Ignition, Starting and Fuel Systems
Ignition system
Ignition system is the most important part of the gasoline engine. Its purpose is to ignite the compressed fuel-air mixture at proper time, producing power to move the car.A good ignition system has a great impact on the engine performance, fuel economy and exhaust pollution.
Ignition system is divided into 3 types: contact-point ignition system (Fig.3-15), non-point ignition system (Fig.3-16) and non-distributor ignition system ( Fig.3-17). First one is convention ignition system (CIS), the last two ones are electronic ignition system (EIS).
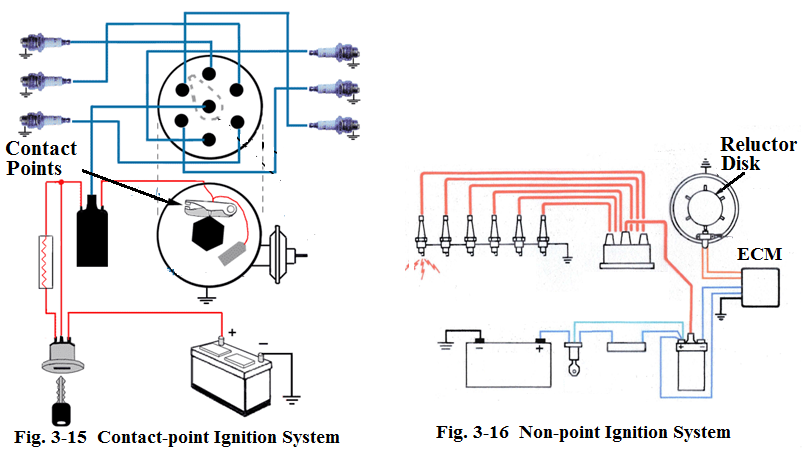
In non-point ignition system, a reluctor disk and an electronic control module (ECM) take the place of the contact points in the contact-point ignition system.
With the development of the automotive technology, non-distributor ignition system is replacing the other two types of the ignition systems mentioned above. So we mainly introduce the non-distributor ignition system.
The major components of a non-distributor ignition system are engine control unit (ECU), ignition control unit (ICU), a set of ignition coils and some sensors such as crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor and knock sensor.
The spark plugs are fired directly from the coils. The spark timing is controlled by ECU and ICU according to the information received from the sensors.There are multiple coils on cars so each one serves one or two spark plugs.
If there are 3 coils that mounted together in a coil pack in a car with a 6-cylinder engine, each coil is connected to two spark plugs with spark plug wires. The coil fires bothspark plugs at the same time. One spark plug fires on the compression stroke igniting the fuel-air mixture to produce power while the other spark plug fires on the exhaust stroke and does nothing (see Fig.3-17a).
If there are 4 coils, each coil is mounted directly on the top of each spark plugas shown in 3-17b.
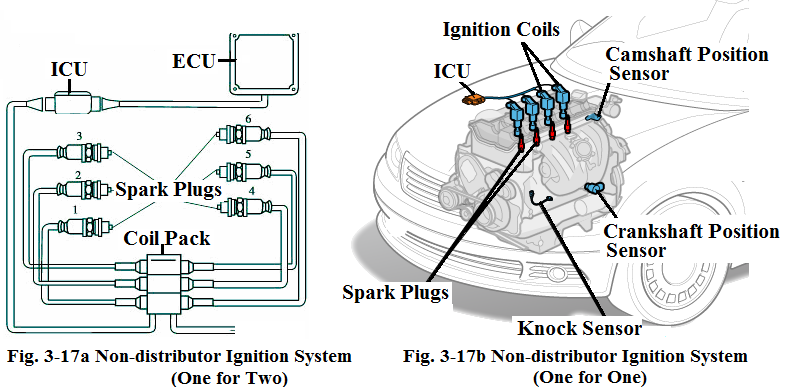
This design completely eliminates the spark plug wires for even better reliability.
Starting system
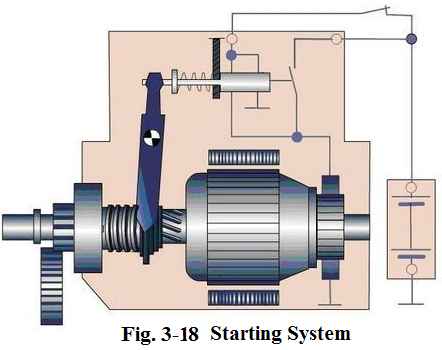
Starting system functions to crank the engine fast enough to allow the engine to start (see Fig.3-18). The starting system and ignition system must work together for good engine starting. This system includes the following main components:
Battery serves as an electrical energy source.It produces electric current for starting the car, powering the ignition system and turning on the lights. The battery converts electrical energy into chemical energy during charging and then converts it back into electricity during discharging.
Ignition switch, also called key switch, controls the ignition circuit, starting system and the power for the car instruments.
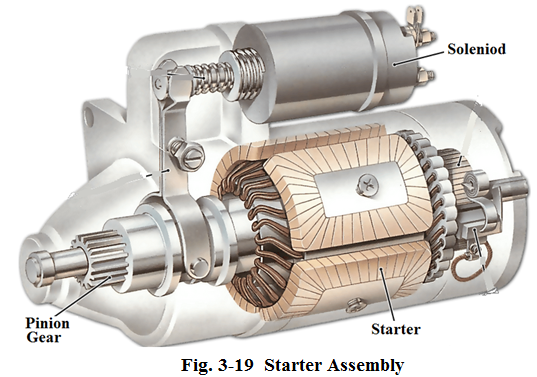
Starter is a very powerful direct-current electric motor designed to crank the engine. The starter has a small pinion gear which meshes with the ring gear on the flywheel. When the driver turns the key switch, the starter drives the pinion gear, which, in turn, drives the flywheel and cranks the engine.
Solenoid is mounted on the top of the starter. It has two important functions: ①it controls the electrical circuit between the battery and starter; ②it shifts the pinion in and out of mesh with the ring gear (see Fig.3-19).
Fuel supply system
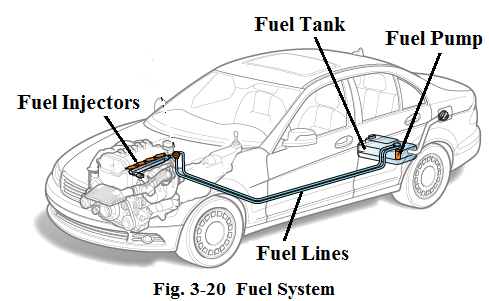
The purposes of the fuel supply system are to supply the right amount of fuel for the engine to burn, and control the speed of the engine. Let’s look at the major parts of the fuel system as shown in Fig.3-20.
Fuel tank (see Fig.3-21) is the energy storage for the engine. All cars have a single tank located in the rear of the cars. In the tank there is a sending unit which tells the fuel gauge how much fuel is left in the tank.


Fuel pump (see Fig.3-22) is usually located inside the fuel tank so as to keep the pump cool and quiet. Nowdays, a fuel injected car uses an electric pump. Its purposes are to draw the fuel from the fuel tank and deliver it to the fuel system.
Fuel line uses steel lines and flexible hoses that carry the fuel from the tank to the engine.
Fuel filter (see Fig.3-23) has an important job that removes dirt, rust and water from the fuel before it can reach the injection system.
Fuel injector (see Fig.3-24) is nothing but an electronically controlled valve. The function of the fuel injector is to deliver finely atomized fuel under high pressure to the combustion chamber of the engine.


译文:
点火系统、 起动系统和燃油系统
点火系统
点火系统是汽油机中最重要的组成部分。其用途是在适当时机点燃压缩的可燃混合气,产生动力使汽车行驶。良好的点火系统对发动机的性能、燃油经济性和排放污染有着极大的影响。
点火系统分为3种类型:触点式点火系统(图3-15),无触点式点火系统(图3-16)和无分电器式点火系统(图3-17)。第一类是传统点火系统(CIS),后两类是电子点火系统(EIS)。
在无触点式点火系统中,磁阻盘和电子控制模块(ECI)取代了触点式点火系统中的触点。
随着汽车技术的发展,无分电器式点火系统正在取代上述两类点火系统。所以,这里主要介绍无分电器式点火系统。
无分电器式点火系统的主要部件是发动机控制单元(ECU)、点火控制单元(ICU)、一组点火线圈和一些传感器(如曲轴位置传感器、凸轮轴位置传感器和爆燃传感器)。
火花塞由点火线圈直接点火。ECU和ICU根据从传感器接收的信息控制点火正时。车上有多个点火线圈,因此,每个点火线圈可服务于一个或两个火花塞。
如果在一辆装备六缸发动机的车上有两个点火线圈安放在一个点火线圈包内,每个点火线圈用火花塞高压线连接到两个火花塞上,则该点火线圈同时给两个火花塞点火。一个火花塞在压缩行程中点火,点燃可燃混合气,产生动力,而另一个是在排气行程中,做无用功(见图3-17a)。
如图3-17b所示,如果有四个点火线圈,每个点火线圈直接安装在每个火花塞的顶部,则该种设计完全淘汰了火花塞高压线,使可靠性增加。
起动系统
起动系统的作用是快速驱动发动机,使其开始运转(见图3-18).起动系统和点火系统必须配合工作,才能使发动机起动良好。起动系统包括下列主要部件:
蓄电池作为电源。它产生电流,用于起动汽车,给点火系统供电,打开灯光。蓄电池在充电时,将电能转变成化学能,并在放电时再转变成电能。
点火开关,也称为钥匙开关,用来控制点火电路、起动系统以及车上仪表盘的电力。
起动机是大电流的直流电动机,其目的是起动发动机。起动机上有个小齿轮,与飞轮上的齿圈啮合。当驾驶人转动起动开关时,起动机驱动小齿轮,小齿轮再驱动飞轮,从而起动发动机。
起动机电磁开关安装在起动机的顶部,它有两个重要功能:控制蓄电池和起动机之间的电路,切换小齿轮与齿圈的啮合和脱离啮合(见图3-19) .
燃油供给系统
燃油供给系统的用途是为发动机提供适量的燃油使其燃烧,并且控制发动机的转速。燃油供给系统的主要部件(见图3-20)如下:
燃油箱(见图3-21)是发动机的能量储备装置。所有的轿车都有一个燃油箱,位于汽车的尾部。在燃油箱内有个燃油表传感器,用于告知燃油箱内的燃油量。
燃油泵(见图13-22)通常位于燃油箱内,以保持油泵冷却和静音。当今,所有采用燃油喷射的汽车都使用电动燃油泵。其目的是从燃油箱泵出燃油,输送到供油系统。
燃油管路采用钢制管路和柔性软管,用于将燃油从燃油箱输送给发动机。
燃油滤清器(见图3-23)的一个重要作用是,将污垢、铁锈和水从燃油中滤出。
喷油器(见图3-24)是个电控阀。其功能是在高压下将微细雾化较完全的燃油喷射到发动机的燃烧室内。