Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles only use electricity to make the vehicles move in place of conventional fuels. They are propelled by one or more electric motors powered by rechargeable battery packs. They are designed to save fossil fuels such as gasoline and diesel, reduce harmful emissions and get an eco-driving.
Battery electric vehicle (BEV)
BEV mainly uses a high-voltage electric motor to drive the car. The electric motor gets its electric power from a high-voltage battery pack which is recharged by plugging into standard 220-volt outlet. BEV is divided into range-extended electric vehicle (RE-EV) and all-electric vehicle (EV).
Range-extended electric vehicle (RE-EV) uses an engine as an on-board range extender to increase its all-electric range (AER). The engine and the generator form a fuel-electric generator set. The engine is connected directly to the generator and is used only when needed to generate electricity to automatically charge the battery. Its generator delivers enough power to charge battery quickly and efficiently while driving (see Fig.9-1a).
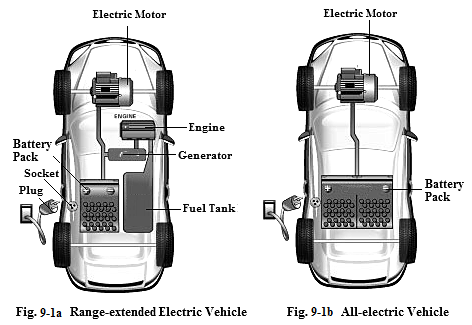
All-electric vehicle (EV) has no internal combustion engine (ICE) at all. It uses a large battery pack to store the electricity that powers the electric motor to move the car. The battery must be recharged by plugging into a power source. Some EVs have on-board chargers.Others need to be plugged into an external charger (see Fig.9-1b). An EV is a zero-emission vehicle, and its electric motor produces no tailpipe exhaust emissions.
There are many pros and cons about electric vehicles. The electric vehicle is known to have faster acceleration in silence but shorter distance range than conventional cars with engine. They produce zero emission but require long charging time. What is the long-term solution?
Fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV)
FCEV also called FCV (Fuel Cell Vehicle) is considered as the next generation electric vehicle. Unlike a conventional car which runs on gasoline, FCEV combines hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity used to move the car without emission pollutants and offers quiet cruising just like BEV. In addition, its long driving range is comparable to conventional cars.
Unlike a BEV, FCEV is quickly refueled only for a couple of minutes at the filling station just like conventional cars as shown in Fig.9-2. But it is little affected by the weather.
A typical FCEV is equipped with the following main components as shown in Fig.9-3 below:
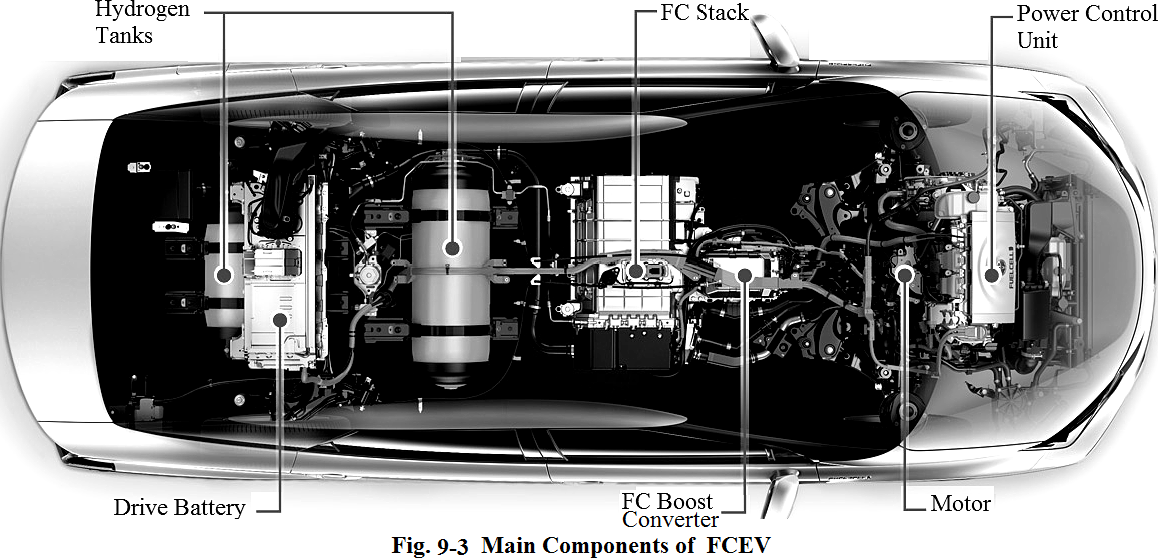
Hydrogen tank: stores hydrogen gas compressed at extremely high pressure to increase driving range;
Fuel cell stack: fuel cell (FC) is nothing more than a battery fueled by hydrogen, and fuel cell stack converts hydrogen gas and oxygen into electricity to power the electric motor;
Electric motor: propels the car much more quietly, smoothly, and efficiently than an internal combustion engine and requires less maintenance;
Drive battery: is a high-output battery that stores electricity generated from regenerative braking and provides additional electric power to the electric motor;
Power control unit: controls the flow of electricity;
Fuel cell boost converter: converts alternate current into direct current.
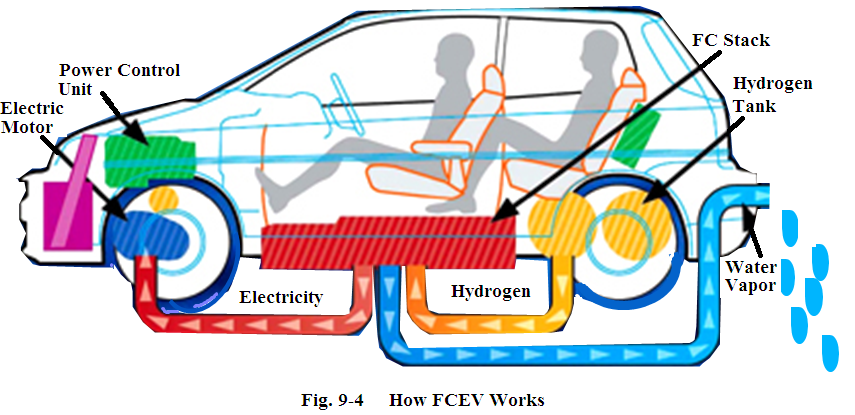
FCEV operates in the following manners: the hydrogen from the tank and oxygen from the air are pulled into the FC stack. When they meet in the FC stack, electricity and water are created through a chemical reaction. The electricity is sent to the electric motor to propel the car, and water vapor is emitted from tailpipe without emission pollutants (see Fig.9-4).
译文:
课文A电动汽车
电动汽车利用电取代传统燃料来使汽车行驶。它是由一个或多个由可充电蓄电池组供电的电动机来驱动的。其目的是节省诸如汽油和柴油这样的化石燃料,减少有害物质的排放,从而实现绿色驾驶.
纯电动汽车(BEW)
BEV主要采用高压电动机来驱动汽车。电动机从高压电池组获得电能,而电池组则可以通过将电源插入标准220V电源插座进行充电。BEV分为增程式电动汽车(RE-EV)和纯电动汽车(EV) .
RE-EV采用发动机作为车载增程器来增大纯电动行驶里程(AER)。发动机和发电机共同组成油电发电机组。发动机直接与发电机连接,只有在需要发电,自动给蓄电池充电时才使用。RE-EV在行驶时,发电机输送足够的电能给蓄电池以进行快速有效的充电(见图9-1a).
EV没有内燃机(ICE)。它采用大的电池组来储存电,并用电来使电动机驱动汽车。蓄电池必须将电源插头插入电源方可充电.在一些纯电动汽车上有车载充电器,另一些需要插入外部充电器(见图9-1b)。纯电动汽车是零排放汽车,其电动机不会产生尾气排放。
电动汽车有许多优缺点。众所周知,电动汽车静音加速比由传统发动机驱动的汽车更快,但其行驶里程却比传统汽车短。虽然是零排放,但需要很长的充电时间。那什么才是长期解决的方法呢?
燃料电池电动汽车(FCEW)
FCEV (或FCV)被认为是下一代电动汽车。燃料电池电动汽车不像传统汽车靠汽油行驶,而是通过将氢气和氧气混合产生电来驱动汽车,且没有排放污染物,如同纯电动汽车一样静音行驶。此外,FCEV的长途行驶行程可与传统汽车相比。
如图9-2所示,FCEV像长途汽车-样,在加油站只需几分钟即可快速加燃料,这与电池电动汽车不同,但是却受天气的影响。
一般燃料电池汽车配有以下主要部件,如图9-3所示。
氢气瓶:储存高压压缩氢气,增加行驶里程。
燃料电池反应堆:燃料电池是电池添加了氢气燃料。燃料电池反应堆将氢气和氧气转变成电供给电动机.
电动机:电动机驱动汽车比内燃机更安静、更平顺、更有效,且不太需要保养。
驱动电池:是高输出电池。它将再生制动产生的电储存起来,并向电动机提
供额外的电能。
电力控制单元:用来控制电流。
燃料电池转换器:将交流电转换为直流电。
燃料电池电动汽车工作的工作原理:氢气瓶中的氢气和空气中的氧气进入到燃料电池反应堆,当两者相遇时,通过化学反应产生电和水。电输送给电动机用来驱动汽车,水蒸气从排气管排出,无排放污染物(见图9-4)。