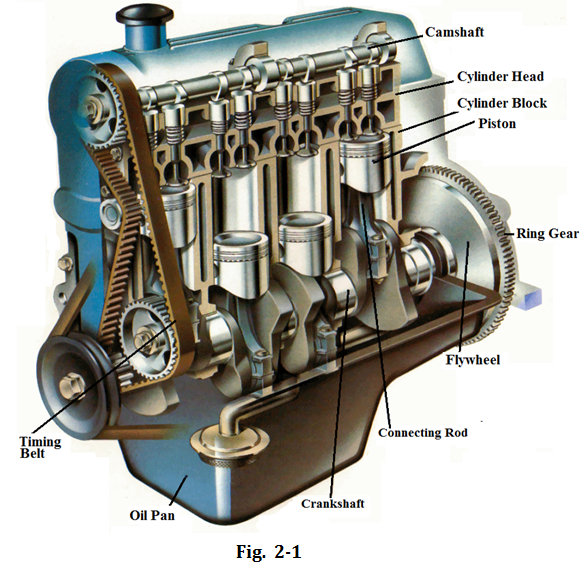
Crank Mechanism and Its Main Components
Crank mechanism is one of the major motion mechanisms of the engine. Its function is to transform the reciprocating movement of pistons into rotary movement of the crankshaft, offering torque to make the drive wheels turn (see Fig.2-1). Crank mechanism is divided into 3 groups: block group; piston and connecting-rod group; and crankshaft and flywheel group.
Block group
The block group contains the following main components (see Fig. 2-2):
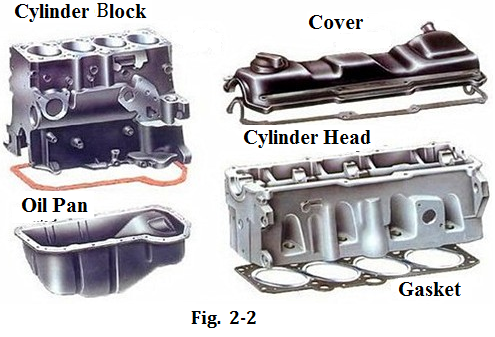
Cylinder block is one of the most important parts in an engine.It is made of cast iron or cast aluminum ,which contains cylinders,water jackets,lubricant passages and crankcase. Cylinder block holds pistons,the cranksaft and other parts. It has four forms:inline,V-type,boxer and w-type.
Cylinder head is bolted to the top of the cylinder block with a gasket in between sealing the block and forming the combustion chambers with the cylinders. Cylinder head holds camshafts, valves, spark plugs and injectors.
Oil pan is at the bottom of the cylinder block. It is a container for storage of engine oil.
Piston and connecting-rod group
Piston and connecting-rod group has some main components as follows ( see Fig.2-3):
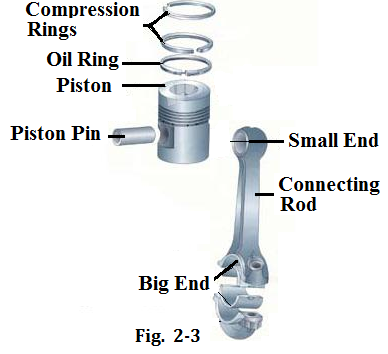
Piston is a cylindrical shaped hollow part made of aluminum alloy. It can be divided into three parts: crown, ring groove and skirt (see Fig.2-4). Its reciprocating movements in the cylinder transform the energy of the expanding gases into mechanical energy.

Piston rings are inserted in the ring grooves on the top of the piston. Most pistons have three rings: the top two are compression rings and the lower ring is an oil ring. They function as sealing between the piston and cylinder wall, lubricating, heat transferring and piston supporting in the cylinder.
Connecting rod connects the piston to the crankshaft. It has a small end and a big end. The small end attaches to the piston with the piston pin and the big end connects to the crank pin of the crankshaft.
Crankshaft and flywheel group
Crankshaft and flywheel group includes the following components (see Fig. 2-5):
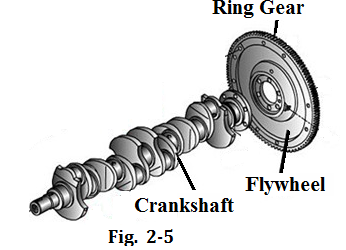
Crankshaft is one of the most important parts in the engine. It is held in the crankcase in the cylinder block and converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into a rotary motion for the drive wheels. In a 4-cylinder engine, the crankshaft usually has three main journals and four crank pins attached to the big ends of the connecting rods. Every crankshaft has counter weights whose purpose is to balance the weight of the connecting rods. Its front end is used to drive the valve train, water pump and cooling fan, and its rear end is used to install the flywheel.
Flywheel is a rotating disk located on one end of the crankshaft. It has a ring gear around the disk. Its purposes are to reduce vibration caused by the power stroke through its inertia, and to start the engine when the starter meshes with it.
译文:
曲柄连杆机构和主要零部件
曲柄连杆机构是发动机主要运动机构之一。 其功能是将活塞的往复运动转变成曲轴的旋转运动,产生转矩使驱动车轮转动(见图2-1)。曲柄连杆机构分为3组:机体组、活塞连杆组和曲轴飞轮组。
机体组
机体组包括下列主要部件(见图2-2):
气缸体是发动机最重要的部件之-,由铸铁或铸铝制成。它包括气缸、冷却水套和润滑油道以及曲轴箱。气缸体用来固定活塞、曲轴和其他部件。气缸体有4种形式:直列式、V型、水平对置式和W型。
气缸盖是用螺栓固定在气缸体顶部的,其中间用气缸垫密封缸体与气缸形成燃烧室。气缸盖用来固定凸轮轴、气门、火花塞和喷油器。
油底壳是在气缸体的底部。它是机油的储存装置.
活塞连杆组
活塞连杆组包括下列主要部件(见图2-3):
活塞是由合金铝制成的圆柱形空心部件。它分为3部分:顶部、环槽部和裙部(见图2-4)。活塞在气缸内的往复运动使膨胀气体的能量转变成机械能。
活塞环镶嵌在活塞顶部的环槽中。大多数活塞有三个环:上两个环是气环,下面的环是油环。活塞环在活塞和气缸壁之间起密封、润滑和导热作用,同时有在气缸中支撑活塞的作用。
连杆用于将活塞连接到曲轴上。它有连杆小头和连杆大头。连杆小头是用活塞销连接到活塞上的,连杆大头则是连接到曲轴上的曲柄销上.
曲轴飞轮组
曲轴飞轮组包括下列部件(见图2-5):
曲轴是发动机中最重要的部件之一。它固定在气缸体上的曲轴箱中,用来将活塞的往复运动转变成旋转运动使驱动车轮转动。在四缸发动机中,通常有3个主轴承和4个与连杆大头连接的曲柄销。每个曲轴有平衡重,其功能是平衡连杆的重量。曲轴前端用来驱动配气机构、水泵和冷却风扇,尾部用来安放飞轮。
飞轮是位于曲轴一端的旋转盘。在盘的周围有个齿圈,其用途是通过惯性减少工作冲程产生的振动,起动机与其啮合起动发动机。