In this section, we write an object-oriented program that dynamically simulates the motion of n bodies under the influence of mutual gravitational attraction.
Bouncing balls.
The data type Ball.java represents a ball with a given position that moves with a fixed velocity in the box with coordinates between −1 and +1. When it collides with the boundary, it bounces according to the law of elastic collision.The client BouncingBalls.java takes a command-line argument n and creates n random bouncing balls.
N-body simulation.
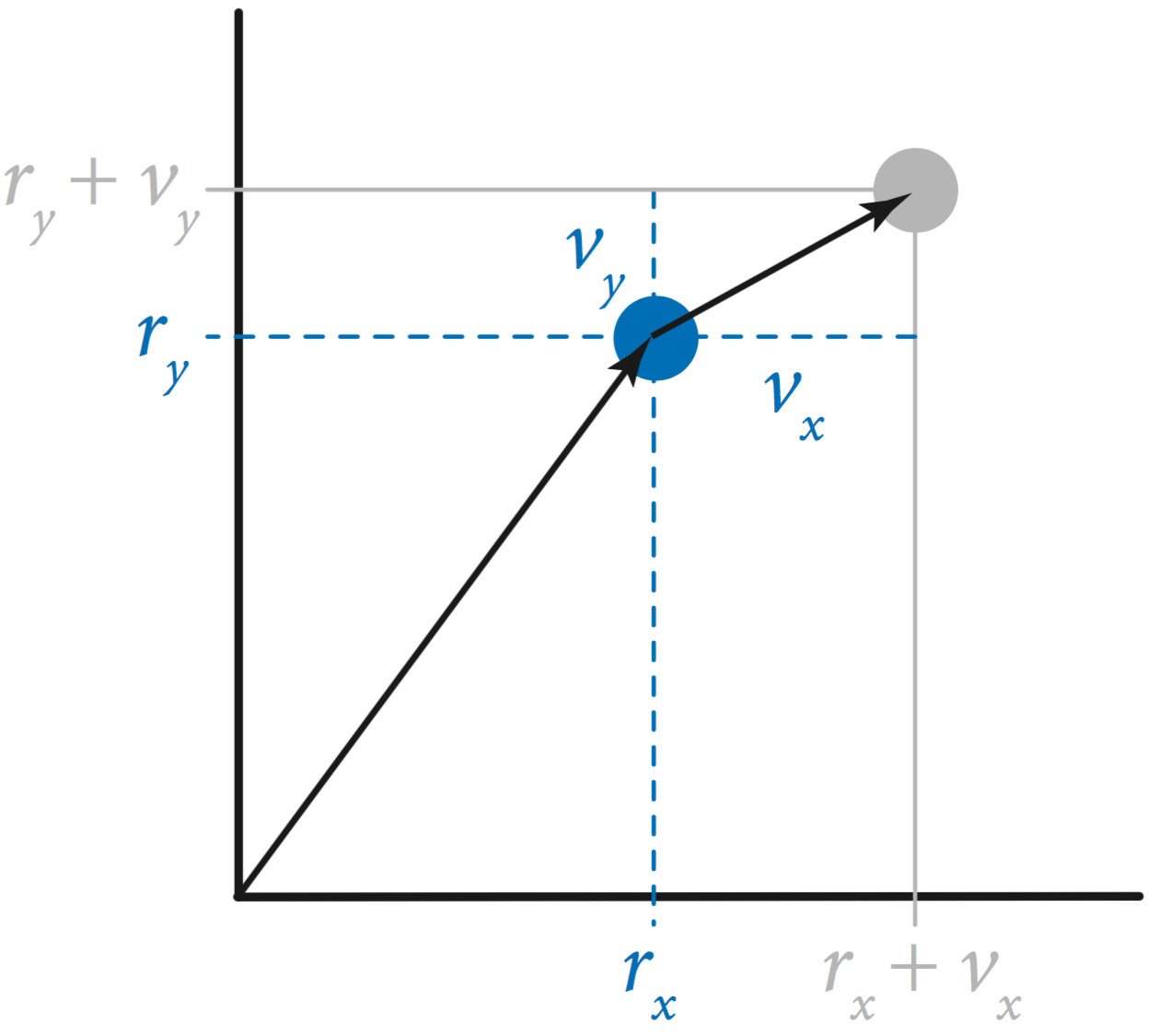
The bouncing ball simulation is based on Newton's first law of motion: a body in motion remains in motion at the same velocity unless acted on by an outside force. Embellishing that example to incorporate gravity leads us to a basic problem that has fascinated scientists for ages. Given a system of n bodies, mutually affected by gravitational forces, the problem is to describe their motion.Body data type. The data type Body.java represents a body with a given position , velocity , and mass . It appliesNewton's third law of motion (which explains the gravitational force between two bodies) to determine the net force acting on a body:
and Newton's second law of motion (which explains how outside forces directly affect acceleration and velocity).
It uses the Vector.java data type to represent displacement, velocity, and force as vector quantities.

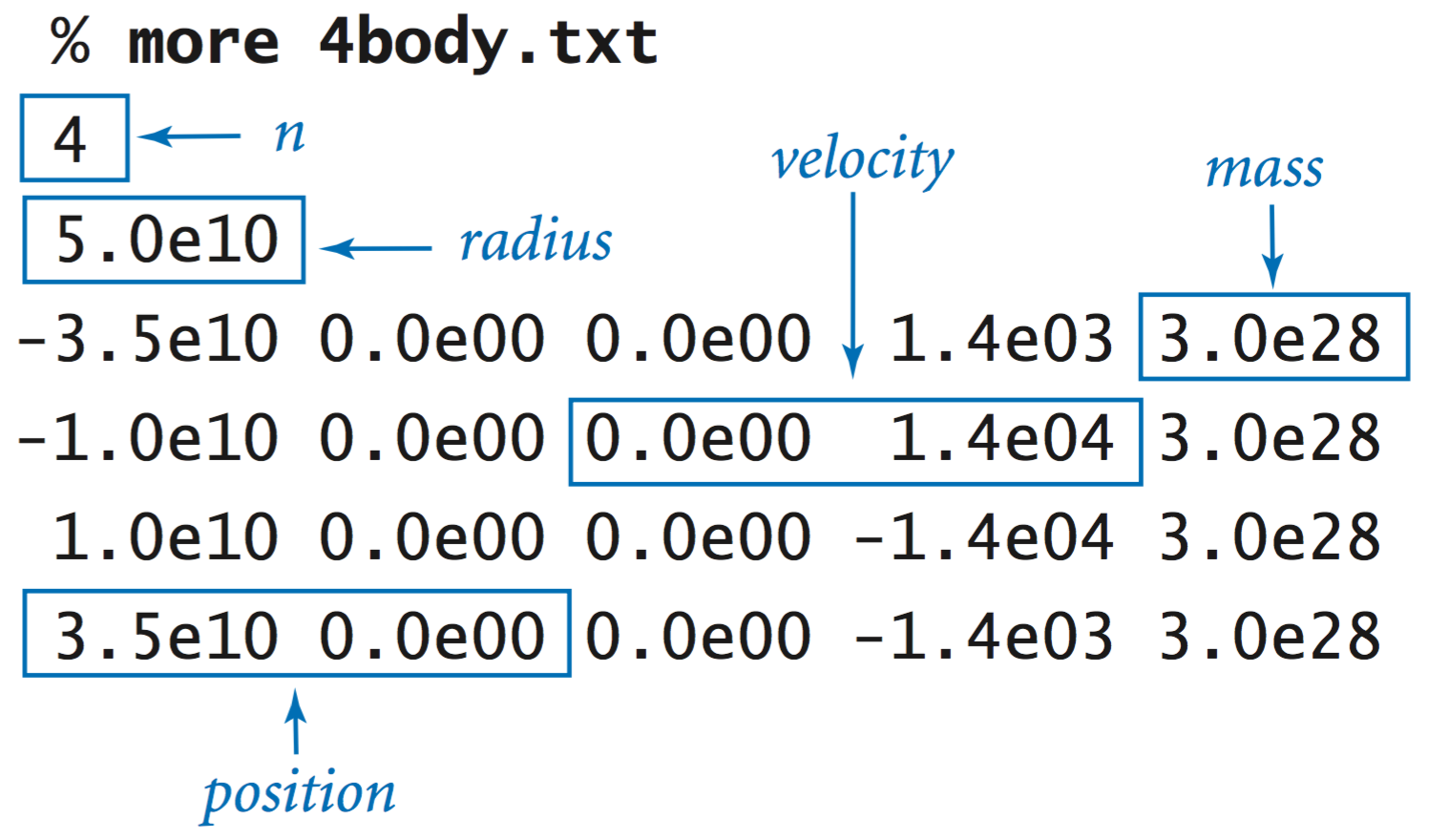
Universe data type. Universe.java takes a command-line argument dt, reads in a universe from standard input, and simulates the universe using time quantum dt. Here is an example of the data file format:
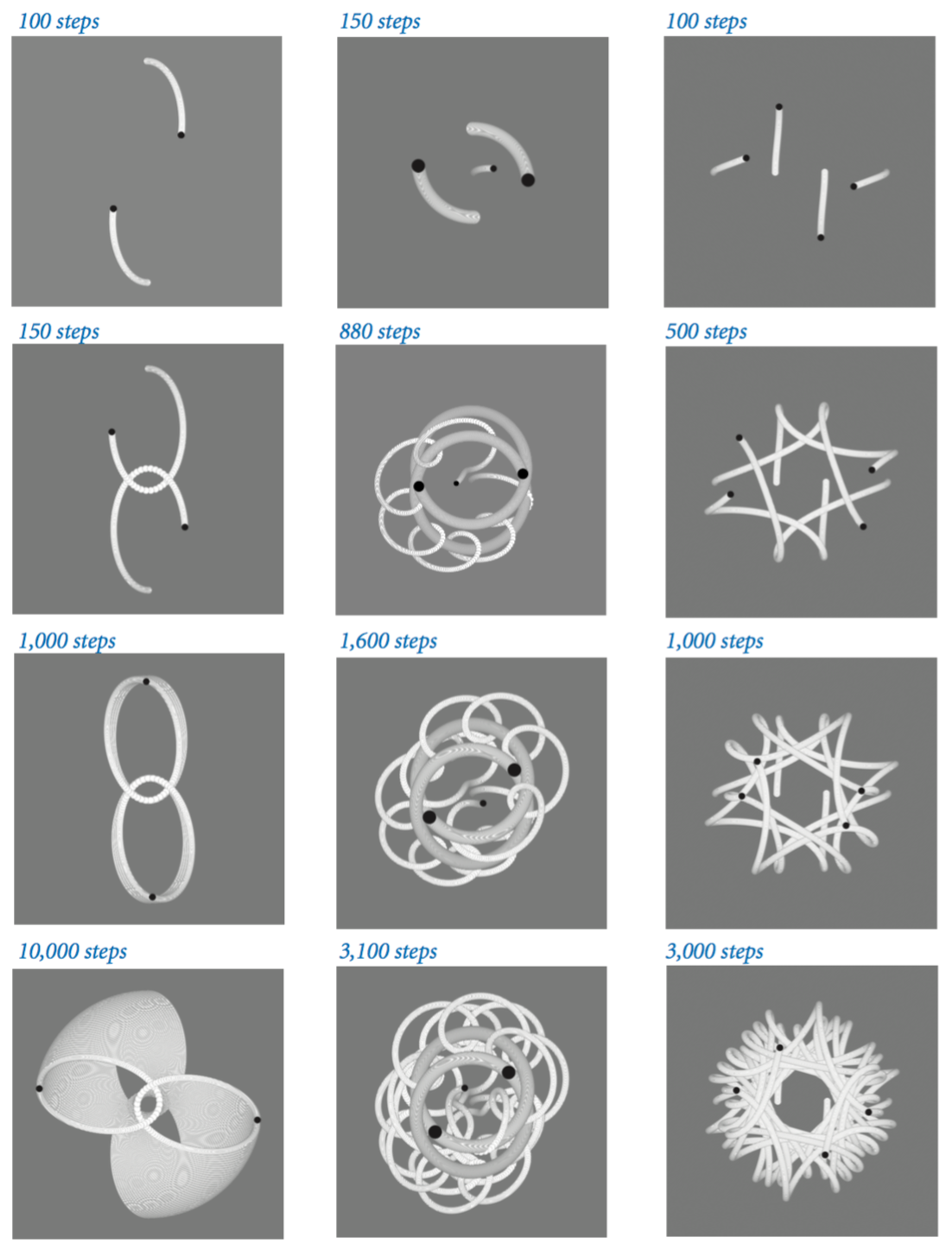
The following static images for 2body.txt, 3body.txt, and 4body.txt are made by modifying Universe.java and Body.java to draw the bodies in white, and then black on a gray background.