§Superclasses tend to be “more general” and subclasses “more specific.”
}Because every subclass object is an object of its superclass, and one superclass can have many subclasses, the set of objects represented by a superclass is typically larger than the set of objects represented by any of its subclasses.
}A super class exists in a hierarchical relationship with its subclasses.
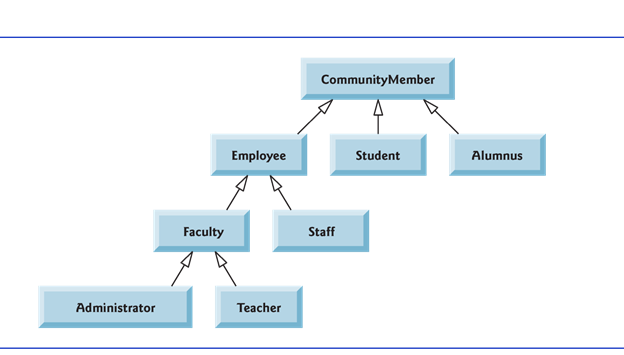
}Objects of all classes that extend a common superclass can be treated as objects of that superclass.
§Commonality expressed in the members of the superclass.
}Inheritance issue
§A subclass can inherit methods that it does not need or should not have.
§Even when a superclass method is appropriate for a subclass, that subclass often needs a customized version ofthe method.
§The subclass can override(redefine) the superclass method with an appropriate implementation.


