Lubrication and Cooling Systems
Lubrication system
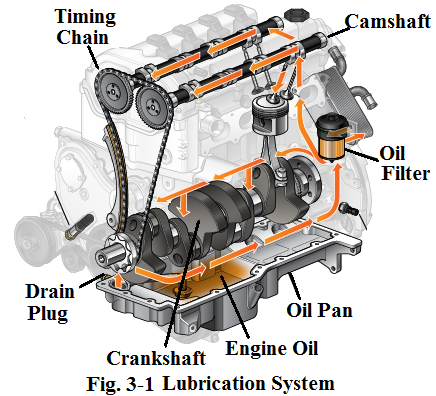
The purpose of the engine lubrication system (see Fig.3-1) is to deliver clean en-gine oil at the correct temperature and pressure to every moving part of the engine to reduce friction between the surfaces of the parts which contact each other.The major parts of thelubrication system are listed below:
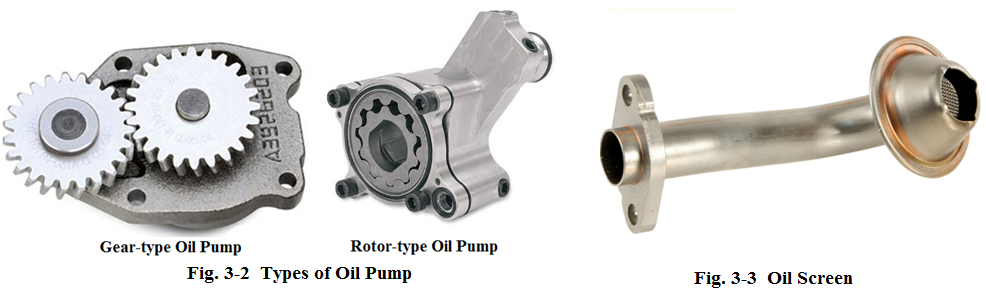
Oil pump is the key part in the lubrication system. Its task is to produce the pressure high enough to draw the engine oil from the oil pan and circulate it throughout the system. Two types of the oil pumps are often found on most cars: gear-type and rotor-type oil pumps as shown in Fig.3-2.
Oil screen (see Fig.3-3) is located at the bottom of the oil pan. It is connected to the oil pump. Its job is to collect any large particles of dirt before the engine oil entering the pump.
Oil filter (see Fig.3-4) is a very important part in this system. It takes in dirty oil, removes crud and keeps it trapped in the filter media, and returns the clean oil back to the engine.

Oil pan(see Fig.3-5) is a container mounted at the bottom of the crankcase which serves as engine oil storage. It collects the oil as it flows down from sides of the crankcase when the engine is at rest.

Engine oil (see Fig.3-6) has several important jobs in the engine. It lubricates the moving engine components with less friction. The circulating oil cools the engine by carry-ing heat away from the hot engine components. It cleans dirt and deposits off the engine parts. It also seals between the cylinder walls and piston rings, improving the engine’s com-pression.

In modern engine designs, two methods of lubrication are combined: pressure lubrication and splash lubrication (see Fig.3-7).
Cooling system
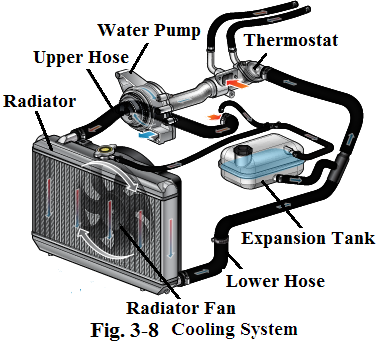
The purposes of the cooling system are to remove excess heat from the engine, to keep the engine operating at its most efficient temperature, and to warm up the engine to the efficient temperature as soon as possible after starting (see Fig.3-8). The major parts of the cooling system are listed below:
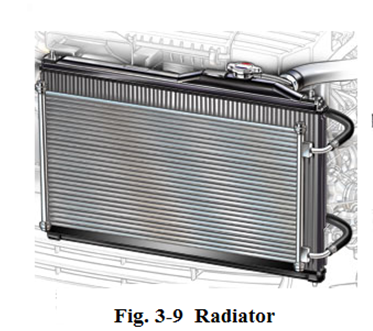
Radiator (see Fig.3-9) is designed to dissipate the heat which the coolant has absorbed from the engine. It consists of radiator core, water-carrying tubes, an inlet tank and an outlet tank. Usually, the radiator is mounted in front of the engine compartment, just behind the grill.
Radiator fan (see Fig.3-10) is designed to keep the air flow going through the radiator while the car is going or it stops with the engine running. Usually, two fans are mounted on the back of the radiator.


Water pump (see Fig.3-11) is a simple device that can keep the coolant flowing as long as the engine is running. It is driven by the engine through the timing belt.
Pressure cap (see Fig.3-12) is designed to maintain pressure in the cooling system.If the pressure rises up higher than the set pressure point, the cap with a spring loaded valve will release the pressure to the expansion tank to prevent loss of coolant and return the coolant to the radiator when it cools down.


Expansion tank (see Fig.3-13) is used to fill the coolant.In addition, when the coolant in the engine expands and is forced out of the radiator, it overflows into the expansion tank. When the engine cools down and coolant contracts, the vacuum draws the coolant back into the radiator in order to make it always completely full.
Thermostat (see Fig.3-14) is simply a valve that measures the temperature of the coolant. The thermostat helps the engine reach the operating temperature sooner by keeping the coolant from flowing to the radiator. As the engine reaches operating temperature, the thermostat opens and allows the coolant to flow to the radiator through the upper hose.

Coolant or antifreeze performs two functions: it keeps the radiator fluid from freezing in wintry conditions and keeps the engine from overheating in warm weather.
译文:
润滑系统和冷却系统
润滑系统
发动机润滑系统(见图3-1)的作用是将洁净的机油以合适的温度和压力输送给每个发动机的运动部件,以减少部件表面相互接触产生的摩擦。润滑系统的主要部件如下:
机油泵是润滑系统的关键部件。它的任务是产生足够高的压力以抽取油底壳中的机油并使其在整个系统中循环。在大多数汽车上,有两种常见的机油泵:齿轮式和转子式,如图3-2所示。
集滤器(图3-3)位于油底壳底部,与机油泵相连。其任务是在机油进入机油泵之前先过滤出油液中的大颗粒脏物。
机油滤清器(图3-4)是润滑系统中非常重要的部件。它吸附脏油,去除杂质并使其留在过滤介质上,然后将洁净的机油送回到发动机中。
油底壳(图3-5)是安装在曲轴箱下面的一个容器,用于储藏机油。当发动机静止时,油底壳可将曲轴箱四周流淌下来的机油收集起来。
机油(图3-6)在发动机中起着重要作用:润滑发动机运动部件以减少摩擦;将炽热的发动机部件产生的热量带走,使其冷却;去除发动机部件上的脏物和沉积物。另外,它还在气缸壁和活塞环之间起着密封的作用,提高发动机压缩性能。
在现代发动机设计中采用两种润滑方法相结合:压力润滑和飞溅润滑(见图3-7).
冷却系统
冷却系统的作用是清除发动机产生的过热:保持发动机在最有效的温度下运行;使发动机起动后尽快热机,达到有效的工作温度(见图3-8)。冷却系统的主要部件如下:
散热器(图3-9)的目的是散发冷却液吸收发动机的热量。它是由散热器芯、载水管、进水箱和出水箱组成的。通常散热器安装在发动机舱前部,格栅的后面。
散热器风扇(图3-10)的目的是在汽车行驶时,或者汽车停止行驶而发动机运转时,使气流通过散热器。通常在散热器的后面安放两个风扇.
水泵(图3-11)是个简单的装置,只要发动机在运转它就要保持冷却液流动。水泵是由发动机通过正时传动带米驱动的。
压力盖(图3-12)的目的是保持冷却系统的压力。如果压力上升到超过设定的压力点,压力盖上的弹簧卸载阀会将压力释放到膨胀水箱中,以防冷却液的缺失。当冷却液冷却下来后,再将其送回到散热器中。
膨胀水箱(图3-13)用来注入冷却液。此外,当发动机中的冷却液膨胀时,流出散热器,冷却液溢流到膨胀水箱。当发动机冷却时,冷却液收缩,真空将冷却液抽回到散热器中,使其始终满水处于充满状态。
节温器(图3-14)是用来测量冷却液温度的阀。节温器通过阻止冷却液流入散热器来帮助发动机更快到达工作温度。当发动机到达工作温度时,节温器打开,使冷却液通过上软管流入散热器中。
冷却液(防冻液)有两个功能:①防止散热器中的液体在严寒状态下结冰:②防止散热器中的液体在炎热的天气里过热。