Objective (学习目标)
the definition and characteristics of International Logistics
国际物流的内涵和特点;
the relationship between International Logistics and International Trade
国际物流与国际贸易两者的关系;
the development of International Logistics and its importance in economic globalization
国际物流的发展历程以及在经济全球化中的作用
Key Points and Difficult Points(学习重点及难点)
1. the definition and characteristics of International Logistics,
2. operations of International Logistics;
3. the relationship between International Logistics and International Trade;
4. the importance of International Logistics
第一节 国际物流概述 Introduction of International Logistics
definition of international logistics
features of international logistics
links of international logistics
relationship between international logistics and international trade
Vocabulary and Terminology
international logistics 国际物流 inter-, national
domestic logistics 国内物流
international trade 国际贸易
multinational company 跨国公司 multi-, national
economic globalization 经济全球化 global, globalize, globalization
tariff [‘tærif] 关税 tax, duty, customs
exchange rate 汇率 change
lean logistics 精细物流
information asymmetry [e‘simitri] 信息不对称
tariff barrier [ˈtærɪf ˈbæriɚ] 关税壁垒 obstacle, hurdle
non-tariff barrier 非关税壁垒 non-
lead time 前置时间,提前期
remittance [rɪ'mɪtəns] 汇付
collection 托收 collect
letter of credit 信用证
raw material 原材料
work-in-process 半成品,在制品
finished products 产成品 finish; component
international division of labor 国际分工, division (部门,分配,分割) divide
documentation 单证 document文档
transportation 运输 transport
warehousing 仓储 ware, house
material handling 装卸搬运 handle, hand
packing (packaging) 包装 pack, package
information management 信息管理
replenishment [ri'pleniʃmənt] 补货 replenish
global supply chain 全球供应链 globalize
upstream and downstream companies 上下游企
stream
integrated service provider 一体化服务提供商
integrate, provide
third-party logistics service providers 第三方物流服务提供商 party, CPC
fourth-party logistics service providers 第四方物流服务提供商 fourth, forth, force
green logistics 绿色物流
green supply chain 绿色供应链


1.1.1 Definition of International Logistics
Trend(趋势):
the originally segmented national or regional markets have gradually evolved into an integrated global market.
原有的国家和区域市场划分逐渐演变成全球化的主体市场。
重点单词: segment, segmented, segmentation, gradual, evolve, integrate
International logistics refers to the flows and transfers of cargos (including raw materials, work-in-process, and finished products) and materials (…,…,…) among various countries and areas.
国际物流是指货物(原材料、半成品和制成品等)及物品(邮品、展品、捐赠物资等)在不同国家(地区)间的流动或转移。
International logistics can be interpreted both broadly and narrowly.
可以从狭义和广义两个角度来理解国际物流
(1) From the narrow side: commercial logistics -- logistical activities to complete an international trade transaction, such as…
狭义的理解是国际贸易物流,是指与国际贸易活动相关的物流活动,如……等活动。
(2) Broadly interpreted, international logistics includes both commercial logistics and non-commercial logistics.
Non-commercial logistics: not for commercial purposes, such as …
广义的理解是国际物流包含国际贸易物流和非国际贸易物流两大部分。
非国际贸易物流是指由非交易活动引起的国际物流活动,如跨越国界的……等。
Three key aspects in the definition of international logistics(国际物流定义的要点):
1. can be called “big logistics” or “macro-logistics”
国际物流是国内物流的延伸和进一步扩展,称为“大物流”
2. It is an internal part of international trade
国际物流是国际贸易活动的重要组成部分
3. Purpose: better serve international trade and multi-national operation.
总目标是为国际贸易和跨国经营服务。
Goods delivered in high quality, high efficiency and at low cost to foreign customers;
Goods transported to its domestic market efficiently and effectively.
以最低的费用和最小的风险,将货物从一个国家运到另一个国家,整体效益最大。
1.1.2 features of International Logistics
Features(特点):
Involving more links and having a longer cycle 物流环节多,周期长
Much more complicated than domestic logistics
物流作业复杂
Being in exposure to greater risks
物流过程具有高风险性
(1) Involving more links and having a longer cycle
Reason: it conducts logistical activities across national boundaries. 跨境物流活动
• Link: such as inspection and declaration are required. 检验(检疫 quarantine )、报关
• Since goods are exposed to greater risks of being damaged or lost, insurance should be effected on goods. 风险大、需保险
(2) more complicated than domestic logistics
Reason:
the significant differences of logistical regulations, infrastructures and technologies
规则和基础设施标准不同
International logistics uses the combination of various transportation modes. 运输方式多
the sheer amount of documentation required. 单证复杂
(3) Being in exposure to greater risks
• Political risks: such as the instability of the country or region and the change of the political and economic relationship 政治风险
• Currency risks: national currency exchange rates and monetary interest rates 金融风险
• Natural risks: the risks incurred by natural calamities including earthquakes, tsunamis, storms… 自然风险
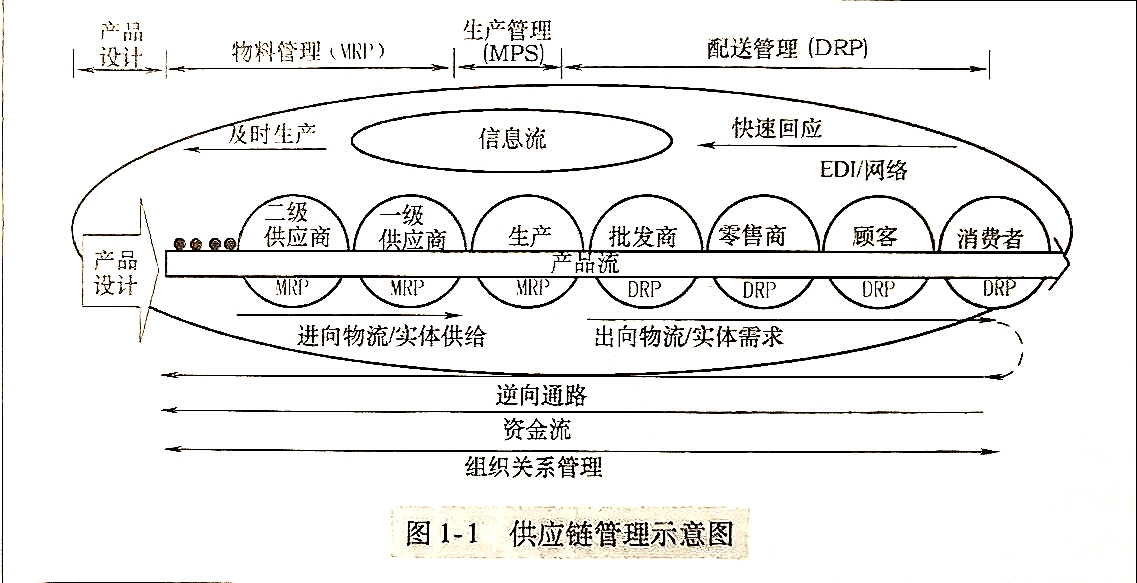
1.1.3 Links of International Logistics
Basic links of international logistics 基本环节
Transportation 运输
Warehousing 仓储
Material handling 装卸搬运
Packing 包装
Information management 信息管理
Distribution 配送
Processing 流通加工
1) Transportation: It refers to the physical movement of goods from a point of origin to a point of consumption 运输
2) Warehousing: is referred to as the storage of goods. 仓储
Broadly interpreted, it includes a wide range of facilities and locations that provide warehousing (finished goods, raw materials, in transit) .
3) Material handling: moving raw material, work-in-process, and finished goods into, through, and out of each facility. 物料搬运
4) Packing: It is mainly concerned with protecting the product in the course of shipment and storage. 包装
5) Information management: It is what links all areas of logistics system together. 信息管理
Special links of International Logistics (国际物流特有环节)
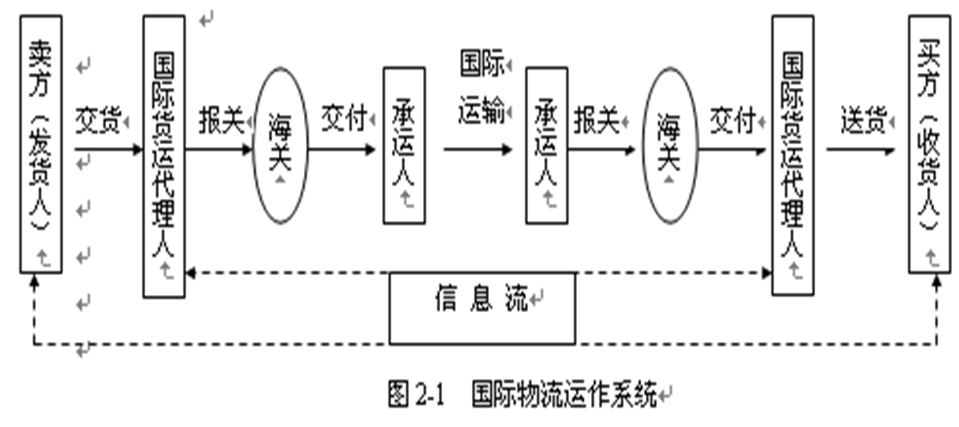
(1) Customs Clearance: the consignors, consignees or other agents are required to apply to the customs. 清关
They need to fill in the forms named “Customs Declaration for Imports and Exports”.
(2) Cargo Insurance: Due to long distance, multiple activities, and various kinds of unpredictable risks, cargo transportation insurance must be effected. 保险
(3) International Settlement: The payment of international trade is complex. The common modes include remittance, collection and letter of credit. 支付(汇款、托收、信用证)
1.1.4 Relationship between International Logistics and International Trade
1. international logistics provides fundamental supports for international trade.
Specifically: 具体来说
1) shipping terms must be stipulated clearly.
2) goods should be transported across customs territories.
3) seller fulfills the delivery of products and presentation of required documents.
2. the development of international trade has raised new requirements to international logistics. 对于国际物流的新要求
Higher quality 高质量
Higher safety 安全
More efficiency 高效
Lower cost 低成本
Real and accurate information 准确信息
(1) Quality Requirements:
Reason:
1) the goods have switched from traditional primary products and raw materials to manufactured products with high-value.
2) diversified customer needs have led to the trend of small-lot, multi-species logistics
(2) Safety Requirements:
Reason: the features of wide geographical span, long cycle, complicated links and various natural and political factors.
Reaction: when making decisions on the routes and modes of international transportation, firms should take into accounts such factors.
(3) Efficiency Requirements:
to accelerate international logistics process, large-scale special logistics equipment should be applied.
(4) Cost Requirements:
There is great potential for controlling and reducing the total costs in the area of international logistics. (International logistics involves many complicated links and lasts a long period of time.)
(5) Information Requirements:
Information is the only driver for the acceleration of logistics process and the cost saving of the entire logistics system.
Requirement: The trend requires that EDI declaration, electronic inspection and quarantine and electronic space booking be widely used.


