Nature and Characteristics of a Service
A company must consider four service characteristics when designing marketing programs: intangibility, inseparability, variability, and perishability (see Figure 7.3).
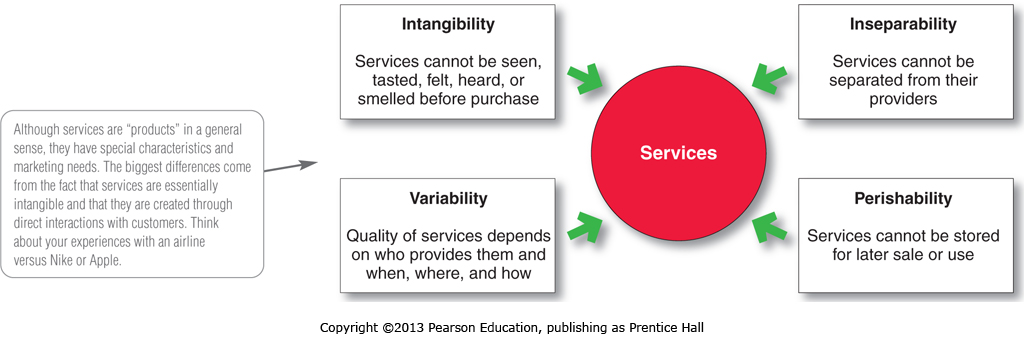
(1) Service intangibility means that services cannot be seen, tasted, felt, heard, or smelled before they are bought.
(2) Service inseparability means that services cannot be separated from their providers, whether the providers are people or machines. Because the customer is also present as the service is produced, provider-customer interaction is a special feature of services marketing.
(3) Service variability means that the quality of services depends on who provides them as well as when, where, and how they are provided.
(4) Service perishability means that services cannot be stored for later sale or use.
Marketing Strategies for Service Firms
Just like manufacturing businesses, good service firms use marketing to position themselves strongly in chosen target markets.
The Service-Profit Chain
In a service business, the customer and front-line service employee interact to create the service.
The service-profit chain consists of five links:
• Internal service quality: superior employee selection and training, a quality work environment, and strong support for those dealing with customers, which results in...
• Satisfied and productive service employees: more satisfied, loyal, and hardworking employees, which results in...
• Greater service value: more effective and efficient customer value creation and service delivery, which results in...
• Satisfied and loyal customers: satisfied customers who remain loyal, make repeat purchases, and refer other customers, which results in...
• Healthy service profits and growth: superior service firm performance.
Service marketing requires internal marketing and interactive marketing. (Figure 7.4)

Internal marketing means that the service firm must orient and motivate its customer-contact employees and supporting service people to work as a team to provide customer satisfaction.
Interactive marketing means that service quality depends heavily on the quality of the buyer-seller interaction during the service encounter.
Service companies face three major marketing tasks: They want to increase their service differentiation, service quality, and service productivity.
Managing Service Differentiation
The offer can include innovative features that set one company’s offer apart from competitors’ offers.
Service companies can differentiate their service delivery by having more able and reliable customer-contact people, by developing a superior physical environment in which the service product is delivered, or by designing a superior delivery process.
Service companies can work on differentiating their images through symbols and branding.
Managing Service Quality
Service quality is harder to define and judge than product quality.
Service quality will always vary, depending on the interactions between employees and customers.
Good service recovery can turn angry customers into loyal ones.
Managing Service Productivity
Service firms are under great pressure to increase service productivity.
• They can train current employees better or hire new ones who will work harder or more skillfully.
• They can increase the quantity of their service by giving up some quality.
• They can harness the power of technology.
The following book will help you know more about service marketing.


