职称:副教授
单位:河海大学
部门:机电工程学院图学教研室
职位:教研室主任
主讲教师:康兰
教师团队:共4位
| 学校: | 河海大学 |
| 开课院系: | 机电工程学院(常州) |
| 课程编号: | ZJ0550082 |
| 学分: | 2 |
| 课时: | 32 |
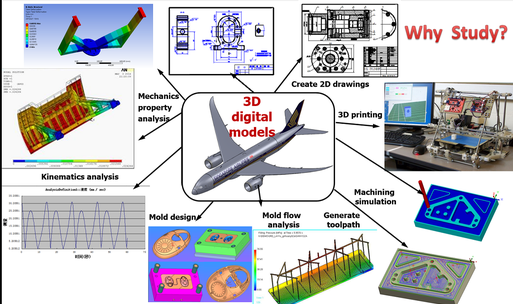
Course Description
This is a graduate level course that teaches fundamental principles and theoretical backgrounds underlying CAD/CAM systems. It covers a broad range of topics including: the current development, applications and future trends in CAD/CAM, mathematics behind free-form curves/surfaces, reverse engineering, parametric feature-based modeling, direct modeling, 3 D printing, basic principles of integration of CAD/CAM, basic principles of CIMS and FMS. Meanwhile guiding students, especially international students to make good use of parametric feature-based software widely used in industry to express design ideas, develop their comprehensive ability to solve complex engineering problems.
Learning Outcome
At the end of this course students should be able to:
(1) have a big picture about CAD/CAM technology; know the current development and future trends in CAD/CAM.
(2) organize and discuss academic issues in CAD/CAM accurately and professionally.
(3) grasp mathematics behind free-form curves/surfaces so that students could be able to create 3D models of curves/surfaces mathematically on the computer.
(4) understand the basic principles, methods and applications of current advanced CAD/CAM technology, including reverse engineering, parametric feature-based modeling, direct modeling, 3 D printing etc.
(5) understand the principles of integration of CAD/CAM, the basic principles of CIMS and FMS.
(6) make a good use of parametric feature-based software widely used in industry to express design ideas, and cultivate students’ comprehensive ability to solve complex engineering problems.
By receiving a thorough fundamental theoretical training and mastering CAD/CAM software, students will be well equipped and more confident to solve difficult problems in design and manufacturing.
Instructors
(1) Associate Prof. Kang Lan (the College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, E-mail: 20031656@hhuc.edu.cn; Tel: 0519-85191929)
(2) Associate Prof. Tong Jing(the College of Internet of Things Engineering, E-mail: 20111853@hhu.edu.cn; 0519-85191912)
(3) Associate Prof. He Gang (the College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, E-mail: 20081786@hhu.edu.cn,Tel: 0519-85191840)
(4) Senior Engineer. Petros Koronidis (Guest lecturer), R&D Director of Suzhou Diao Elevator Co.Ltd.
Textbook
Required: 《CAD/CAM:Principles and Applications》 published by China Machine Press in 2016. (Kanglan editor in chief)
References: (1) CAD/CAPP/CAM集成技术(英文版), 薛建彬编著,科学出版社,2018.1
(2) Other reference materials will be provided during teaching process, including materials in forms of text, videos online and offline.
(3)Some reference materials can be downloaded in each chapter of the online course.
(4)《3D Printing》(English version, manuscript), wrote by Kang Lan and Tong Jing.
Grade Policy:
Academic performance : 10%
Seminar: 20%
Homework: 30%
Course project: 40%
Time and Place:
To be determined
Office Hour: Monday-Friday, 8:30am - 4pm, room: Ying Cai building B506;
P.S: Send me text message or give me a call and see whether I am available before you come to my office.
Syllabus and Tentative Schedule
Introduction to the course (about 0.5 period)
Introduction to course project (about 1.5 periods)
Chapter 1 Introduction to CAD/CAM (about 3 periods)
1.1 Concept of CAD/CAM
1.2 Process of Computer Aided Design
1.3 Process of Computer Aided Manufacturing
1.4 Integration of CAD and CAM
1.5 CAD Environment
1.6 Applications of CAD/CAM
1.7 History and Trends of CAD/CAM
Chapter2 Solid modeling (Feature-based modeling) (about 4 periods)
2.1 An overview of solid modeling
2.2 Wireframe Model
2.3 Solid Model Creation Scheme
2.4 Constructive Solid Geometry Scheme (CSG)
2.5 Boundary Representation Scheme ((B-Rep)
2.6 Sweeping Scheme
2.7 Parametric Featured-based Solid modeling
2.8 Trends of Solid Modeling
2.9 Introduction to Solidworks
Chapter 3 Reverse Engineering (about 2 periods)
3.1 What is reverse engineering (RE)?
3.2 Why RE is needed?
3.3 RE hardware
3.4 RE software
3.5 Process of RE?
3.6 RE modeling methods
3.7 RE applications
Chapter 4 Surface Modeling (about 8 periods)
4.1 Introduction to Surface Model
4.2 Mathematical representations of curves
4.3 Introduction to Splines
4.4 Bezier Curves/Surfaces
4.5 B-spline
4.6 Intuitive Understanding of B-splines
4.7 NURBS
4.8 Introduction of Matlab
Chapter 5 3D printing (about 3 periods)
5.1 History of 3D Printing
5.2 What is 3D Printing?
5.3 3D Printing Process
5.4 3D Printing Materials
5.5 Principles Behind 3D Printing
5.6 A Survey of 3D Printers
5.7 Acquiring a 3D Model
5.8 Applications and the Future of 3D Printing
5.9 The Emerging Applications of 3D Printing
5.10 4D printing
5.11 Case Studies
Lab practice: (after class practice)
Seminars: (about 2 periods)
Chapter 6 A comprehensive case study (about 8 periods)
备注:以下内容为课程的扩展部分,由于时间关系无法在课堂中完成,所以将此部分教学内容放到网上在线课程中供学生课后自学用,每一部分提供了学习指导,软件学习部分提供全英文教学视频。
PS:Because of limited class time, the following chapters are provided on the online course. If students want to study these parts, please use the following contents as references.
Chapter 7 CAD/CAM Integration
7.1 Introduction
7.2 Initial Graphics Exchange Specifications (IGES)
7.3 Standard for the Exchange of Product Model Data (STEP)
7.4 STEP-NC
7.5 Feature Recognition
7.6 Group Technology
7.7 Benefits of Integrated CAD/CAM
Chapter 8 Computer-Integrated Manufacturing(CIM)
8.1 Introduction
8.2 Key Challenges
8.3 Subsystems in Computer Integrated Manufacturing
8.4 Application
8.5 Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS)
Chapter 9 Case studies based on CAM: CAMWorks
Chapter 10 AUTOCAD
Chapter 11 SOLIDWORKS