PART II: Mucosal diseases in children
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1)Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis/thrush
Key point:
Clinical features:
1)Commonly seen in neonate, infants younger than 6 months, and immunosuppressed patients.
2)The lesions of oral candidiasis is appear as raised, furry white patches, which can be removed easily to produce a bleeding underlying surface.
3)Lesions can be found on lips, tongue, buccal mucosa, soft and hard palate.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
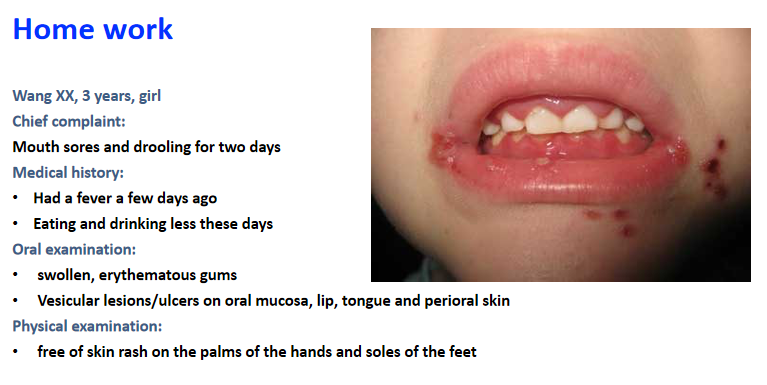
2)Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis
Key point:
Clinical features:
1)Age: commonly seen in children younger than 6 years old, especially 6 months to 3 years.
2)Incubation period : about 1 week.
3)Prodrome:
Febrile illness;
Headache;
Malaise;
Oral pain;
Cervical lymphadenopathy.
4)Gingivitis:
Gingivitis is the most striking feature;
With markedly swollen, erythematous, friable gums.
5)Vesicular lesions:
Vesicular lesions develop on oral mucosa, lip and tongue;
Can occur anywhere in the oral cavity, on the perioral skin, on the pharynx.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3)Traumatic ulcer
Key point:
1.Riga–Fede disease:
1)An oral condition that manifests as an ulceration on the ventral surface of the tongue.
2)Caused by trauma to the soft tissue from erupted baby teeth
3)Although it begins as an ulceration, it may progress to a large fibrous mass with repeated trauma.
2.Bednar ulcer:
1)Suction ulcers on the posterior lateral parts of the hard palate.
2)It has been associated with the traumatic effect of the bottle‘s nipple, pacifier and/or finger sucking.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question for review:
1.Please give the definitions for the following terms:
1)Eruptive gingivitis
2)Localized aggressive periodontitis
3)Riga–Fede disease
2.What is the common pathogen of primary herpetic gingivostomatitis?
A. HSV-2 B.HSV-1 C. Candida albicans
D. Coxsackie virus A4 E.Enterovirus
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Homework(please send your answers to email):
Questions:
1)Please give the diagnosis.
2)Please give the common pathogen of the disease.
3)Please give your treatment plan.
4)Please give the purposes of treatment for this type of disease.


