Exception Types
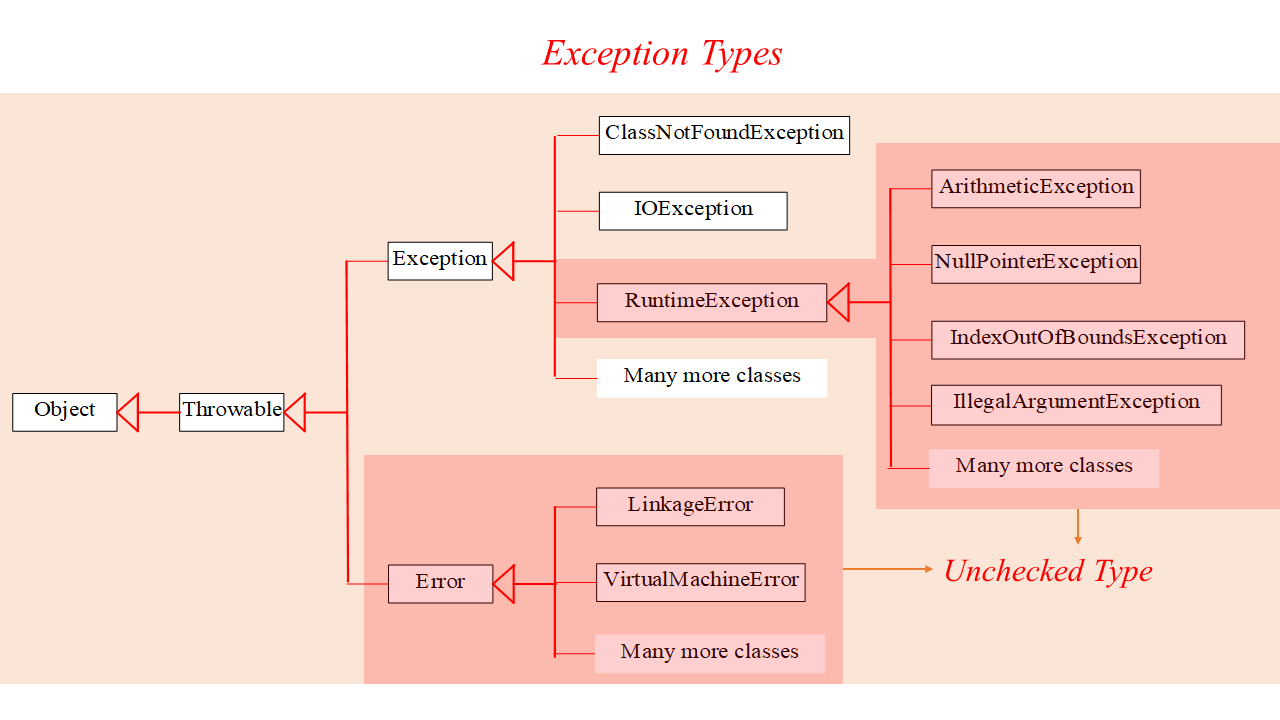
RuntimeException, Error and their subclasses are known as unchecked exceptions. All other exceptions are known as checked exceptions, meaning that the compiler forces the programmer to check and deal with the exceptions. unchecked类型异常不需要进行异常处理,checked类型异常需要对异常进行捕获和处理。
Exception Declaring
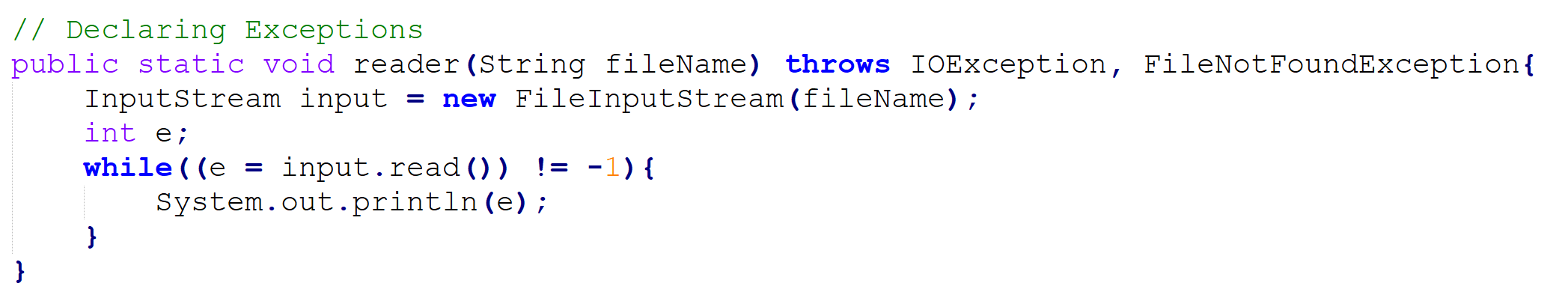
若函数执行过程中可能抛出异常,则需要进行捕获或声明,例如这里的reader()函数中执行了FileInputStream构造器及其read()函数,通过查API知道这两个函数的调用可能抛出IOException和FileNotFoundException异常,如果不在reader()函数中对这两个函数进行捕获和处理,则需要声明,表示reader()函数会继续将这两种异常抛出。声明异常采用throws关键词,有多个异常则用逗号分离。
Exception Throwing
在设计函数时,业务中可能发生的异常进行判断,在异常点创建并抛出异常。抛出异常采用throw关键词,注意要和声明异常的throws关键词进行区分。

这里在设计除法运算division()函数时,除数不能为0,当输出的除数为0时就可以抛出一个异常对象,这里Java API中已经存在专门针对算术计算的异常类,因此直接创建一个ArithmeticException对象,并用throw关键词抛出。通过异常处理的设计,使得上层应用代码必须去考虑处理该异常,从而增强程序的鲁棒性。
Declaring or Handling
抛出异常是将程序运行中发生的异常状态打包成一个对象抛出给上层代码(例如调用者),当发生异常后,上层代码(调用者)需要对checked类型的异常进行捕获和处理,如果不处理,则需要在当前层(当前调用者)对该类异常进行声明,异常会想冒泡一样继续抛给上层代码。
声明后继续抛出:
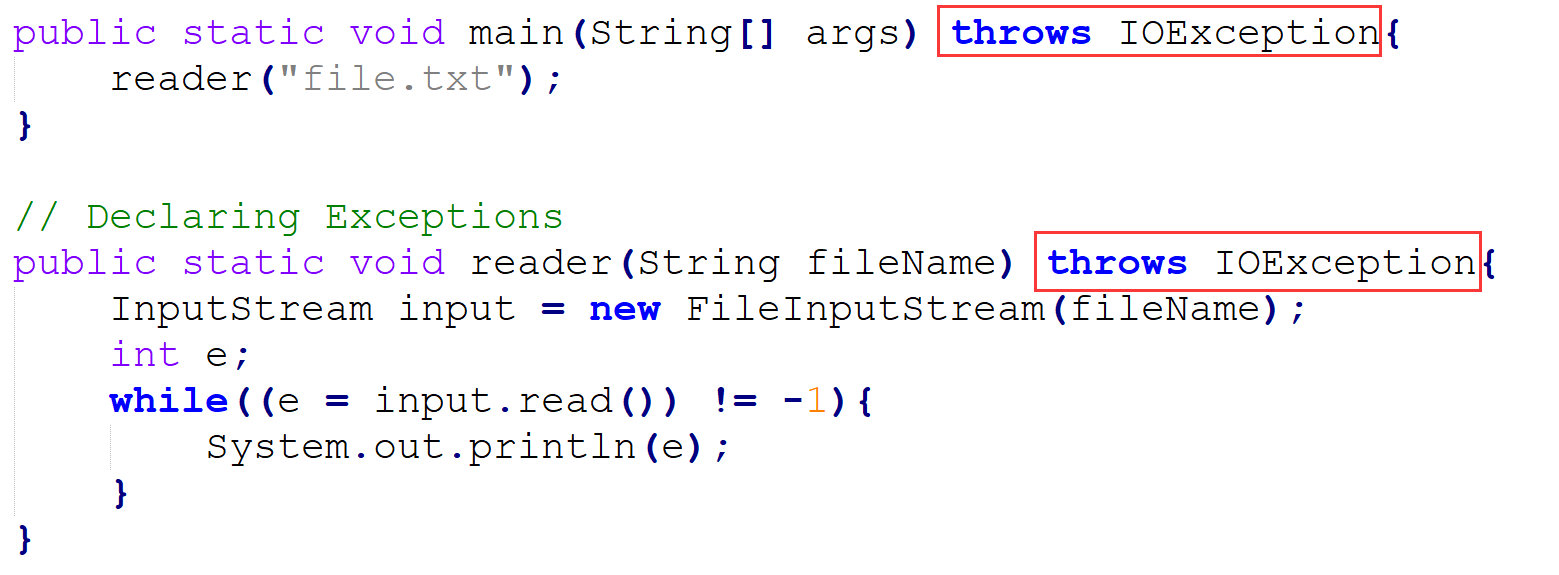
直接捕获并处理: