Other Main Components of a Drive Train
In addition to transmission, the drive train also includes other main components such as clutch, only used in MT cars; torque converter, only used in AT cars; differential system; drive shaft and transfer case.
Clutch Assembly
Clutch is used to engage with the engine to transmit the power to the transmission, or disengage with the engine in order to shift gears. It is located between the engine and the transmission. Basically, clutch assembly consists of following main parts: flywheel, clutch disk, pressure plate assembly, release bearing, release fork, clutch pedal and linkage as shown in Fig.4-7.
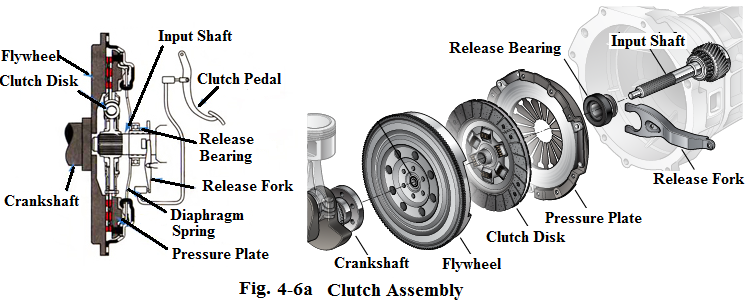
Flywheel is a drive plate bolted to the crankshaft. Its functionas a drive plate is to transfer the engine torque from the engine to the transmission.
Clutch disk is a driven plate covered with a frictional material that moves between the flywheel and the pressure plate.
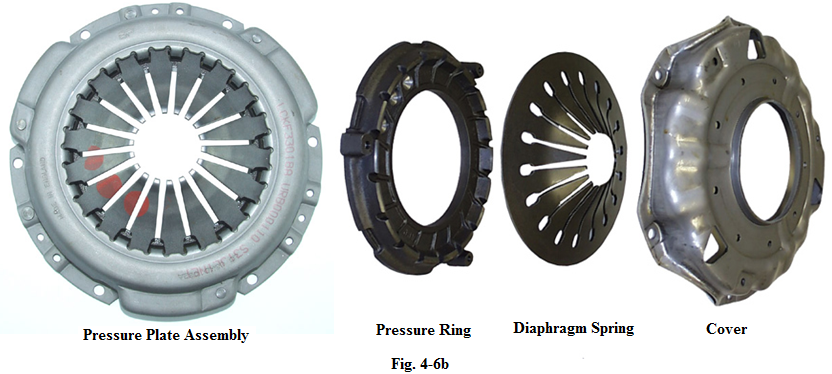
Pressure plate assembly bolted to the flywheel includes a metal cover, a diaphragm spring and a metal pressure ring, which provides a friction surface for the clutch disk (see Fig.4-8).
Release bearing is the heart of clutch operation. It activates the release fingers of the diaphragm spring that moves the pressure ring back and forth to make the clutch disk engage or disengage with the flywheel.
Release fork is used to transfer the force from the pedal to the release bearing.
Clutch pedal is located on the flooron your left. When you step the clutch pedal, the clutch disconnects the engine from the transmission to allow the car to change gears.
The clutch linkage is divided into a mechanical linkage such as a cable and a hydraulic linkage such as clutch master cylinder, reservoir and hydraulic line and slave cylinder.
Torque Converter
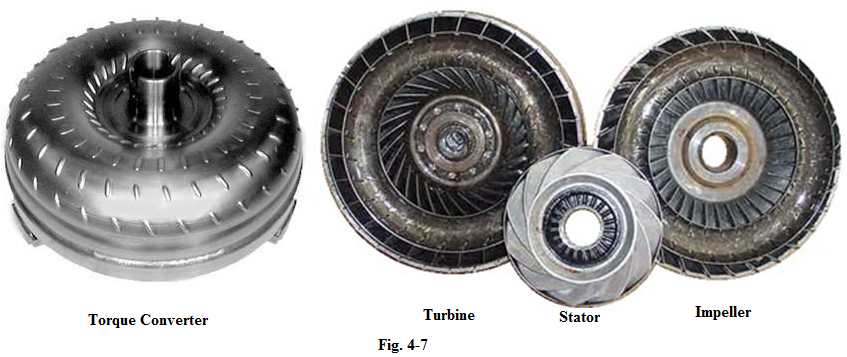
AT cars use a torque converter instead of the clutch used on MT cars. The torque converter is mounted between the engine and the transmission and turns as the same speed as the engine.A torque converter has three main parts: impeller, turbine and stator that work together to transmit power from the engine to the transmission (see Fig.4-9) . It uses hydraulic pressure to control the amount of engine power transmitted to the transmission input shaft.
Differential System
The functions of differential system are to send power to two drive wheels and to help the car change moving direction while the car is going around the corner. On a front-wheel-drive car, the differential and the transmission combine together within one housing, called “transaxle” . On a rear-wheel-drive car or on a four-wheel-drive (4WD) car, the differential is connected to the drive shaft (see Fig.4-10).
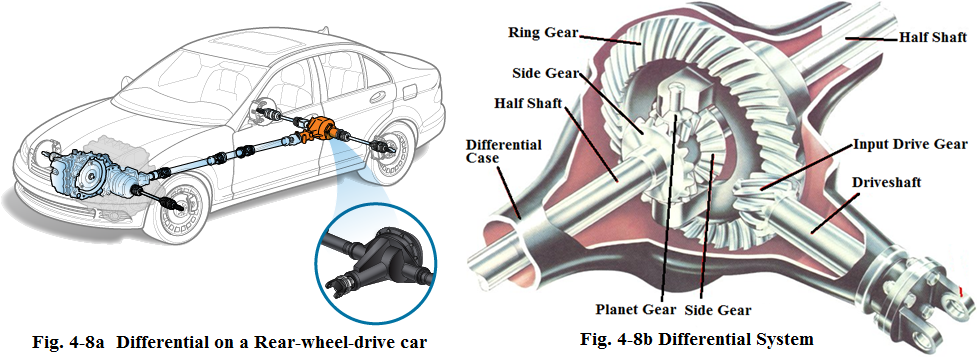
Generally, the differential mainly consists of two side gears, two planet gears and a ring gear. They are all housed in one differential case. The side gears are connected to the two half shafts; the planet gears are connected to the ring gear. The ring gear is also called output driven gear which constantly meshes with the input drive gear on the end of the drive shaft. We often call them final drive (see Fig.4-11).
When the car is going straight ahead, the both side gears rotate at the same rate. So do the right and left wheels. When the car is going around the corner, the two side gears rotate at different rate. This means that the inner wheel must slow down, and the out wheel must speed up.
Drive shaft and Transfer Case
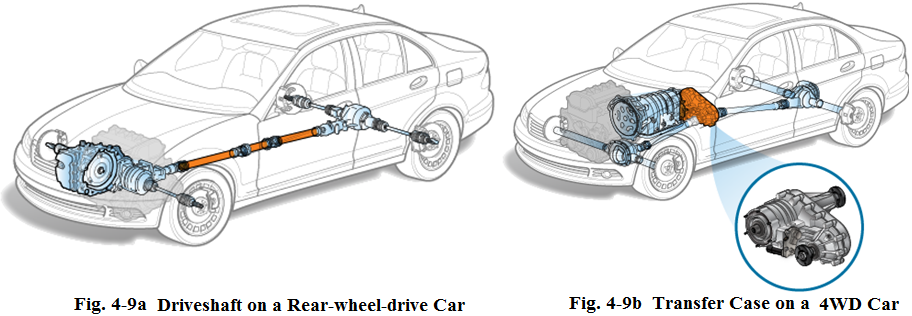
On a rear-wheel-drive car, a drive shaft is used to transmit the power from the transmission to the differential between the two rear drive wheels (see Fig.4-12). Many 4WD cars use two drive shafts, with one drive shaft between the transfer case and rear drive axle and the other one between the transfer case and front drive axle (see Fig.4-13). The transfer case is only used to control the power to the front and rear drive axles.
Four-Wheel-Drive (4WD) and All-Wheel-Drive (AWD) Vehicles
4WD and AWD are often found on off-road vehicles such as SUV. 4WD is divided into two types: part time drive and real time drive. The former is switched from two-wheel drive to four-wheel drive manually with a button.The latter is automatically switched from two-wheel drive to four-wheel drive according to the road conditions. AWD is full time drive , that is, 4 wheels offer driving force all the time.
译文:
传动系统的其他主要部件
除了变速器,传动系统还有其他主要部件,如离合器——仅用于手动变速器的车上,液力变矩器——仅用于自动变速器车上,差速器系统,传动轴以及分动器等。
高合器总成
离合器用来与发动机啮合将动力传递给变速器,或与发动机脱离啮合,便于换档。它位于发动机和变速器之间。一般地,离合器总成由如下主要部件组成:飞轮、从动盘、压盘总成、分离轴承、分离叉、离合器踏板和离合器拉杆传动机构,如图4-7所示。
飞轮是一个驱动盘,用螺栓固定在发动机曲轴上。其功能是将发动机转矩传递给变速器。
从动盘是从动件,在飞轮和压盘之间运行,其表面附有摩擦材料。
压盘总成由螺栓固定在飞轮上。它包括一个金属压盘盖、膜片弹簧和一个金属压环,为从动盘提供摩擦面(见图4-8)。
分离轴承是离合器工作的心脏。它推动膜片弹簧上的分离指,使压环前后来回移动,从而使离合器盘与飞轮啮合或脱离啮合。
分离叉是用来将离合器踏板的力传递给分离轴承的。
离合器踏板位于左脚一侧的地板上。踩离合器踏板时,离合器使发动机与变速器分离,进行换档。
离合器拉杆传动机构分为机械式拉杆传动机构(如离合器拉索)和液压式拉杆传动机构(如离合器主缸、储液罐、液压管路和从动缸)。
液力变矩器
自动变速器汽车使用液力变矩器取代手动变速器汽车上使用的离合器。液力变矩器安装在发动机和变速器之间,并与发动机转速相同。液力变矩器有三个主要部件:泵轮、涡轮和导轮(见图4-9),共同把发动机动力传递给变速器。液力变矩器利用液压来控制发动机传递给变速器输入轴的动力大小。
差速系统
差速系统的作用是将动力传输给两个驱动轮,并帮助车辆在转弯时改变行驶方向。前驱汽车,差速器和变速器合在一起,安装在一个壳体内,称为“变速驱动桥”。后驱或四驱汽车,差速器与传动轴连接(见图4-10)。
通常,差速器是由两个半轴齿轮、两个行星齿轮和一个齿圈构成的。它们都安装在一个差速器壳中。半轴齿轮与两个半轴连接,行星齿轮与齿圈连接。齿圈也称为输出从动齿轮,它与传动轴末端的输入驱动齿轮啮合。我们通常称它们为主减速器(见图4-11)。
当汽车直线行驶时,两侧半轴齿轮以相同速度旋转.左右两侧车轮也是如此。当车辆转弯时,两侧半轴齿轮以不同速度旋转。这就意味着内侧车轮必须减速,而外侧车轮必须加速。
传动轴和分动器
后轮驱动汽车,用传动轴将动力从变速器传递给两个后驱动轮之间的差速器上(见图4-12)。很多四驱的汽车有两个传动轴,一个位于分动器和后驱动桥之间,另一个位于分动器和前驱动桥之间(见图4-13)。分动器仅用于控制前、后驱动桥的动力。
四轮驱动汽车(4WD)和全轮驱动汽车
四轮驱动和全轮驱动常见于越野车上,如SUV汽车。四驱有两种:分时四驱和实时四驱。前者用手动按键将两驱切换到四驱。后者则是根据路况自动地完成两驱到四驱的切换。全驱是指全时驱动,也就是说,四个车轮始终提供驱动力。