Figure below shows the eight major steps in the new-product development process.
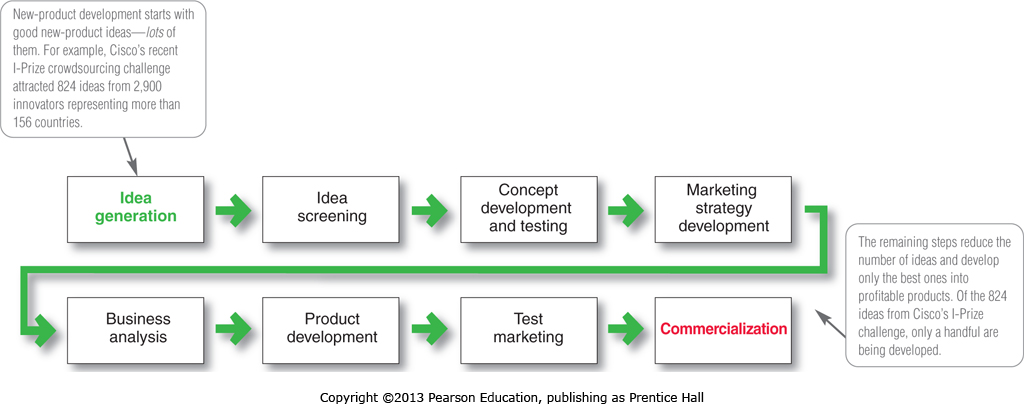
1. Idea Generation
Idea generation is the systematic search for new-product ideas.
Internal Idea Sources
Using internal sources, the company can find new ideas through formal research and development. Or it can pick the brains of employees—from executives to salespeople to scientists, engineers, and manufacturing staff.
External Idea Sources
Companies can also obtain good new-product ideas from any of a number of external sources, such as distributors and suppliers or even competitors.
Perhaps the most important source of new-product ideas is customers themselves.
Crowdsourcing
Many companies are now developing crowdsourcing new-product idea programs. Crowdsourcing invites broad communities of people into the new-product innovation process.
2.Idea Screening
The first idea-reducing stage is idea screening, which helps spot good ideas and drop poor ones as soon as possible.
3.Concept Development and Testing
A product idea is an idea for a possible product that the company can see itself offering to the market.
A product concept is a detailed version of the idea stated in meaningful consumer terms.
A product image is the way consumers perceive an actual or potential product.
Concept Development
In concept development, several descriptions of the product are generated to find out how attractive each concept is to customers. From these concepts, the best one is chosen.
Concept Testing
Concept testing calls for testing new-product concepts with groups of target consumers. (Table 8.1)
Marketing Strategy Development
4.Marketing strategy development involves designing an initial marketing strategy for a new product based on the product concept.
The marketing strategy statement consists of three parts.
1. A description of the target market; the planned value proposition; and the sales, market share, and profit goals for the first few years
2. An outline of the product’s planned price, distribution, and marketing budget for the first year
3. A description of the planned long-run sales, profit goals, and marketing mix strategy
5.Business Analysis
Business analysis involves a review of the sales, costs, and profit projections for a new product to find out whether they satisfy the company’s objectives.
6.Product Development
In product development, R&D or engineering develops the product concept into a physical product.
The product development step calls for a large jump in investment.
7.Test Marketing
Test marketing is the stage at which the product and marketing program are introduced into realistic market settings.
8.Commercialization
Commercialization involves introducing the new product into the market.
Decisions must be made about introduction timing as well as where to launch the new product.
MANAGING NEW-PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
Customer-Centered New-Product Development
New-product development must be customer centered.
Customer-centered new-product development focuses on finding new ways to solve customer problems and create more customer-satisfying experiences.
Team-Based New-Product Development
Under the sequential product development approach, one company department works individually to complete its stage of the process before passing the new product along to the next department and stage.
This orderly, step-by-step process can help bring control to complex and risky projects. But it also can be dangerously slow.
In order to get their new products to market more quickly, many companies use a team-based new-product development approach.
Under this approach, company departments work closely together in cross-functional teams, overlapping the steps in the product development process to save time and increase effectiveness.
Instead of passing the new product from department to department, the company assembles a team of people from various departments that stay with the new product from start to finish.
Systematic New-Product Development
An innovation management system can be used to collect, review, evaluate, and manage new-product ideas.
The innovation management system approach yields two favorable outcomes.
1. It helps create an innovation-oriented company culture.
2. It will yield a larger number of new-product ideas, among which will be found some especially good ones.
New-Product Development in Turbulent Times
In difficult times, innovation more often helps than hurts in making the company more competitive and positioning it better for the future.


