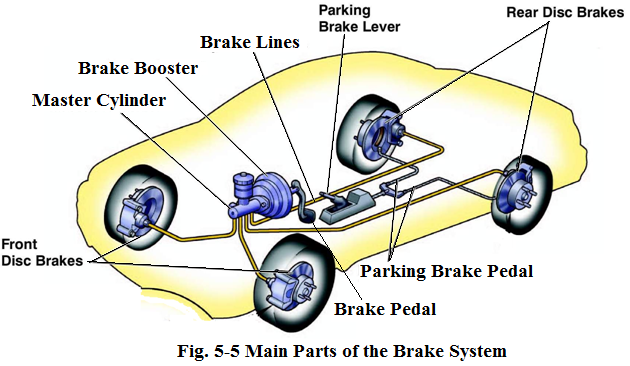
Basic Brake Parts and Safety Brake System
Typical braking system has the following basic parts: brake pedal, brake booster, master cylinder, brake lines and brake fluidas shown in Fig.5-8.
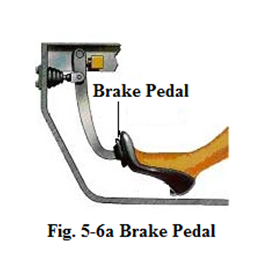
Brake pedal
Brake pedal located on the right foot side in the car can amplify the force of your leg and evenly transmit it to the brake fluid when the right foot steps on the pedal (see Fig.5-9).
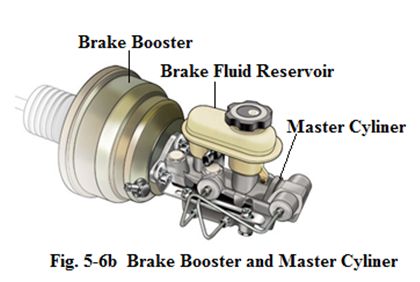
Brake booster
Brake booster mounted on the firewall between the brake pedal and master cylinder increases the force applied to the pistons in the master cylinder so that the car can stop with less effort. The two most common types of power brake boosters are vacuum booster and hydraulic booster, both of which accomplish the same thing.
Master cylinder
A master cylinder has actually two completely independent working chambers respectively with one piston, each controlling two wheels. If only the two of the wheels lose their brakes, the other two wheels will still be able to stop the car. On the top of the master cylinder is a brake fluid reservoir that is transparent so as to see the fluid level without opening the cover (see Fig.5-10).
Brake lines
The brake lines run from the master cylinder along the frame of the car to each wheel (see Fig.5-8). The lines are made of steel and reinforced rubber hoses which are flexible enough to use only at the front wheels and rear axles where the suspension system works and wheels turn when you steer.
Brake fluid
Brake fluid travels from the master cylinder to the wheels through the brake lines. It is special oil that has specific properties. It must withstand cold temperature in winter without thickening as well as very high temperature in summer without boiling.
Safety brake system
One cannot think of the safety brake system without thinking of ABS, nor of ABS without EBD, EBA and ESC, etc.
ABS, short for Anti-lock Brake System, is designed to prevent the car from skidding on a wet and slippery road, and make the car shorten brake distance and stop in a straight line without loss of the directional control.without loss of the directional control.
ABS consists of ECU (Electronic Control Unit), 4 wheel speed sensors and APV (Anti-lock Pressure Valve) as shown in Fig.5-11. ECU continuously monitors the rotating speed of each wheel through the 4 wheel speed sensors. When one or more wheels are going to lock up, the ECU immediately commands the APV to ease the brake pressure on the affected wheels. ABS “pumps” brakes up to 15 times per second, much faster and more effective than a human driver can.
EBD, short for Electronic Brake-force Distribution, as the subsystem of ABS, is designed to automatically modulate the brake force on the front wheels and the rear wheels according to the load of the car, the condition of the road and the adhesion between the tire sand road surface in order to get more balanced and closer to the ideal brake force distribution.
EBA, short for Emergency Brake Assist, is designed to keep the electronic eye on how you are braking, and if you suddenly get into an emergency and have to stop your car shortly, EBA automatically boosts the brake force to help you in order to save you in an emergency.
ESC, short for Electronic Stability Control, is designed to keep the car from rolling over in a panic swerve when running on a wet and slippery road. It uses some sensors such as wheel speed sensors, steering wheel position sensors and yaw sensors to determine whether the car goes the right direction you want. If the car is not going in the direction you want, ESC can apply the brakes on individual wheels to bring the car back under control.
译文:
课文 基本制动部件和安全制动系统
一般制动系统包括以下基本部件:制动踏板、制动助力器、制动主缸、制动管路和制动液,如图5-8所示。
制动踏板
制动踏板位于车内驾驶人的右脚边。它能在驾驶人踩下踏板时增加助力,均匀地将力量传给制动液(见图5-9)。
制动助力器
制动助力器安装在制动踏板和制动主缸之间的发动机舱壁上。它可以增大制动主缸内活塞的推力,用较小的力便使汽车停下来。最常见的两种制动助力器是真空助力器和液压助力器。
制动主缸
制动主缸实际上有两个完全独立的工作缸,分别有一个活塞,每个工作缸控制两个车轮。如果有两个车轮制动失灵,其他两个轮子仍可使汽车停下来。制动主缸的顶部有制动液储存罐,它是透明的,可以看见液面高度,而无需打开储液罐盖(见图5-10)。
制动管路
制动管路从制动主缸沿着车架一直到每个车轮(参见图5-8)。管路由钢管和强化橡胶管制成。橡胶软管要有足够的柔性,仅用在前轮和后桥上,即悬架系统工作和车轮转向的地方。
制动液
制动液从制动主缸通过制动管路流至车轮。制动液是特殊的油,具有独特的性能。既能在冬季承受低温而不变稠,又能在夏季耐住高温而不沸腾。
安全制动系统
提到安全制动系统,就不能不想到ABS,想到ABS,就不能不想到EBD、EBA和ESC等。
ABS是防抱死制动系统的简称,旨在防止汽车在湿滑的路面上漂移,使汽车缩短制动距离,并且直线停车而不失去方向性控制。
ABS包括ECU(电控单元),4个车轮转速传感器和APV(防抱死压力阀),如图5-11所示。ECU通过4个车轮转速传感器实时监控每个车轮的旋转速度。当一个或
多个车轮将要抱死的时候,ECU会立即“告知”APV对受到影响的车轮减轻制动压力。ABS每秒“点刹”大约15次,比驾驶人的动作更快更有效。
EBD是电子制动力分配的缩写,是ABS的子系统。根据车载,路况以及轮胎与路面的附着力,EBD自动调节前轮和后轮的制动力,得到更好的平衡,更接近理想的制动力分配。
EBA是紧急辅助制动系统的简称,旨在让电子眼始终监视制动行为。如果遇到突发紧急情况需要马上停车时,EBA会自动增加制动力,紧急情况下挽救生命。
ESC是电子稳定控制系统的简称,旨在防止汽车行驶在湿滑路面突然转向时,发生侧翻。它使用一-些传感器如车轮转速传感器、转向盘位置传感器、横摆传感器来判别汽车是否在预想的正确方向行驶。如果汽车未能按预想的方向行驶, ESC能够在个别的车轮上进行制动,把汽车带回到控制之下。