Classification of Engines
Classification of Engines
All automotive engines are internal combustion engines (ICE), which burn fuel within the cylinders and convert the expanding force of the combustion into rotary force used to drive the automobile.So an engine is the source of power and it is considered as the heart of an automobile.
Automotive engines are classified as the reciprocating engine and rotary engine according to the way they work; as the gasoline engine and diesel engine according to fuel they burn;and as the inline engine, V-type engine, boxer engine and W-type engine according to the number and the arrangement of cylinders.
Reciprocating Engine and Rotary Engine
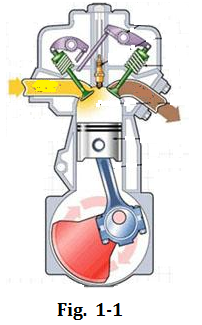
Reciprocating engines are also called piston engines. The engines use one or more pistons that move up and down or back and forth in the cylinders and convert the pressure into rotational kinetic energy transmitted to drive wheels (see Fig.1-1.). The reciprocating engines are often found in almost all modern automobiles.

A rotary engine was developed in 1954. In this engine a three-sided rotor revolves within a combustion chamber as shown in Fig.1-2. The expanding gas turns the rotor, producing power and the exhausted gas is expelled. The rotary engine has no reciprocating parts such as pistons and valves. It develops a high horsepower, and produces no vibration, but its fuel consumption is higher than that of the reciprocating engine.
Gasoline Engine and Diesel Engine
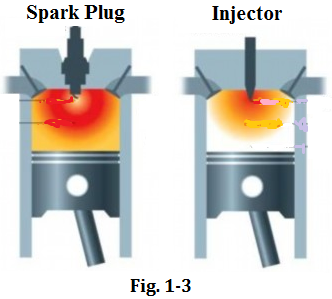
Gasoline engines use gasoline as fuel. Spark plugs are used to ignite the mixture of fuel and air inside the cylinder, creating power to make a car run as shown in Fig. 1-3a.It is also called the spark ignition engine. The features of the engine are high in speed, smooth in operation, simple in the structure, light in weight and low in cost. Almost all cars use gasoline engines.
Diesel engines use diesel as fuel. It works by compressing the air inside the cylinder to make diesel coming in from the injector burn, producing the power to drive a car (see Fig.1-3b). So it is called the compression ignition engine. A diesel engine is more powerful and delivers better fuel economy than a gasoline engine. Diesel engines are often found on large trucks, buses and some of cars.

Inline engine, V-type engine, boxer engine and W-type engine
Engine structures are identified by the number of cylinders and the ways the cylinders are laid out.
Nowadays, all compact cars are equipped with 4-cylinder engine, some intermediate cars with 6-cylinder engine, and full-size cars with 8- or 12-cylinder engine.
In a multi-cylinder engine, the cylinders are usually arranged in one of four ways: inline engine, V-type engine, boxer engine and W-type engine.
Inline engine has the cylinders arranged in a straight line with a single cylinder head. Almost all 4-cylinder engines use this arrangement (see Fig. 1-4). There are also some 5- and 6-cylinder-inline engines.
V-type engine has two rows of cylinders side-by-side with two cylinder heads, and it is commonly used in V-6, V-8, and V-12 configurations at a 90 or 60 degree angle to each other (see Fig.1-5).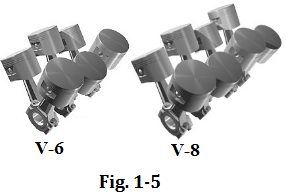
Boxer engine uses two opposing rows of cylinders with two cylinder heads at a 180 degree angle to each other, and it is less common than the above two designs.Boxer engines are usually either 4-or 6-cylinders (see Fig. 1-6).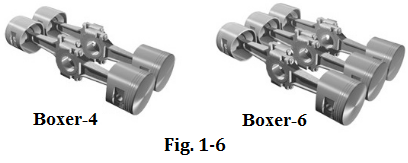
W-type engine is a newly developed engine. Some Audi A8 is equipped with a W12 engine.
W-type engine has a shorter crankshaft, but it is complicated in structure and expensive in cost, compared to a V-type engine.
Different configurations of engine types have different advantages and disadvantages in terms of smoothness, manufacturing cost and shape characteristics. These advantages and disadvantages make them more suitable for certain vehicles.
译文:
发动机的分类
所有的汽车发动机都是内燃机(ICE),就是将燃油在气缸内进行燃烧,并将燃烧产生的膨胀压力转变成转动力,用来驱动汽车。所以说,发动机是动力源,并被认为是汽车的心脏。
汽车发动机根据工作方式分为往复式发动机和转子发动机;根据发动机燃烧的燃料分为汽油机和柴油机;根据发动机的气缸数量和气缸排列方式分为直列发动机、V型发动机、对置式发动机和w型发动机。
往复式发动机和转子发动机
往复式发动机也称为活塞式发动机。该发动机采用一个或多个活塞在气缸内上下运动或前后运动,将压力转变为转动动能传递给汽车驱动轮(见图1-1)。往复式发动机广泛应用现代汽车上。
转子发动机是于1954年研发出来的。如图1-2所示,在该发动机中,有个三角形的转子在燃烧室内旋转。膨胀气体使转子旋转,产生动力并排出废气。转子发动机没有活塞和气门等往复部件。转子发动机产生马力大、无振动,但其燃油消耗比往复式发动机要高。
汽油机和柴油机
汽油机以汽油作为燃料。采用火花塞点燃缸内的可燃混合气,产生动力使汽车行驶,如图1-3a所示。汽油机也称为火花点燃式发动机。该发动机的特点是转速高,运行平顺,结构简单,重量轻,成本低。几乎所有轿车都采用汽油机。
柴油机以柴油作为燃料。该发动机的工作原理是通过压缩缸内的空气使其升温,再使喷油嘴喷入的柴油燃烧,产生动力驱动汽车(见图1-3b),所以也称为压燃式发动机。柴油机要比汽油机的动力更强劲,燃油经济性更好。常见于所有的大型货车、客车和部分轿车上。
直列发动机,V型发动机,水平对置式发动机,w型发动机
通过气缸数量和气缸排列方式可以识别发动机结构。
当今所有的紧凑型轿车都配有4缸发动机,一些中型级轿车配有6缸发动机,大型轿车配有8缸或12缸发动机。
在多气缸发动机上,气缸通常以四种排列方式中的一种排列,有:直列式、V
型、水平对置式和W型。
直列式发动机中的气缸按直线排列,采用一个气缸盖。几乎所有4缸发动机都采用该种排列(见图1-4)。另外,还有直列5缸发动机和6缸发动机。
V型发动机中并列有两排气缸,用两个气缸盖。该种排列方式常用于V6,v8和V12发动机中,角度互为90°或60°(见图1-5)。
水平对置式发动机采用两个相对的气缸排,两个缸盖,互为180°,要比上述两种发动机少见。通常水平对置式发动机可以是4缸或6缸的(见图1-6)。
W型发动机是新研发的发动机。一些奥迪A8车上装有W12发动机。与V型发动机相比,W型发动机曲轴较短,但是结构复杂,成本昂贵。
根据平顺性、制造成本及形状特点,不同结构的发动机有着不同的优缺点。这些优缺点使其更适用于某些车辆。