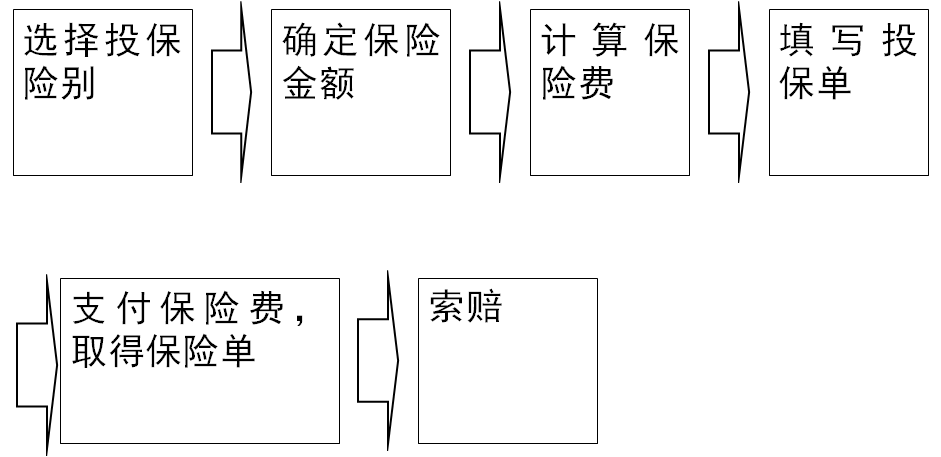
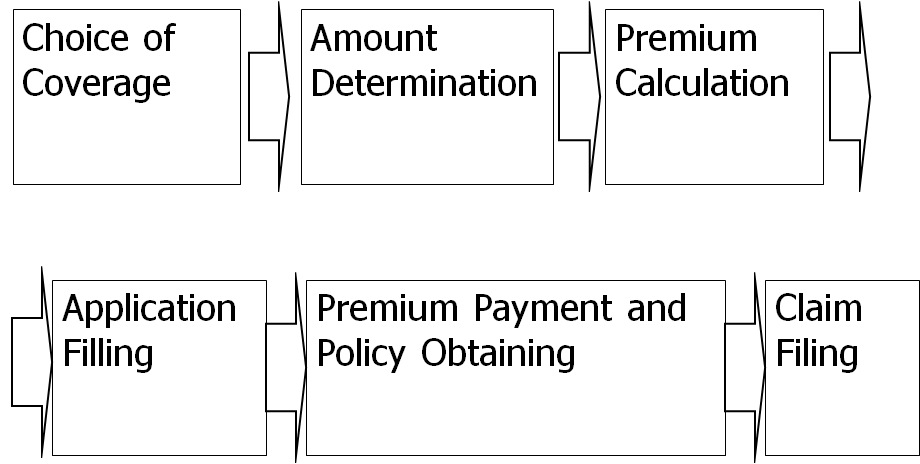
the general procedure of insurance arrangement 保险的流程
1. Choice of Coverage 选择投保险别
2. Amount Determination 确定保费金额
3. Premium Calculation 计算保险费
4. Application Filling 填写投保单
5. Premium Payment and Policy Obtaining 支付保险单、取得保险单
6. Claim Filing 索赔
General Procedure of Insurance Arrangement
General Procedure of Insurance Arrangement
10.3.1 Choice of Coverage
The following factors will influence the choice of coverage: 选择险别的考虑因素
(1) Nature of Goods货物的性质
(2) Packing of Goods 货物的包装
(3) Route of Shipping and Port of Call 运输线路及停靠港口
(4) Shipping Season 运输季节
(5) Trade Customs and International Conventions 各国贸易习惯和国际惯例
(1) Nature of Goods
Goods of different nature may face different risks and probability of loss. Therefore, nature of goods must be considered before determining insurance coverage. For instance, All Risks is needed to product of brittle glass but not product of durable iron. For special goods
(2) Packing of Goods
Packing is important in safeguarding the goods in transport. When applying for insurance and choosing coverage, the applicant should take into consideration the possible damage to the package and subsequently to the goods in the transit.
(3) Route of Shipping and Port of Call
The loss of goods will increase in route of hot weather and the possibility of accidental loss rises if the vessel passes turbulent or martial sea area. Apart from that, ports of call differ in their facility, handling capacity and security, which may lead to different damage to or missing of goods in the handling.
(4) Shipping Season
Different seasons have different impact on the risk to cargo shipment. Carrying vessel is in great exposure to risk of collision with moving iceberg when shipping in cold ocean area in winter, but to risk of mildew or worm when shipping grain and vegetables in summer.
(5) Trade Customs and International Conventions
• If goods are exported under CIF terms, the coverage applied by the seller should be clearly defined in the trade contract.
• Any different insurance requirement by one party after the entrance of contract should be submitted to the counter party for the modification of contract or L/C.
• If no such provision is provided in the contract, international trade conventions and relative national laws should be followed in insurance arrangement.
To summarize, one should consider many factors when choosing an insurance coverage.
Generally speaking, the basic risk covered by cargo transport insurance is the loss of and damage to the goods in transit rising from natural calamities and accidents.
If the nature, packing and transport of the goods imply that they are exposed to wider extraneous risk and greater possibility of loss, the goods need to be covered by All Risks.
保险金额与保险费的计算
保险金额的计算公式是:
保险金额=CIF(或CIP)×(1+投保加成率)

保险金额=FOB(或FCA)×(1+平均运费率+平均保险费率)
或:
保险金额=CFR(或CPT)×(1+平均保险费率)
保险费=保险金额×保险费率
10.3.2 Amount Determination
Insured Amount=CIF (or CIP)*(1+Insured Markon Percentage)
If FOB or CFR is known, the premium under CIF (or CIP) is calculated as:
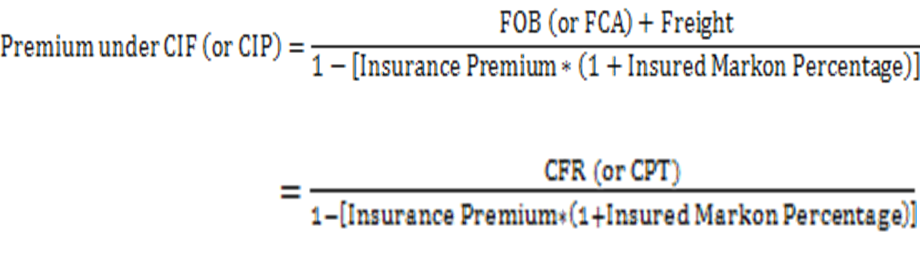
Insured amount=FOB (or FCA)*(1+ average freight rate+ average insurance premium)
Or
Insured amount=CFR (or CPT)*(1+ average insurance premium)
10.3.3 Premium Calculation
Insurance Premium=Insured Amount*Premium Rate
Premium rate is the rate of premium charged to insured amount, which is the basis on which the insurer calculates the premium.
It is determined by the insurer after considering the possible danger to the insured cargo, loss ratio, claim ratio, and operation expenses, as well as the nature of commodity, different destination, and different insurance coverage. Higher loss ratio usually accompanies higher premium.
10.3.4 Application Filling
When applying for cargo transport insurance, the applicant needs to make an insurance offer in writing by filling an application form. With the signature and seal of the insurer on the form, or a policy issued by the insurer, the contractual relationship between the parties is confirmed.
The application form involves the applicant informing the insurer of facts of the insured object, on which the insurer issues Policy and determines the premium.
10.3.5 Premium Payment and Policy Obtaining
The applicant (the insured) obtains the Policy only after he pays premium.
Two forms of Policy:
(1) Insurance Policy (or Policy), a formal certificate proving the contractual relationship between the insurer and the insured
(2) Insurance Certificate (also called Small Policy), the document issued by the insurer to the insured proving that the cargo has been insured and the insurance contract has taken effect.
The Policy is a formal document with which the insured could file a claim and the insurer could settle the claim. The Policy is transferable and usually be used as one of the collateral documents by the insured to his bank. Under CIF contract, the seller must provide the buyer with Policy.
Certificate is not valid, however, when an L/C regulates the submission of a Policy, despite the fact that it has the same effect as Policy.
保单类型:
(1)保险单(又称大保单):是保险人和被保险人之间成立保险合同关系的正式凭证。
(2)保险凭证(又称小保单):是保险人签发给被保险人,证明货物已经投保和保险合同已经生效的文件。
10.3.6 Claim Filing
Insurance claim(索赔) refers to the act of the insured lodging a claim to the insurer for compensation against the loss of insured goods caused by the insured risks.
Settlement of Claim(理赔)After receiving the claim requirement, the insurer should handle the compensation requirement from the insured, which is called settlement of claim.
When filing a claim, the insured should follow the following steps:
(1) Notification of Loss
(2) Inspection Application
(3) Submission of Claims Document
(4) Collection of Claim Indemnity and Conduction of Subrogation
被保险人在索赔时必须履行如下手续:
(1)发出损失通知
(2)申请检验
(3)提交索赔单证
(4)领取保险赔款与代位追偿
In a claim, exporter and importers should:
(1) Actively salvage and organize the damaged goods.
(2) If a third responsible party is involved, the insured should in the first place raise an objection to the party in order to retain right of recourse before he files a claim to the insurer.
进出口索赔中需要注意的问题:
(1)对受损失货物应积极采取措施进行施救和整理
(2)如果涉及第三者责任,虽然赔款一般先由保险人赔付,但被保险人应首先向责任方提出异议,以保留追偿权利。


