机器学习与文本数据

文本预处理
参考第一节课实验NLTK以及中文自然语言处理,主要包括分词,去除停用词,归一化等。
给出以下例子供大家预习复习使用
# We will use a tokenizer from the NLTK library
import nltk
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
filtered_sentence = []
# Stop word lists can be adjusted for your problem
stop_words = ["a", "an", "the", "this", "that", "is", "it", "to", "and"]
# Tokenize the sentence
words = word_tokenize(text)
for w in words:
if w not in stop_words:
filtered_sentence.append(w)
text = " ".join(filtered_sentence)
# We will use a tokenizer and stemmer from the NLTK library
import nltk
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.stem import SnowballStemmer
# Initialize the stemmer
snow = SnowballStemmer('english')
stemmed_sentence = []
# Tokenize the sentence
words = word_tokenize(text)
for w in words:
# Stem the word/token
stemmed_sentence.append(snow.stem(w))
stemmed_text = " ".join(stemmed_sentence)
# Importing the necessary functions
import nltk
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.corpus import wordnet
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
# Initialize the lemmatizer
wl = WordNetLemmatizer()
# This is a helper function to map NTLK position tags
# Full list is available here: https://www.ling.upenn.edu/courses/Fall_2003/ling001/penn_treebank_pos.html
def get_wordnet_pos(tag):
if tag.startswith('J'):
return wordnet.ADJ
elif tag.startswith('V'):
return wordnet.VERB
elif tag.startswith('N'):
return wordnet.NOUN
elif tag.startswith('R'):
return wordnet.ADV
else:
return wordnet.NOUN
lemmatized_sentence = []
# Tokenize the sentence
words = word_tokenize(text)
# Get position tags
word_pos_tags = nltk.pos_tag(words)
# Map the position tag and lemmatize the word/token
for idx, tag in enumerate(word_pos_tags):
lemmatized_sentence.append(wl.lemmatize(tag[0], get_wordnet_pos(tag[1])))
lemmatized_text = " ".join(lemmatized_sentence)
需要注意等是, 英文文本的预处理有自己特殊的地方——拼写问题,很多时候,对英文预处理要包括拼写检查,比如“Helo World”这样的错误,我们不能在分析的时候再去纠错。还有就是词干提取(stemming)和词形还原(lemmatization),主要是因为英文中一个词会会不同的形式,这个步骤有点像孙悟空的火眼金睛,直接得到单词的原始形态。比如,"faster"、"fastest", 都变为"fast";“leafs”、“leaves”,都变为"leaf"。但是中文并不存在这样的问题,中文进行处理的时候并不需要词干提取(stemming)和词形还原(lemmatization),直接进行分词与去除停用词就可以了,当然也有一些其他预处理,比如去除一些特殊的符号以及一些特殊的数字之类的。
文本向量化
词袋模型(bag of words,BOW)
词袋模型能够把一个句子转化为向量表示,是比较简单直白的一种方法,它不考虑句子中单词的顺序,只考虑词表(vocabulary)中单词在这个句子中的出现次数。 下面给出一个例子:

sklearn提供了相关的函数共大家使用,下面给出一个例子供大家预习
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
sentences = ["This document is the first document",
"This document is the second document",
"and this is the third one"]
# Initialize the count vectorizer with the parameter: binary=True
binary_vectorizer = CountVectorizer(binary=True)
# fit_transform() function fits the text data and gets the binary BoW vectors
x = binary_vectorizer.fit_transform(sentences)
大家可以先运行下这段代码,看下x是什么样子
TF-IDF(Term Frequency / Inverse Document Frequency,词频-逆文本频率)
BOW模型有很多缺点,首先它没有考虑单词之间的顺序,其次它无法反应出一个句子的关键词。
比如说
"John likes to play football, Mary likes too"
这个句子若用BOW模型,它的词表为:[‘football’, ‘john’, ‘likes’, ‘mary’, ‘play’, ‘to’, ‘too’],则词向量表示为:[1 1 2 1 1 1 1]。若根据BOW模型提取这个句子的关键词,则为 “like”,但是显然这个句子的关键词应该为 “football”
TF-IDF包括两部分TF和IDF,TF(Term Frequency,词频)的公式为:

而IDF(inverse document frequency,逆文本频率)的公式为:

分母之所以加1是为了防止分母为0。所以,TF-IDF的公式为:
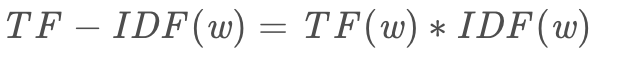
TF-IDF值越大说明这个词越重要,也可以说这个词是关键词。
sklearn同样提供函数供大家使用
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
tfidf_vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(use_idf=True)
sentences = ["This document is the first document",
"This document is the second document",
"and this is the third one"]
xf = tfidf_vectorizer.fit_transform(sentences)
xf.toarray()
大家可以先跑下这段代码
机器学习模型之KNN

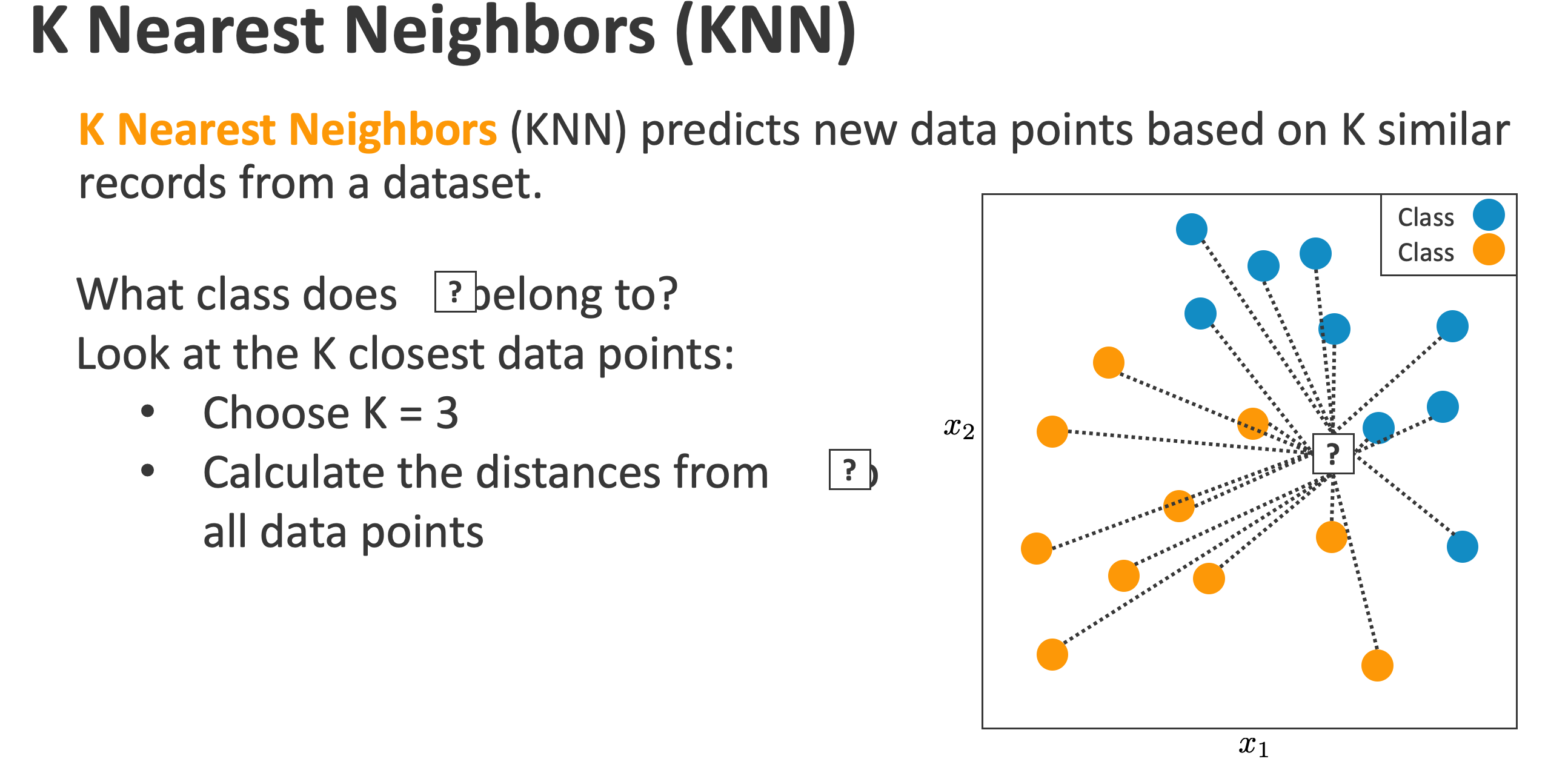
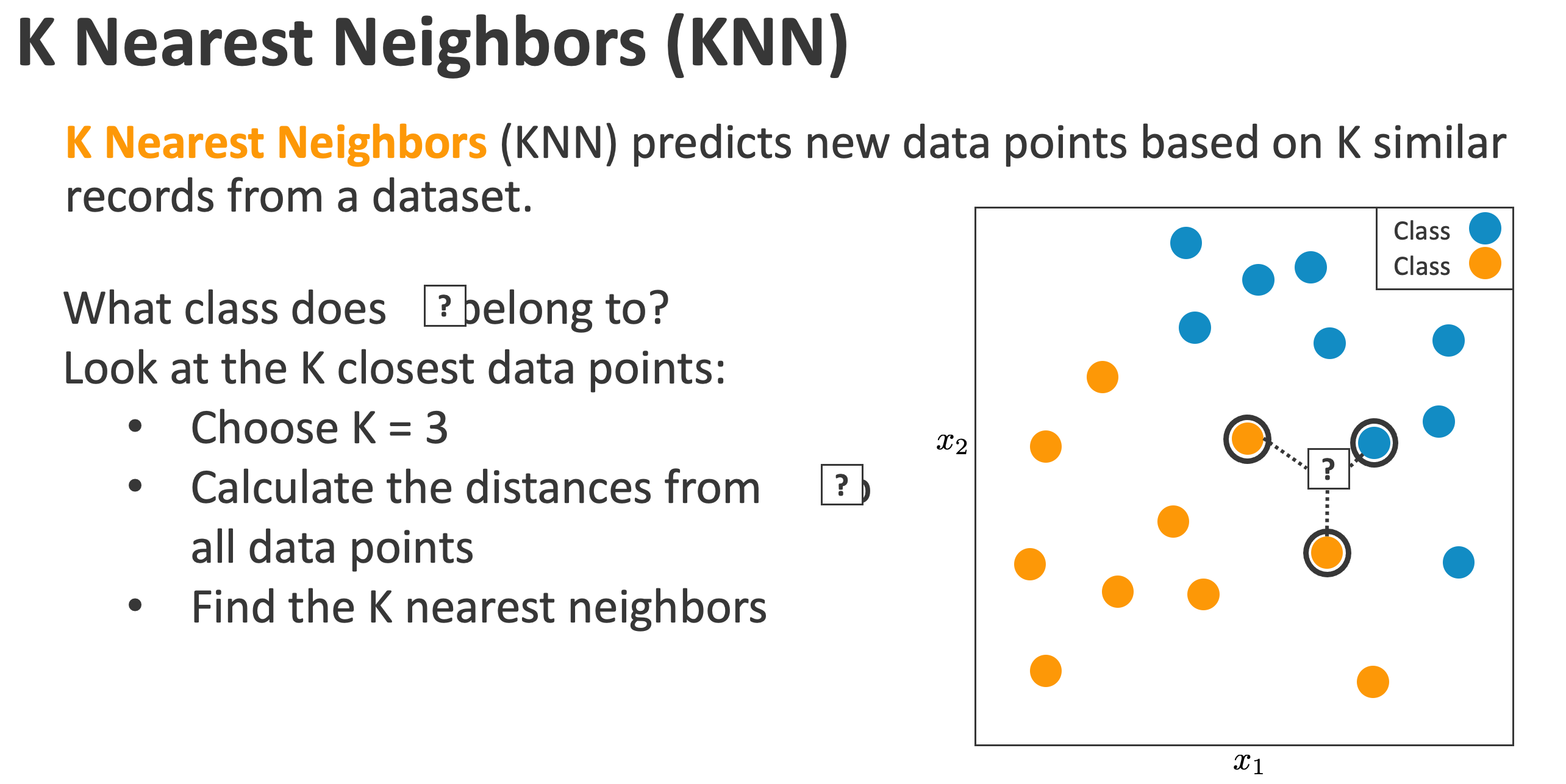
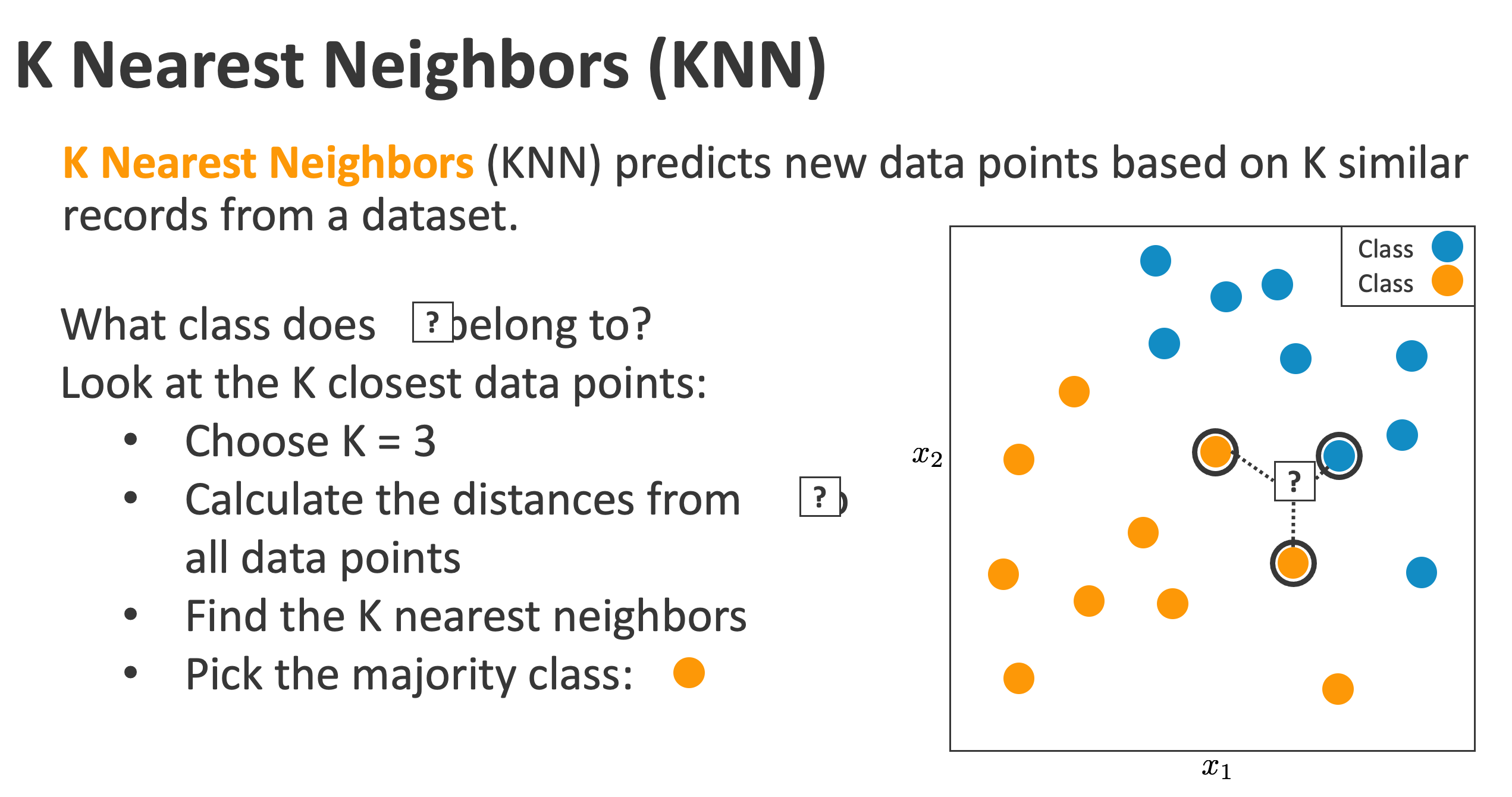

完整的代码在这
数据在这
大家记得修改数据路径,自己可以先跑跑看看,课堂我们再详细讲述


