It falls into four kinds:
1. Scheduled airliner 班机运输
2. Charted carrier 包机运输
3. Consolidation 集中托运
4. Air express 急件运送
6.2.1 Modes of Air Transport
(1)Scheduled airline
• Aircrafts fly regularly between fixed airports. in fixed time, fixed routes, fixed points
• It is usually a mixed type of passenger flight and freight flight. Many major airlines operate aircrafts designed to carry cargo only
(2)Chartered carrier
• A flight can be chartered by only one charterer or by several charterers.
• The latter case is suitable for less than the whole consignment and heavy cargo transport.
班机运输是指在固定的开航时间、固定的航线、固定的始发站、目的站和途经站飞行的运输方式。
• 通常为客货混合型飞机(combination carrier),货舱容量较小,运价较贵,难以满足大批量货物运输要求。但由于航期固定,可以确切掌握发货和到货的时间,因此国际间货物流通多使用班机运输方式,能安全迅速地到达世界上各通航地点。
• 适用于运送急需物品、鲜活物品、贵重商品和技术资料等。缺点是舱位有限,不能使大批量的货物及时出运,往往需要分期、分批运输。
包机运输可分为整包机和部分包机两种。
• 整包机指航空公司或航空货运代理公司按照约定的条件和费率,将整架飞机租给租机人,从一个或几个航空站装运货物至目的地。包机人一般要在货物装运前一个月与航空公司联系,以便航空公司安排运载和向起降机场及有关政府部门申请、办理过境或入境的有关手续。它适合大批量货物,费用一次一议,随国际市场供求情况变化。
• 部分包机指由几家航空货运公司或发货人联合包租一架飞机或者由航空公司把一架飞机的舱位分别租给几家航空货运公司装载货物,它主要用于托运不足一整架飞机舱,但货量又较重的货物运输。
(3)Consolidation 集中托运
• the air freight forwarder delivers cargoes of different consignors together and consigns the cargoes as one batch.
航空公司和货运代理合作
• This mode is more popular and cheaper.
集中托运方式(consolidation)是指航空货运代理公司将若干批单独发运(目的地相同或相近)的货物集中成一批(一大票)向航空公司办理托运,填写一份总运单送至同一目的地,货到国外后由其委托当地的代理人负责收货、报关并分拨给各实际收货人。
集中托运的货物越多,支付的运费越低。集中托运方式已在世界范围内普遍开展,形成了较完善、有效的服务系统,为促进国际贸易发展和国际科技文化交流起了良好的作用。集中托运成为我国进出口货物的主要运输方式之一。
集中托运的具体做法:
① 航空货运代理将每一票货物分别制定航空运输分运单,即出具货运代理的运单 HAWB (house airway bill)。
② 航空货运代理将所有货物区分方向,按照其目的地相同的同一国家、同一城市来集中,制定出航空公司的总运单MAWB (master airway bilI)。总运单的发货人和收货人均为航空货运代理公司。
③ 打出该总运单项下的货运清单 (manifest),即此总运单有几个分运单,号码各是什么,其中件数、重量各多少等。
④ 航空货运代理把该总运单和货运清单作为一整票货物交给航空公司。一个总运单可视货物具体情况随附分运单(也可以是一个分运单,也可以是多个分运单)。例如,一个MAWB内有10个HAWB,说明此总运单内有10个票货,发给10个不同的收货人。
⑤ 货物到达目的站机场后,当地的货运代理公司作为总运单的收货人负责接货、分拨,按不同的分运单制定各自的报关单据并代为报关、为实际收货人办理有关接货送货事宜。
⑥ 实际收货人在分运单上签收以后,目的站货运代理公司以此向发货的货运代理公司反馈到货信息。
集中托运的特点:
① saving on freight 节省运费:航空货运公司的集中托运运价一般都低于航空协会的运价,从而为发货人节省费用。
② more convenience 提供方便:将货物集中托运,可使货物到达航空公司到达地点以外的地方,延伸了航空公司的服务,方便了货主。
③ settlement at the earlier time 提早结汇:发货人将货物交与航空货运代理后,即可取得货物分运单,可持分运单到银行尽早办理结汇。
(4)Air express service 航空快递
• Air express service is provided by the organization specializes in the service with cooperation of airlines.
快递公司和航空公司合作
• Goods of emergency are normally delivered in this way. (desk to desk)
6.2.2 Airway Bill 空运提单
• Air Waybill is the key document in air transport, also called consignment note
• features:
a. It is a transport contract signed between the consignor/shipper and the carrier/airline. 运输协定
b. It is receipt from the airline acknowledging the receipt of the consignment from the shipper. 收据
c. It is an internationally standardized document.
• mostly printed in English and the official language of the country of departure.
• There are usually 12 copies of airway bill (3 original copies) for distribution to the various parties.
There are two forms of the airway bill:
Master Airway Bill (MAWB) 空运主运单
• signed by the airline company
• it is the transport contract between the consolidation shipper and the carrier.
House Airway Bill (HAWB) 空运分运单
• issued by the freight forwarder and
• it is the transport contract between the actual shipper and the freight forwarder
空运提单
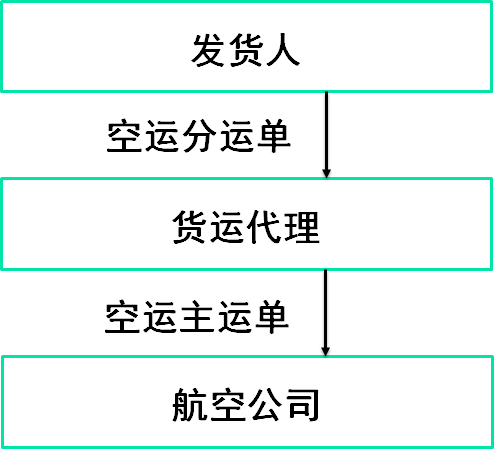
在集中托运的情况下,除了航空运输公司签发主运单外,集中托运人还要签发航空分运单。
在这中间,航空分运单作为集中托运人与托运人之间的货物运输合同,合同双方分别为货主A、B和集中托运人;而航空主运单作为航空运输公司与集中托运人之间的货物运输合同,当事人则为集中托运人和航空运输公司。货主与航空运输公司没有直接的契约关系。
6.2.3 Air Cargo Charges and Rates
1. General Cargo Rates 普通运价
• applicable to any type of commodity, without the restriction of hazardous consignment size.
• The disadvantage is they are pitched at an extremely high level.
2. Minimum Charges 最低运价
• in most cases a shipper cannot be charged less than the appropriate rate of 4kg
运费标准不低于四公斤
• On some routes, minimum charges apply at higher weighs of up to 8kg.
有些线路最低标准提高到8公斤
3. Class Rates 等级运价
• Class Rates are a further supplement to the General Cargo Rate tariff, are applied by most airlines. 多数商品收取附加费
• certain commodities are offered a discount, and many more commodities are surcharged under class ratings. 某些商品给与折扣
4. Specific Commodity Rates 指定商品运价
• applicable to named types of freight.
• they have a number of features that separate them as a distinct form of pricing.
• Over 5000 different commodities
制定目录,对5000种商品进行了定义
5. Bulk Unitization Rates
大宗货集装运价
• offering low unit rates, substantially below comparable General Cargo Rates.
• They are available for all types of freight, irrespective of commodity type.
按照集装单位定价
6. Contract FAK Rates 全包价
• many airlines are offering substantial discounts for large consignments, if they are presented to the airline in containerized or palletized form.
• In some cases, these rates have been offered only to those prepared to sign a contract to give the airline a minimum annual tonnage.
Laws on airway transport
International laws
《华沙公约》是最基本的,随后的一些议定书是对《华沙公约》的补充或修改。
它们彼此内容相关却又各自独立,《华沙公约》的缔约国并不自然成为以后各次议定书的参加国,也不一定受其管辖。
我国参加《华沙公约》和《海牙议定书》的时间分别是1958年和1975年。
Laws on airway transport
Civil law
• 《中华人民共和国民用航空法》诞生于1995年,并于1996年3月1日起正式施行。
• 该法是适用于民航企业航空器适航、人员管理、飞行安全、机场建设等的综合性法规。
• 针对承运人对货物灭失或损坏的责任,《民航法》采取了更为严格的态度。


