8.2 Introduction to management of occlusal development
① Introduction about the management of occlusal development. I.
Keypoints:
1.The concept of the management of occlusal development includes 3 parts:
A.Malocclusal prevention;
B.Occlusal guidance;
C.Malocclusal interceptive treatment.
2.Oral maturation during which malocclusion could happen:
A.Tooth development and eruption;
B.Dental arch development: dental arch (dental alveolar bone) alveopedics;
C.Upper and lower jaw development:Maxilla orthopedics;
D.Oral functions maturation:tongue position; respiratory pattern; mastication.
E.Para-oral soft tissues activities/masticatory muscle functions.
3.The contents of occlusive guidance:
A.Oral health maintaining and caries controlling;
B.Tooth development abnormalities;
C.Bad oral habits;
D.Premature tooth loss and space maintaining;
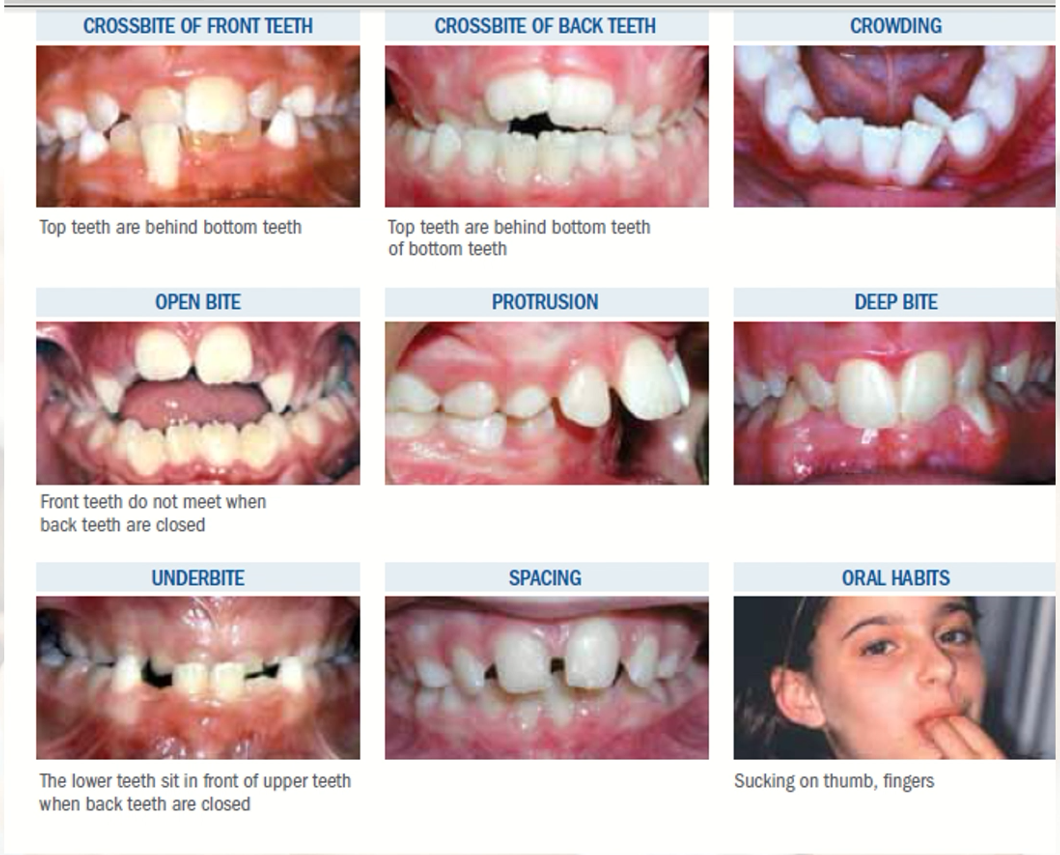
E.Malocclusions:
Primary anterior crossbite;
Crowding, series extraction;
F.Malocclusion preventions.
4.EARLY TREATMENT MAY GIVE YOUR ORTHODONTIST THE CHANCE TO:
●Guide jaw growth;
●Lower the risk of trauma to protruded front teeth;
●Correct harmful oral habits;
●Improve appearance;
●Guide permanent teeth into a more favorable position;
●Create a more pleasing arrangement of teeth,lips and face.
5.The indications for early orthodontictreatment:
② Introduction about the management of occlusal development .II.
Keypoints:
1.The relationships between the growth and orthodontic treatment:
A. Growth can improve or worsen malocclusion as growth continues;
B. Growth can affect the progress and outcome of treatment results;
C. Growth can affect the stability of results;
D. Orthodontic treatment can affect facial growth.
2.The criteria to start the management of occlusal development:
Oral functions; Oral health; Maxilla development; Aesthetics.


