cutting apart of body structures to study their relationships.Today,a variety of imagingtechniques also contribute to the advancement of anatomical knowledge.The anatomy of the human body can be studied at various levels of structural organization,ranging from microscopic(visible only with the aid of a microscope) to macroscopic (visible without the use of a microscope).These levels and the different methods used to study them provide the basis for the subdisciplines of anatomy,such as sectional anatomy(断层解剖学),gross anatomy(大体解剖学),systematic anatomy(系统解剖学),regional anatomy(局部解剖学),surface anatomy(表面解剖学),radiographic anatomy(X线解剖学),pathological anatomy(病理解剖学),and so forth.
Notes
dissection
[di'sekʃ(ə)n]
n. the action of cutting and separating parts of a body or an organ 解剖;切开
imaging
['imidʒiŋ]
n. the process of capturing, storing and showing an image on a computer screen成像
microscopic
[.maikrə’skɔpik]
adj. 显微镜(下才)可见的;使用显微镜才可见的;微观的
microscope
[̩'maikrəskəup]
n.(micro-,prefix small;-scope,suffix instrument for viewing or examining)an instrument used in scientific study for making very small things look larger so that you can examine them carefully显微镜
microscopically
[maikrə'skɔpikəli]
adv.用显微镜(观察、分析等)
macroscopic
[ˌmækrə(u)'skɔpik]
adj. visible to the naked eye肉眼可见的
subdiscipline
[sʌb'disəplin]
n.(学科的)分支



