Kinds of Vehicle Tests
Any newly designed and developed cars must be carried on a series of vehicle tests before they are put into mass production. Vehicle test refers to the working process in which a vehicle or some assemblies must be carried on various tests according to the test outline as well as some standards concerned.Vehicle test must use specialized equipment, the laboratory and the specialized vehicle proving grounds. The major aims of vehicle test are to evaluate the car performance, find out its defects and weak links in order to further research and put forward improving implement to improve the vehicle performance.
Vehicle tests are classified in accordance with test purpose, test object and test site.
According to the test purpose, vehicle tests are divided into quality test, new product test and scientific research test.
Quality test is to evaluate the car’s quality, find out existing problems in time and make sure the quality control.
New product test is to assess whether the new developed product accords with the designed requirements before the new developed cars are put into mass production.
Scientific research test is a series of activities to promote the technology advance for vehicles.
According to the test object, vehicle tests are divided into complete vehicle test, assembly test and component test.
Complete vehicle test is to assess the main technical performances of a vehicle, such as dynamic property, fuel economy, ride comfort, maneuverability, stability and trafficability.
Assembly test is mainly to assess the operating performance and durability of each assembly in a vehicle, such as engine power, transmission efficiency and suspension unit.
Component test is to determine main components for their reasonable structure and design and measure their rigidity, strength and durability and service lifetime.
According to the test site, vehicle tests are divided into indoor bench test, outdoor road test and proving ground test.
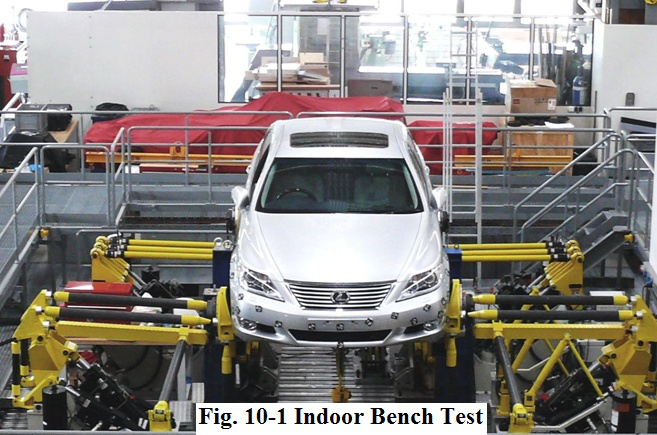
Indoor bench test (see Fig.10-1) is carried on in a room equipped with a specialized test bench, on which a complete vehicle is put to have a road simulation test. Through the road simulation, some parameters from the test bench are precisely controlled in order to simulate the vehicle in actual operation condition. It is also called remote parameter control (RPC).
Outdoor road test (see Fig.10-2) is conducted outdoor on ordinary road. It is designed to verify a vehicle running on the actual road for the real technical performance.

Proving ground test (see Fig.10-3) is used to conduct all kinds of vehicle performance tests without being affected by traffic. In the same ground there are many different kinds of roads for different test purposes. Through the proving ground test, we can determine vehicles’ reliability, durability, fuel economy and service lifetime, and so on.

译文:
课文A汽车试验种类
任何一款新设计开发出来的汽车必须进行一系列的汽车试验才能投入大规模生产。汽车试验是指,整车或部分汽车总成根据试验大纲以及相关标准进行各种试验的工作过程。汽车试验必须使用专业设备、实验室和专业试验场。汽车试验的目的是鉴定汽车的性能,发现瑕疵和薄弱环节以便进行进一步的研究, 提出改进措施,提高汽车性能。
汽车试验是根据试验目的、试验对象和试验场所进行分类的。
根据试验目的,汽车试验分为质量试验,新产品试验和科学研究试验。质试验用于评价汽车的质量,及时找出现有问题,保证质量控制。新产品试验是在汽车投入大规模生产前鉴定新产品是否符合设计要求。科学研究试验是促进汽车技术进步的一系列活动。
根据试验对象不同,汽车试验分为整车试验、总成试验和零部件试验。
整车试验用于鉴定汽车的主要技术性能,如动力性、燃油经济性、行驶平顺性、机动性、稳定性和通过性。
总成试验主要用于评价汽车每个总成的工作性能,如发动机功率、变速器效率和悬架装置等。
部件试验用于确定主要零部件的合理结构和设计, 测量其硬度、强度、耐久性和使用寿命。
根据试验场所不同,汽车试验分为室内台架试验、室外道路试验和试验场试验。
室内台架试验(见图10-1)是在有专业的试验台架装备的室内进行的试验,即将一辆整车放在台架上,进行道路模拟试验。通过道路模拟,精确控制试验台架上的数据,对汽车在实际工况下进行模拟。室内台架试验也称为远程数据控制(RPC).
室外道路试验(见图10-2)是在户外普通道路上进行的试验。其目的是判定汽车在实际道路上行驶的真实技术性能。
试验场试验(见图10-3)可用来进行所有种类的汽车性能试验,且不受交通情况影响。在同一场地上,有许多针对不同试验目的的道路。通过试验场试验,可以确定汽车的可靠性、耐久性、燃油经济性及使用寿命等。