8.4 Oral habits.
Oral habits
Keypoints:
1.Oral habits
A.Thumb and finger habits: openbite;
B.Tongue thrust (tongue anterior positioning):openbite, bimaxilla protrusion; proclined anterior teeth; anterior crossbite;
C. Lip habits: anterior deepbite; proclined anterior upper teeth; retruded mandible; anterior crossbite;
D.Month breathing: narrowed arches; protruded maxilla; retruded mandible;incompentent lips;
E.Bruxism: primary and permanent teeth worn; deep overbite;
F. Unilateral mastication: imbalance development of jaws.
2.The functional factors which can cause bad oral habits:
A. masticatory function
B. habits
C.tongue thrust
D. respiratory function
3.Equilibrium theory
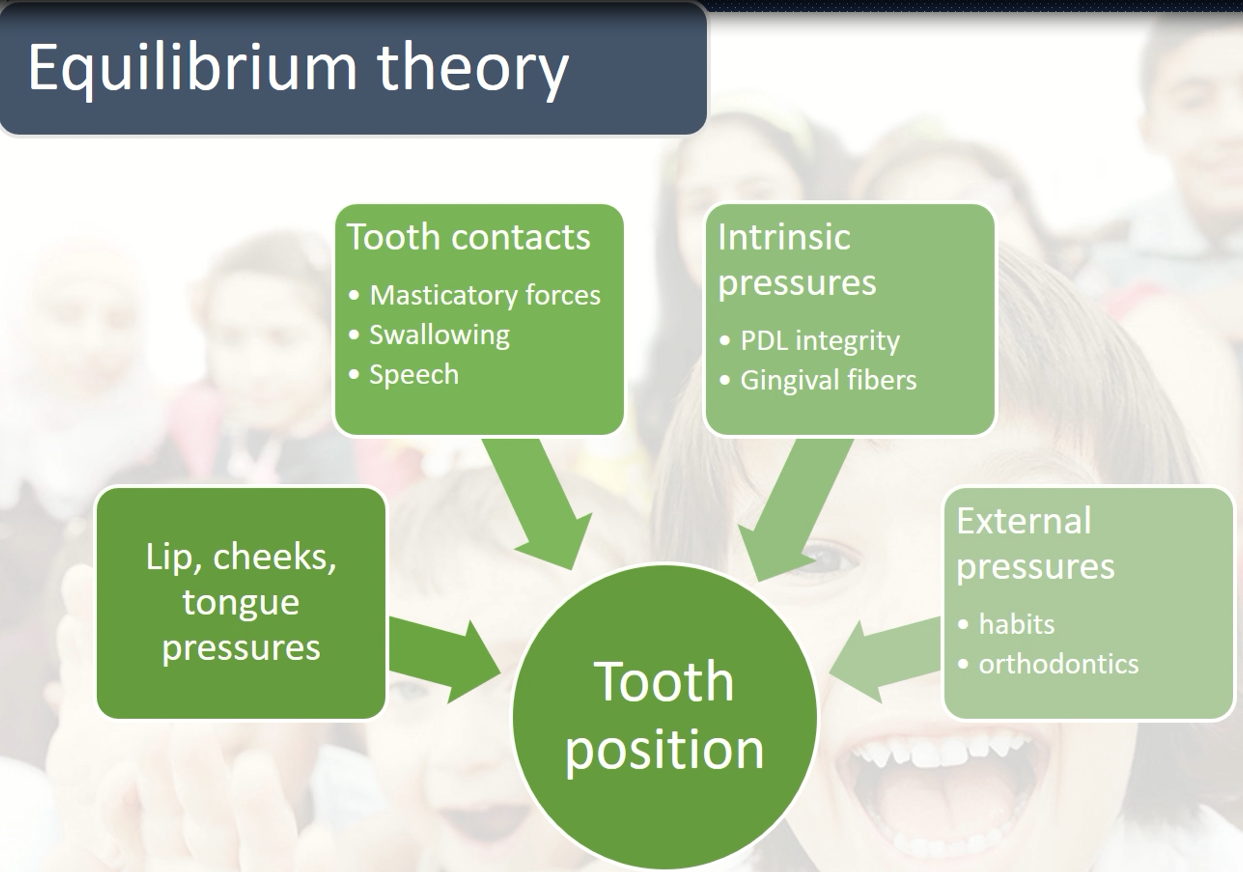
4.Digit sucking
A kind of bad oral habit during which the tongue is lowered and the cheeks contract during sucking , the pressure balance against the upper teeth is altered, and the upper but not the lower molars are displaced lingually;
A.Digit sucking beyond the time that the permanent teeth begin to erupt (7 years of age) can lead to malocclusion:
●Flared and spaced maxillary incisors;
●Lingually positioned lower incisors;
●Anterior open bite;
●Narrow upper arch:
B.Greater effect on dental development
●Features
●Narrow V shaped maxillary arch
●Anterior open bite
●Retroclined lower incisors
●Buccal crossbite
5.Tongue thrust.
Clinically, tongue thrust is defined as a forward placement of the tip of tongue, usually happens in the mixed dentition period, which causes openbite and tooth labially/buccally tipping. Tongue thrust needs to be treated in time.
●Infantile swallowing pattern:
●Active contractions of the musculature of the lips
●A tongue tip brought forward into contact with lower lip
●Little activity of the posterior tongue or pharyngeal musculature
●Adult swallowing pattern:
●No contracting the muscles
●Teeth are momentarily in contact
●Tongue remains inside the mouth
6.month breathing habits and respiratory problems
●Incompetent lips;
●Priclination of maxillary incisors;
●High and narrow palatal vault;
●Narrowed dental arches;
●Mandibular clockwise rotation:
●Skeletal class II, long face syndrome;
Mouth breathing: Change in posture that secondarily altered long-duration pressures from the soft tissues.
7.Bruxism: Teeth grinding while sleeping;
●Causes:
●Occlusal interference
●Psychological factors;
●Sleep posture;
●Intervention:
●Occlusal adjustment;
●Psychological therapy;
●Tooth weatriness prevention;
●Others:
●Sleep posture adjustment;
●Masticatory muscle tense release: massage;
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Homework(please send your answer to email):
Please illustrate your understanding of the clinic specialties of Pediatric Dentistry.


