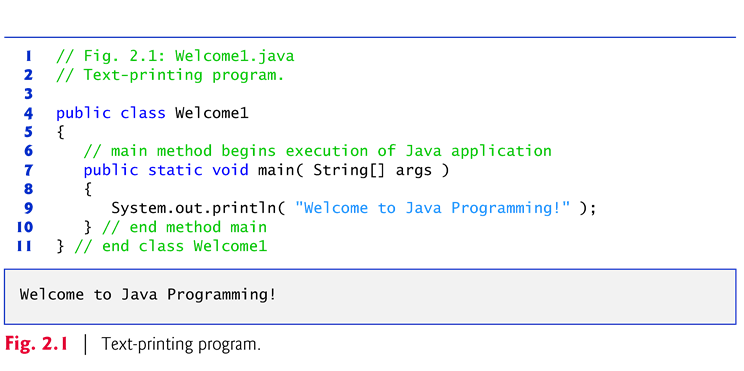
}Declaring the main Method
public static void main(String[] args)
§Startingpoint of every Java application.
§Parentheses after the identifier mainindicate that it’s a program building block called a method.
§Javaclass declarations normally contain one or more methods.
§main must be defined as shown; otherwise, theJVM will not execute the application.
§Methodsperform tasks and can return information when they complete their tasks.
§Keywordvoid indicates that this method will notreturn any information.
}Body of the method declaration
§Enclosedin left and right braces.}Statement
System.out.println("Welcometo Java Programming!");
§Instructsthe computer to perform an action
Print the string of characters contained between thedouble quotation marks.
§Astring is sometimes called a characterstring or a string literal.
§White-spacecharacters in strings are not ignored by the compiler.
§Stringscannot span multiple lines of code.
}System.out object
§Standard output object.
§Allows Java applications to display strings in the command window from which the Java application executes.
}System.out.println method
§Displays (or prints) a line of textin the command window.
§The string in the parentheses the argument to the method.
§Positions the output cursor at the beginning of the next line in the command window.
}Most statements end with a semicolon.


