Valve Train and Its Main Components
The function of the valve train or valve gear is to open and close the intake and exhaust valves at the exact time to let the air-fuel mixture enter the combustion chamber and let the exhaust gas get out of the cylinder according to the firing order and requirement of working cycle of the engine.The valve train contains the following main parts as shown in Fig.2-6:
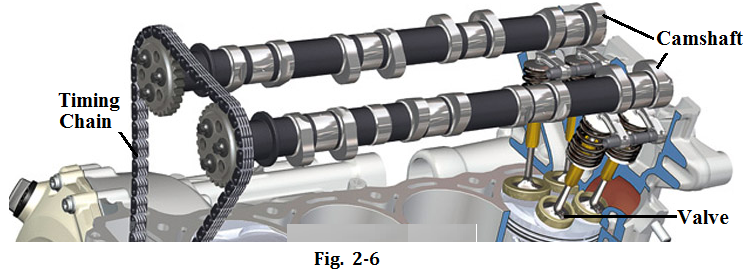
Valves are usually made from steel alloy. They are divided into the intake valve and exhaust valve. There are always at least one intake and one exhaust valve in each cylinder.In many modern cars, there are two intake valves and two exhaust valves, or three intake valves and two exhaust valves in each cylinder. They are held in the cylinder head.
The intake valve opens, letting the fuel-air mixture into the combustion chamber. In the compression stroke, the intake valve closes, and the fuel-air mixture is compressed and ignited by the spark plug. Then the exhaust gases get out of the cylinder when the exhaust valve opens. The exhaust valves must withstand extremely high temperature without damaging the valves.
The valve face must seat evenly against the valve seat in the cylinder head to prevent leaking from the cylinder during the compression and power strokes. Many valve faces and seats have an angle of 45 degrees (see Fig.2-7).
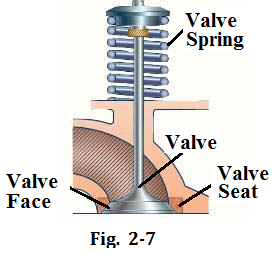
Valve springs return the valves to their closed position after the valve opening. These springs have to be strong enough because the valves are pushed down very quickly at high engine speed.
Camshaft plays a very important role in the valve train, which controls the valve timing.When it rotates, the camshaft opens and closes the intake and exhaust valves in time with the motion of the piston.
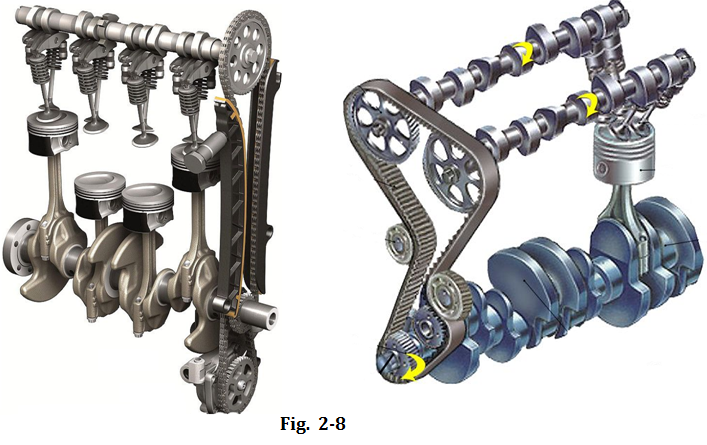
In most modern cars, the camshaft is fixed in the cylinder head rather than in the cylinder block in the traditional engine. If there is only one camshaft in each cylinder head, it is called the single overhead camshaft (SOHC) as shown in Fig.2-8a. If there are two camshafts in each cylinder head, we call the double overhead camshaft (DOHC), one responsible for intake, the other for exhaust as shown in Fig.2-8b.
We know that it is the crankshaft that drives the camshaft through the timing chain or timing belt. In the 4-stroke engine, each time one working cycle is completed, the crankshaft rotates 2 revolutions, and the intake valve and exhaust valve in each cylinder respectively open once. That is, the camshaft rotates at a half speed of the crankshaft.
Timing belt and chain are used to deliver the power from the crankshaft to the camshaft, making the valves open and close at the right time in order to ensure the proper intake and exhaust of the engine.
Timing belt is made from rubber. It is low in noise, small in resistance, cheap in cost and easy in replacement.
Timing chain is made of steel. With the development of auto technology, timing chain is fast to take the place of the timing belt. Comparing with the rubber belt, the timing chain is reliable, durable and space-saving. What’s more, it is long-life free maintenance .((see Fig.2-9)

译文:
配气机构和主要部件
配气机构的功能是根据发动机的点火顺序和发动机的工作循环要求,以确切的时间将进、排气门打开或关闭,使可燃混合气进入燃烧室,使废气排出气缸。如图2-6所示,配气机构包括下列主要部件:
气门通常是由合金钢制成的,分为进气门和排气门。每个气缸至少有一个进气门和一个排气门。在许多现代汽车中,每个气缸上有两个进气门和两个排气门或者三个进气门和两个排气门。它们都是固定在气缸盖上的。
进气门打开,使可燃混合气进入燃烧室。在压缩行程中,进气门关闭,可燃混合气被压缩,并被火花塞点燃。然后在排气门打开时,废气排出气缸。排气门必须承受极高的温度而不损坏。
气门锥面必须平稳地坐落在气缸盖上的气门座上,以防在压缩行程和做功行程时气缸漏气。许多气门锥面和气门座的角度都为45° (见图2-7)。
气门弹簧(见图2- 7)的作用是使气门打开之后可以返回到关闭位置。弹簧必须足够结实,因为在发动机高速运转时,需快速向下推动气门。
凸轮轴在配气机构中起着非常重要的作用,用于控制气门正时。当凸轮轴旋转时,它随着活塞的运动及时打开和关闭进、排气门。
在大多数现代汽车.上,凸轮轴是固定在气缸盖上的,而不是在传统发动机的缸体内部。如果每个缸盖只有一个凸轮轴,称为单顶置凸轮轴(SOHC),如图2-8a所示。如果每个缸盖上有两个凸轮轴,称为双项置凸轮轴(DOHC),-一个负责进气,一个负责排气,如图2-8b所示。
我们知道,曲轴是通过正时链或正时带来驱动凸轮轴的。在四冲程发动机中,每当一个工作循环完成时,曲轴旋转2周,每个气缸中的进、排气门各开启一-次。也就是说,凸轮轴是以曲轴的1/2速度旋转的。
正时链和正时带用来将曲轴产生的动力传递给凸轮轴,使气门在恰当时间打开或关闭以保证发动机正常进气排气。
正时带是由橡胶制成的。它具有噪声低、阻力小、成本廉价和易于更换的特点。
正时链是由钢制成的。随着汽车技术的发展,正时链快速取代正时带。与橡胶带相比,正时链可靠、耐用、节省空间,而且终身免维护(见图2-9)。