A product is anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisfy a want or need.
Broadly defined, “products” also include services, events, persons, places, organizations, ideas, or mixes of these.
Services are a form of product that consists of activities, benefits, or satisfactions offered for sale that are essentially intangible and do not result in the ownership of anything.
Products, Services, and Experiences
A company’s market offering often includes both tangible goods and services.
At one extreme, the offer may consist of a pure tangible good, such as soap or toothpaste.
At the other extreme are pure services, for which the offer consists primarily of a service.
To differentiate their offers, marketers are creating and managing customer experiences with their brands or companies.
Levels of Product and Services (Figure below)
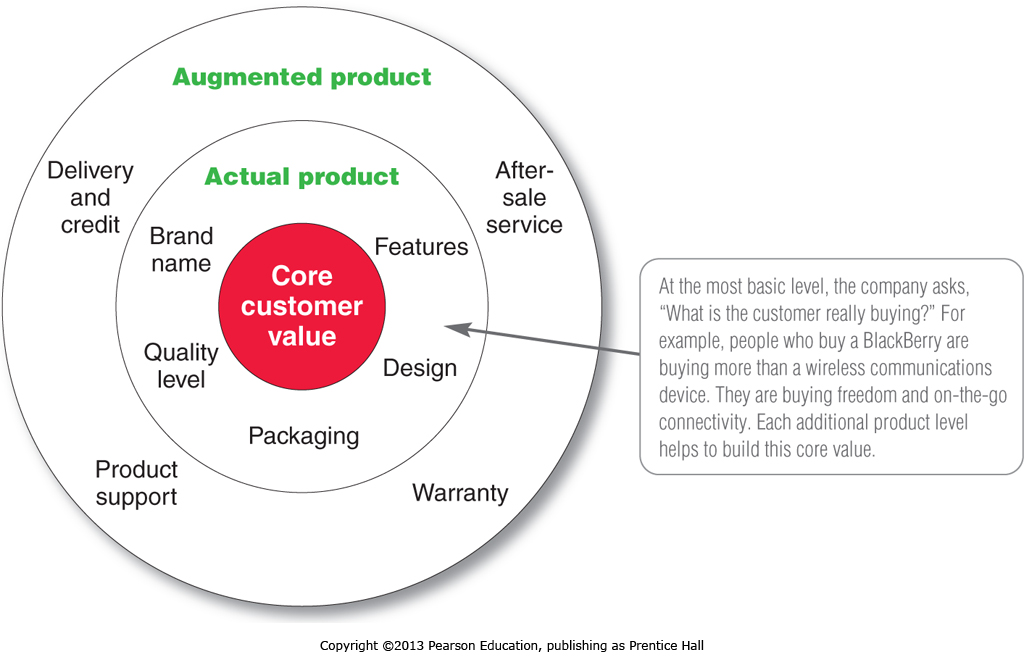
Product planners need to think about products and services on three levels.
1. Core customer value addresses the question: What is the buyer really buying?
2. Actual product
3. Augmented products are built around the core benefit and actual product by offering additional consumer services and benefits.
When developing products, marketers first must identify the core customer value that consumers seek from the product. They must then design the actual product and find ways to augment it in order to create this customer value and the most satisfying customer experience.
Product and Service Classifications
Consumer Products
Consumer products are products and services bought by final consumers for personal consumption.
Consumer products include the following (see Table 7.1 course book):
• Convenience products are consumer products and services that customers usually buy frequently, immediately, and with a minimum of comparison and buying effort.
• Shopping products are less frequently purchased consumer products and services that customers compare carefully on suitability, quality, price, and style.
• Specialty products are consumer products and services with unique characteristics or brand identifications for which a significant group of buyers is willing to make a special purchase effort.
• Unsought products are consumer products that the consumer either does not know about or knows about but does not normally think of buying.
Industrial Products
Industrial products are those purchased for further processing or for use in conducting a business.
The distinction between a consumer product and an industrial product is based on the purpose for which the product is bought.
There are three groups of industrial products and services:
• Materials and parts include raw materials and manufactured materials and parts.
• Capital items are industrial products that aid in the buyer’s production or operations, including installations and accessory equipment.
• Supplies and services include operating supplies and maintenance and repair services.
Organizations, Persons, Places, and Ideas
Organization marketing consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change the attitudes and behavior of target consumers toward an organization.
Person marketing consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes or behavior toward particular people.
Place marketing involves activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes or behavior toward particular places.
Social marketing is the use of commercial marketing concepts and tools in programs designed to influence individuals’ behavior to improve their well-being and that of society.


