Arrays
}Array
§Group of variables (called elements) containing values of the same type.
§Arrays are objects so they are reference types.
§Elements can be either primitive or reference types.
}Referto a particular element in an array
§Usethe element’s index.
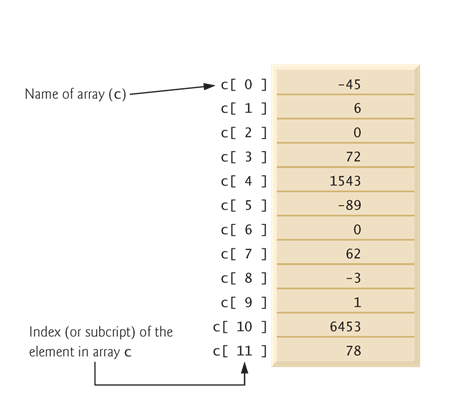
§Array-access expression—the name of the array followed bythe index of the particular element in square brackets, [].
}The first element in every array has indexzero.
}The highest index in an array is one less than the number of elements in the array.
}Array names follow the same conventions as other variable names.
}An index must be a non negative integer.
§Can use an expression as an index.
}An indexed array name is an array-access expression.
§Can be used on the left side of an assignment to place a new value into an array element.
}Every array object knows its own length and stores it in a length instance variable.
§length cannot be changed because it’s a finalvariable.
Declaring and Creating Arrays
}Array objects§Created with keyword new.
§You specify the element type andthe number of elements in an array-creationexpression, which returns a reference thatcan be stored in an array variable.
}Declaration and array-creation expressionfor an array of 12 intelements
int[] c= new int[ 12 ];
}Can be performed in two steps as follows:
int[] c;// declare the arrayvariable
c = new int[ 12]; // creates the array
}Every element of a primitive-type array contains a value of the array’s declared element type.
§Every element of an int array is an intvalue.
}Every element of a reference-type arrayis a reference to an object of the array’s declared element type.
§Every element of a String array is a reference to a String object.
Using Arrays
}Array initializer
§A comma-separated list of expressions (called an initializer list) enclosed in braces.
§Used to create an array and initialize its elements.
§Array length is determined by the number of elements in the initializer list.
int[]n = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
Creates a five-element array with index values 0–4.
}Compiler counts the number of initializers in the list to determine the size of the array
§Sets up the appropriate new operation “behind the scenes.”
Enhanced for Statement
}Enhanced for statement
§Iterates through the elements of an array without using a counter.§Avoidsthe possibility of “stepping outside” the array.
§Alsoworks with the Java API’s prebuilt collections (see Section 7.14).
}Syntax:
for ( parameter : arrayName )
statement
where parameter has a type and an identifier and arrayName is the array through which to iterate.
}Parameter type must be consistent with the array’s element type.
}The enhanced for statement simplifies the code for iterating through an array.
Multidimensional Arrays
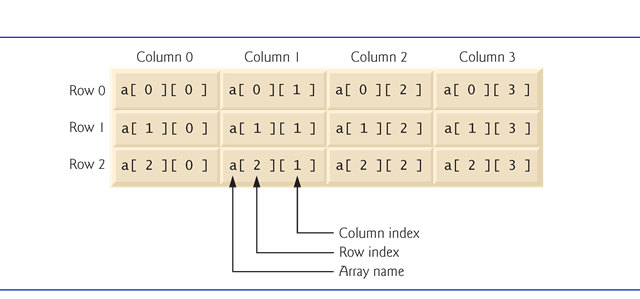
}Two-dimensional arrays are often used to represent tables of values consisting of information arranged in rows and columns.
}Identifya particular table element with two indices.
§By convention, the first identifies the element’s row and the second its column.
}Multidimensional arrays can have more than two dimensions.
}Java does not support multidimensional arrays directly
§Allows you to specify one-dimensional arrays whose elements are also one-dimensional arrays, thus achieving the same effect.
}In general, an array with m rowsand n columnsis called an m-by-narray.
}Multidimensional arrays can be initialized with array initializers in declarations.
}A two-dimensional array b with two rows and two columns could be declared and initialized with nested array initializers as follows:
int[][]b = { { 1,2}, { 3,4} };
§The initial values are grouped by row in braces.
§The number of nested array initializers (represented by sets of braces within the outer braces) determines the number of rows.
§The number of initializer values in the nested array initializer for a row determines the number of columns in that row.
§Rows can have different lengths.
}A multidimensional array with the same number of columns in every row can be created with an array-creation expression.
int[][]b = new int[ 3 ][ 4 ];
§3 rows and 4 columns.
}The elements of a multidimensional array are initialized when the array object is created.
}A multidimensional array in which each row has a different number of columns can be created as follows:
int[][]b = new int[ 2 ][ ]; // create 2 rows
b[ 0 ] = new int[ 5]; // create 5 columns for row0
b[ 1 ] = new int[ 3]; // create 3 columns for row 1
§Creates a two-dimensional array with two rows.
§Row 0 has five columns, and row 1 has three columns.
Class Arrays
}Arrays class
§Provides static methods for common array manipulations.
}Methods include
§sort for sorting an array (ascending order bydefault)
§binarySearch for searching a sorted array
§equals for comparing arrays
§fill for placing values into an array.
}Methods are overloaded for primitive-type arrays and for arrays of objects.
}System class staticarraycopy method
§Copies contents of one array into another.


